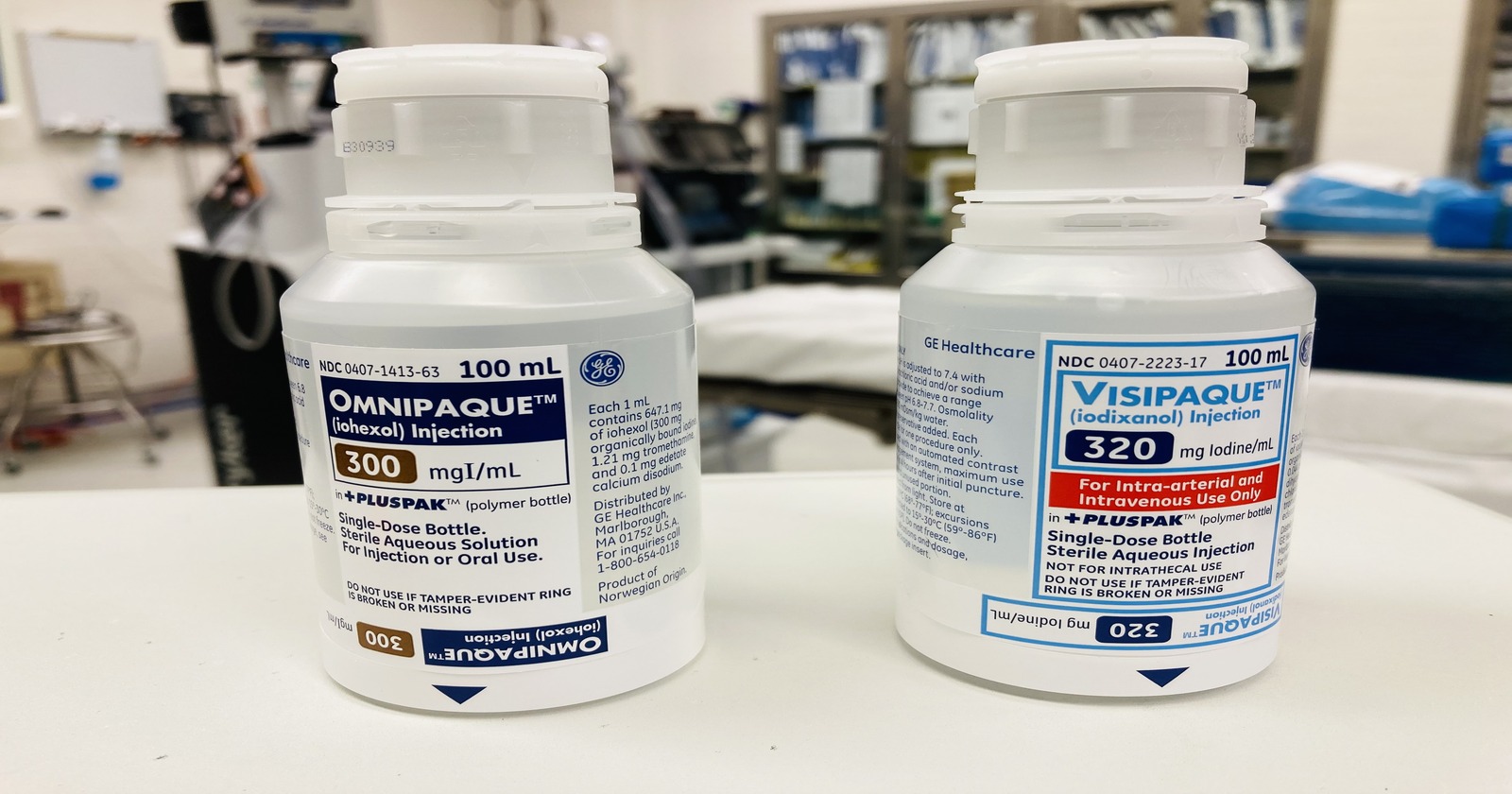
Visipaque is a type of contrast injectable agent for intravascular use only, active ingredient is iodixanol, which is an iodine-based compound, has two iodine atoms per molecule and has an osmolarity similar to that of blood with a higher viscosity compared to Omnipaque ( Iohexol).
Omnipaque is brand name for Iohexol, a non-ionic contrast agent but is monomeric and has a lower osmolarity compared to iodixanol the ingredient in Visipaque. An iodinated contrast agent, use for medical imaging, used in various diagnostic procedures, such as computed tomography (CT) scans, angiography, and certain types of X-rays.

| Visipaque (Iodixanol) | Omnipaque (Iohexol) |
|---|---|
| Chemical Structure: Non-ionic, dimeric contrast agent | Chemical Structure: Non-ionic, monomeric contrast agent |
| Route of Administration: Intravascular injection | Route of Administration: Intravascular injection |
| Metabolism: Not metabolized | Metabolism: Not metabolized |
| Excretion: Renal | Excretion: Renal |
| Half-life: Approximately 2 hours | Half-life: Approximately 1.5-2 hours |
| Osmolality: (290 mOsm/kg) | Osmolality: Low-osmolar (600-850 mOsm/kg) |
| Iodine Content: 320 mg I/mL | Iodine Content: 300 mg I/mL |
| Viscosity: Higher viscosity compared to Omnipaque | Viscosity: Lower viscosity compared to Visipaque |
| Pharmacodynamic Effect: Opacifies blood vessels for imaging | Pharmacodynamic Effect: Opacifies blood vessels for imaging |
| Less likely to cause allergic reactions | Faster renal clearance |
What is Visipaque?

Visipaque is Iso-Osmolar to blood and isotonic at all concentrations this means that Visipaque has the same concentration of particles as blood and matches its balance of electrolytes. This helps in preventing any adverse reactions or discomfort when it’s injected into the body for medical imaging. It’s basically designed to be very compatible with the body’s own fluids used in medical imaging procedures, particularly in radiographic examinations like X-rays and computed tomography (CT) scans.
Indications and usage of VISIPAQUE for intra-arterial and intravenous procedures procedures
Intra-arterial Uses
| Procedure | Adult and Pediatric Patients (12 years and older) |
|---|---|
| Intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography (IA-DSA) | 270 mg and 320 mg Iodine/mL |
| Angiocardiography (left ventriculography and selective coronary arteriography) | 320 mg Iodine/mL Pediatric Patients (< 12 years)320mg Iodine/mL |
| Peripheral arteriography | 320 mg Iodine/mL |
| Visceral arteriography | 320 mg Iodine/mL Pediatric Patients (< 12 years): 320 mg Iodine/mL |
| Cerebral arteriography | 320 mg Iodine/mL Pediatric Patients (< 12 years): 320 mg Iodine/mL |
Intravenous Uses
| Procedure | Indications and Usage |
|---|---|
| CT imaging of the head and body | Diagnostic evaluation of head and body structures: 270 mg Iodine/mL |
| Diagnostic evaluation of head and body structures: 320 mg Iodine/mL | |
| Excretory urography | Diagnostic evaluation of urinary tract structures: 270 mg Iodine/mL |
| Diagnostic evaluation of urinary tract structures: 320 mg Iodine/mL | |
| Peripheral venography | Diagnostic evaluation of peripheral veins: 270 mg Iodine/mL |
| Coronary computed tomography angiography | Assist in the diagnostic evaluation of patients with suspected coronary artery disease: 320 mg Iodine/mL |
Comparison of the effectiveness and safety profiles of Visipaque and Omnipaque

Effectiveness:
- Both Visipaque (Iodixanol) and Omnipaque (Iohexol) are effective contrast agents for enhancing imaging results.
- Visipaque and Omnipaque are both non-ionic, which means they are less likely to cause adverse reactions compared to older, ionic contrast agents.
- Both agents provide excellent opacification of blood vessels and organs, allowing for clear visualization of anatomical structures during imaging procedures.
Safety:
- In terms of safety, both Visipaque and Omnipaque have a similar overall safety profile.
- Adverse reactions to contrast agents can include allergic reactions, nephrotoxicity (damage to the kidneys), and cardiovascular effects such as hypotension or arrhythmias.
- However, non-ionic contrast agents like Visipaque and Omnipaque are generally considered safer and have a lower risk of adverse reactions compared to ionic contrast agents.
- The risk of adverse reactions can be further minimized by ensuring proper patient screening for allergies and renal function before administering the contrast agent, as well as using appropriate dosages.

Differences in how Visipaque and Omnipaque are metabolized and excreted
Visipaque (iodixanol) and Omnipaque (iohexol) are both iodinated contrast agents used for diagnostic imaging, particularly in computed tomography (CT) scans. While they share similarities in their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties, there are some differences in how they are metabolized and excreted, which can affect their clinical use.
Metabolism:
- Visipaque (Iodixanol):
- Iodixanol is not metabolized in the body. It remains unchanged and is excreted primarily via the kidneys.
- Omnipaque (Iohexol):
- Iohexol is also not metabolized in the body. Like iodixanol, it is excreted primarily via renal filtration.
Excretion:
- Visipaque (Iodixanol):
- Iodixanol is primarily excreted unchanged via the kidneys. It is eliminated from the body through glomerular filtration without being metabolized to a significant extent. Due to its higher molecular weight and iso-osmolar nature, it is associated with slower renal clearance compared to Omnipaque.
- Omnipaque (Iohexol):
- Similarly, iohexol is primarily excreted unchanged via renal filtration. It is rapidly eliminated from the body through glomerular filtration due to its lower molecular weight and lower viscosity compared to Visipaque.
Clinical Use:
- Visipaque (Iodixanol):
- Due to its non-ionic nature, iso-osmolar properties, and slower renal clearance, Visipaque is associated with a lower risk of causing adverse reactions such as contrast-induced nephropathy and allergic reactions. This makes it a preferred choice in patients with compromised renal function or a history of contrast reactions.
- The slower renal clearance of Visipaque may result in a longer duration of contrast enhancement, which could be advantageous in certain imaging studies requiring prolonged imaging windows.
- Omnipaque (Iohexol):
- Omnipaque, with its lower viscosity and faster renal clearance, may be preferred in patients with normal renal function who require rapid imaging studies or in situations where rapid contrast clearance is desired.
- It is also commonly used in patients undergoing procedures where a lower volume of contrast agent is required, as it can provide adequate opacification with smaller volumes compared to Visipaque.

Clarity of Imaging Results of Visipaque and Omnipaque
- Both Visipaque and Omnipaque provide high-quality imaging results with excellent contrast enhancement.
- The choice between the two agents may depend on the specific imaging requirements of the procedure and the preferences of the healthcare provider.
- Some studies suggest that Visipaque may offer slightly better image quality and lower incidence of adverse reactions compared to Omnipaque in certain patient populations, but the differences are generally minimal.
In conclusion, both Visipaque and Omnipaque are effective and safe contrast agents commonly used in medical imaging procedures. The choice between the two depends on factors such as imaging requirements, patient characteristics, and healthcare provider preferences. Overall, both agents provide clear imaging results with minimal side effects, and the selection between them is often based on clinical judgment and institutional protocols.
Drugs that may interact with Visipaque:
1. Drugs that affect renal function: Since Visipaque is excreted through the kidneys, drugs that affect renal function may interact with it. Examples include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen.
- ACE inhibitors such as lisinopril or enalapril.
- Diuretics like furosemide or hydrochlorothiazide.
2. Metformin: There is a risk of lactic acidosis when metformin, a drug commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes, is combined with contrast agents. This interaction can occur due to the effect of contrast agents on renal function.
3. Nephrotoxic drugs: Drugs that are nephrotoxic (toxic to the kidneys) may increase the risk of kidney damage when used with Visipaque. Examples include certain antibiotics (e.g., vancomycin, aminoglycosides), chemotherapy drugs, and some antiviral medications.
4. Lithium: Lithium, commonly used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, can interact with contrast agents and may increase the risk of lithium toxicity.
5. Beta-blockers: There have been reports of interactions between contrast agents and beta-blockers, although the mechanism and significance of these interactions are not fully understood.
6. Thyroid medications: Some thyroid medications, such as levothyroxine, may interact with contrast agents and affect thyroid function tests.

Clinical procedures Visipaque and Omnipaque are use for
Visipaque (Iodixanol):
- Angiography: Visipaque is commonly used in angiography procedures to visualize blood vessels, including coronary angiography, peripheral angiography, and cerebral angiography.
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scans: Visipaque is frequently used as a contrast agent in CT scans to enhance the visibility of blood vessels, organs, and tissues, aiding in the diagnosis of conditions such as pulmonary embolism, abdominal tumors, and vascular abnormalities.
- Cardiac Imaging: Visipaque may be preferred in cardiac imaging studies due to its lower osmolality and reduced risk of adverse reactions, particularly in patients with cardiovascular disease or renal impairment.
- Urography: Visipaque can be used in urography procedures to visualize the urinary tract and detect abnormalities such as kidney stones or obstruction.
Omnipaque (Iohexol):

- CT (Computed Tomography) Scans: Omnipaque is widely used as a contrast agent in CT scans for a variety of indications, including head and neck imaging, chest imaging, and abdominal imaging.
- Myelography: Omnipaque is commonly used in myelography procedures to visualize the spinal cord and diagnose conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or spinal tumors.
- Arthrography: Omnipaque can be used in arthrography procedures to evaluate joint structures such as the shoulder, knee, or hip, particularly in cases of suspected ligament or cartilage injuries.
- CT Angiography: Omnipaque may be preferred in certain CT angiography studies, such as pulmonary angiography or aortic angiography, depending on the specific imaging requirements and patient characteristics.
Individuals who Visipaque should not be used on.
1. Patients with Severe Kidney Impairment: Visipaque can exacerbate kidney problems, especially in individuals with severely impaired renal function. Using Visipaque in such patients can increase the risk of further kidney damage or acute kidney injury.
2. Those with Known Allergies to Iodinated Contrast Agents: Individuals who have a history of allergic reactions to iodinated contrast agents, including Visipaque, should avoid its use. Allergic reactions can range from mild skin reactions to severe anaphylaxis, which can be life-threatening.
3. Patients with Hyperthyroidism: Visipaque contains iodine, which can affect thyroid function. Individuals with hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) may be at increased risk of adverse effects if they receive Visipaque.
4. Pregnant Women: While Visipaque is generally considered safe for use during pregnancy when the benefits outweigh the risks, it should be used with caution. The potential risks to the fetus, particularly related to iodine exposure, should be carefully considered before administering Visipaque to pregnant women.
5. Breastfeeding Mothers: There is limited information available regarding the excretion of Visipaque in breast milk. Breastfeeding mothers should consult with their healthcare providers to weigh the potential risks and benefits before using Visipaque.
6. Patients with Cardiovascular Disease: Individuals with certain cardiovascular conditions, such as severe congestive heart failure or unstable angina, may be at increased risk of adverse events when exposed to Visipaque. Close monitoring and careful consideration of alternative imaging options may be necessary in such cases.
7. Patients with Multiple Myeloma or Other Blood Disorders: Visipaque can increase the risk of developing a rare but serious condition called contrast-induced nephropathy, particularly in patients with underlying blood disorders like multiple myeloma.
Who should not use Omnipaque
1. Patients with Severe Kidney Impairment: Similar to Visipaque, Omnipaque can exacerbate kidney problems, especially in individuals with severely impaired renal function, leading to an increased risk of kidney damage or acute kidney injury.
2. Patients with Hyperthyroidism: Omnipaque contains iodine, which can affect thyroid function. Individuals with hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) may be at increased risk of adverse effects if they receive Omnipaque.
3. Those with Known Allergies to Iodinated Contrast Agents: Individuals with a history of allergic reactions to iodinated contrast agents, including Omnipaque, should avoid its use due to the risk of allergic reactions ranging from mild to severe, including anaphylaxis.
4. Pregnant Women: While Omnipaque is generally considered safe for use during pregnancy when the benefits outweigh the risks, caution should be exercised due to potential risks to the fetus, particularly related to iodine exposure.
5. Patients with Multiple Myeloma or Other Blood Disorders: Omnipaque, like other iodinated contrast agents, can increase the risk of contrast-induced nephropathy, particularly in patients with underlying blood disorders like multiple myeloma.
6. Patients with Cardiovascular Disease: Individuals with certain cardiovascular conditions, such as severe congestive heart failure or unstable angina, may be at increased risk of adverse events when exposed to Omnipaque. Close monitoring and consideration of alternative imaging options may be necessary.
7. Breastfeeding Mothers: Limited information is available regarding the excretion of Omnipaque in breast milk, so breastfeeding mothers should consult with healthcare providers to weigh potential risks and benefits before using Omnipaque.
Adverse effects of Visipaque and Omnipaque
Allergic Reactions:
- Both Visipaque and Omnipaque can induce allergic reactions, ranging from mild skin rashes to severe anaphylaxis.
- The risk of allergic reactions is generally low but may be higher in patients with a history of allergies, asthma, or previous reactions to contrast agents.
- Precautions such as pre-medication with corticosteroids and antihistamines may be taken to reduce the risk of allergic reactions.
Nephrotoxicity:
- Nephrotoxicity, or kidney damage, is a concern with both Visipaque and Omnipaque, particularly in patients with pre-existing renal impairment.
- The risk of nephrotoxicity is higher with higher doses of contrast agents, prolonged exposure, dehydration, and concurrent use of nephrotoxic medications.
- Monitoring of renal function before and after contrast administration is recommended, and hydration protocols may be employed to mitigate the risk.
Neurotoxicity:
- Neurotoxicity refers to adverse effects on the central nervous system, such as seizures, altered mental status, or focal neurological deficits.
- While rare, neurotoxicity has been reported with both Visipaque and Omnipaque, particularly in high-risk populations such as elderly patients or those with compromised blood-brain barriers.
- Factors influencing neurotoxicity risk include the dose and rate of contrast administration, as well as the presence of underlying neurological conditions.
Incidence and Severity:
- Studies comparing the incidence and severity of adverse effects between Visipaque and Omnipaque have yielded mixed results, with no clear consensus on which agent carries a higher risk.
- Some studies suggest that Visipaque may have a lower incidence of nephrotoxicity compared to older contrast agents like Omnipaque, attributed to its lower osmolality and reduced viscosity.
- However, other studies have found no significant differences in safety profiles between the two agents.
Patient Populations at higher risk of adverse effects from Visipaque and Omnipaque
- Patients with a history of allergies or previous reactions to contrast agents.
- Individuals with pre-existing renal impairment or renal insufficiency.
- Elderly patients, particularly those with comorbidities.
- Patients receiving concurrent nephrotoxic medications or undergoing procedures associated with increased nephrotoxicity risk, such as cardiac catheterization.
Resources
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/018956s099lbl.pdf
https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-176043/omnipaque-oral/details
https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=2d964c13-88ad-43be-88d4-a3a7ea4d5b5e