Tanning oil, sunscreen oil, and sunscreen lotion are three popular products designed to enhance and protect the skin during sun exposure. Each serves a distinct purpose in the realm of sun care.
Tanning oil is primarily used to accelerate the tanning process, containing ingredients that help absorb UV rays to promote a deeper and faster tan. Sunscreen oil, on the other hand, offers a compromise between tanning and sun protection, often providing a lower SPF while still aiding in achieving a sun-kissed glow.
Conversely, sunscreen lotion is a critical tool in safeguarding the skin against the harmful effects of UV radiation, providing a higher level of protection against sunburn, premature aging, and potential skin cancers. Understanding the differences and benefits of these products is crucial in choosing the right one for your specific sun care needs.

Tanning Oil Sunscreen Oil Sunscreen Lotion
What is Tanning Oil and How it works
Tanning oil is a product used to enhance the tanning process of the skin when exposed to sunlight. It typically comes in the form of spray, or oil and is applied to the skin before sunbathing. Tanning oils usually contain ingredients that help attract and retain UV rays from the sun, thereby accelerating the tanning process. These products often include moisturizers and, in some cases, low levels of sunscreen to provide minimal sun protection.
It’s important to note that while tanning oils can help you achieve a deeper tan, they do not offer significant protection from harmful UV radiation. Prolonged and unprotected exposure to the sun can lead to sunburn, premature aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer.
Therefore, if you plan to use tanning oil, it’s crucial to also use a sunscreen with a sufficient sun protection factor (SPF) to shield your skin from harmful UV rays. Remember to reapply sunscreen regularly, especially after swimming or sweating. Additionally, consider seeking shade during peak sun hours (usually between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.) to minimize sun exposure.
Tanning oils are specially formulated to enhance the tanning process, requiring exposure to sunlight for optimal results. They typically offer minimal or no sun protection (SPF), allowing for increased absorption of UV rays.
How Tanning Oil works
Tanning oils are designed to expedite the tanning process by encouraging the body to produce more melanin. When applied to the skin, they stimulate melanocytes, prompting them to increase melanin production at an accelerated rate. With a higher melanin concentration, the skin is more predisposed to tanning and becomes darker.
4 Key Steps to take to get the best result from your Tanning Oil
- Apply the oil evenly over your entire body to ensure a uniform tan.
- Allow the oil to absorb into your skin, which helps maintain hydration and provides essential nutrients.
- Reapply the tanning oil every 2-4 hours, or more frequently if you’ve been in contact with water.
- If your chosen tanning oil does not include sunscreen, apply a separate sunscreen before using the oil to protect your skin from UV damage.
It’s important to strike a balance between achieving a tan and protecting your skin from harmful UV rays. Prioritize your skin’s health and take appropriate precautions when using tanning oils. Tanning oils have little or no SPF to enable a quicker tan.


Benefits and things to Considered when using Tanning Oil
- Accelerated Tanning: Tanning oils typically contain ingredients that help to attract and absorb UV rays. This can potentially result in a faster and deeper tan compared to tanning without any products.
- Enhanced Moisturization: Many tanning oils contain moisturizing ingredients like oils and emollients. This can help keep your skin hydrated during tanning, which can be especially beneficial in dry or arid environments.
- Rich in Nutrients: Some tanning oils contain vitamins and antioxidants that can nourish the skin. For example, oils rich in vitamin E can help protect against free radicals generated by UV exposure.
- Improved Appearance: Tanning oils can give the skin a subtle sheen, which can enhance the appearance of your tan.

After a Tan.
5 Key Considerations For Tanning Oil.
- Risk of Sunburn: Tanning oils can intensify the effects of UV radiation on the skin, which increases the risk of sunburn. It’s important to use tanning oil responsibly and always apply a suitable sunscreen with a high SPF in conjunction with it.
- Risk of Skin Damage: Prolonged or excessive exposure to UV radiation, especially without adequate sun protection, can lead to skin damage, premature aging, and increase the risk of skin cancer.
- Risk of Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may be sensitive or allergic to certain ingredients in tanning oils. Always do a patch test before applying a new product to your entire body.
- Environmental Impact: Some tanning oils contain ingredients that can be harmful to the environment, particularly if they are washed off and enter natural waterways.
- Not Suitable for Everyone: Tanning oils may not be suitable for individuals with certain skin conditions, such as sun allergies, eczema, or psoriasis. They should also be avoided by individuals with a history of skin cancer.
5 important Tips for Safe Tanning:
- Use Sunscreen: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF before applying tanning oil, and reapply it regularly, especially after swimming or sweating.
- Limit Sun Exposure: Avoid tanning during peak hours when the sun’s rays are the strongest (usually between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.).
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, as sun exposure can lead to dehydration.
- Gradual Exposure: Gradually increase your time in the sun to allow your skin to adapt and minimize the risk of sunburn.
- Protect Sensitive Areas: Use extra caution on sensitive areas like the face, ears, and the back of your knees, which can be more prone to sunburn.
Remember that a natural tan is a result of your skin’s response to UV radiation, which can damage the skin. If you desire a tanned look, consider using a self-tanning product or bronzer as a safer alternative. Always prioritize the health and safety of your skin when tanning.

People On a Beach Tanning.
Sunscreen Oil Characteristics and features, How it works
sunscreen oils are oil-based formulations, a type of sun protection product designed to be applied to the skin to help prevent sunburn and protect against the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Unlike traditional sunscreen lotions, which are typically water-based, sunscreen oils are oil-based formulations. Sunscreen SPF oils are unique because they glide on to and spread really easily on the skin. Oils also usually contain hydrating ingredients
Characteristics and features of sunscreen oil:
- Texture: Sunscreen oil has a lightweight, non-greasy texture. It is designed to be easily absorbed by the skin.
- Ingredients: Sunscreen oils often contain a combination of sunscreens (chemical or mineral UV filters) and various oils. The oils can include natural oils like coconut oil, jojoba oil, or argan oil, which are included for their moisturizing and skin-nourishing properties.
- Sun Protection Factor (SPF): Sunscreen oils come in a range of SPF levels, just like traditional sunscreens. SPF indicates the level of protection against UVB rays, which are the primary cause of sunburn.
- Broad-Spectrum Protection: Many sunscreen oils provide broad-spectrum protection, which means they guard against both UVA and UVB rays. UVA rays are responsible for premature aging of the skin.
- Tanning Enhancers: Some sunscreen oils are marketed as “tanning oils” and may contain ingredients that claim to accelerate the tanning process. These products usually contain low SPFs and may not provide sufficient protection against harmful UV rays.
- Water Resistance: Some sunscreen oils are formulated to be water-resistant, meaning they offer protection even when you’re in the water.
Caution: While sunscreen oils can be effective in protecting the skin from sunburn, they may not be suitable for everyone. People with certain skin conditions or sensitivities should consult a dermatologist before using a sunscreen oil.
How sunscreen oil works
- Sunscreen Agents: Sunscreen oils contain active ingredients known as UV filters. These filters can be either chemical or physical (mineral).
- Chemical UV filters work by absorbing UV radiation and converting it into heat, which is then released from the skin. These chemicals include compounds like avobenzone, oxybenzone, and octinoxate.
- Physical UV filters (mineral sunscreen) work by reflecting and scattering UV rays away from the skin. They contain ingredients like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide.
- Carrier Oils: In addition to the sunscreen agents, sunscreen oils also contain carrier oils. These are often natural oils like coconut oil, jojoba oil, argan oil, or avocado oil. These oils serve several purposes:
- Moisturizing: Oils help to moisturize and hydrate the skin, which can be especially beneficial in dry or sunny conditions.
- Emollient Properties: They form a protective barrier on the skin’s surface, helping to lock in moisture and prevent water loss.
- Nourishment: Many oils are rich in vitamins, antioxidants, and fatty acids that can help nourish and improve the overall health of the skin.
- Absorption: The skin absorbs both the sunscreen agents and the oils. The UV filters work to protect the skin from harmful UV rays, while the oils get absorbed into the skin, providing moisturization and nourishment.
- Protection: The UV filters in the sunscreen oil either absorb or reflect the UV rays, preventing them from penetrating the skin. This helps to reduce the risk of sunburn, premature aging, and skin cancer.
Tips to applying Sunscreen Oil

Applying sunscreen
Here are some tips for applying sunscreen oil effectively:
1. Choose the Right SPF: Select a sunscreen oil with a broad-spectrum SPF of at least 30. This will offer good protection against both UVA and UVB rays.
2. Apply Generously: Don’t be stingy with sunscreen oil. Apply a generous amount to all exposed areas of your skin, including your face, neck, arms, legs, and any other areas that will be exposed to the sun.
3. Apply Before Sun Exposure: Apply sunscreen oil about 15-30 minutes before you go out into the sun. This gives the product some time to be absorbed by your skin.
4. Reapply Regularly: Sunscreen should be reapplied every two hours, or more frequently if you are sweating heavily or swimming. Even if the sunscreen claims to be water-resistant, it’s a good idea to reapply after swimming or excessive sweating.
5. Use After Swimming or Sweating: If you’ve been swimming or sweating, towel off and reapply the sunscreen oil. Even if it’s labeled as water-resistant, it’s always best to reapply after these activities.
6. Don’t Forget High-Risk Areas: Pay special attention to areas that are often overlooked, such as the tops of your ears, the back of your neck, your lips, and the tops of your feet.
7. Avoid the Eye Area: Be careful when applying sunscreen oil around your eyes. Some oils may cause irritation. If you want to protect your eye area, it’s better to use a specific eye cream with SPF.
8. Combine with Other Protection Measures: Sunscreen oil is just one part of your sun protection arsenal. Wear protective clothing like wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved shirts when possible. Seek shade during peak sun hours, typically between 10 AM and 4 PM.
9. Check Expiry Dates: Like any skincare product, sunscreen has an expiration date. Make sure you’re using a product that is still effective.
10. Patch Test: If you’re trying a new sunscreen oil for the first time, it’s a good idea to do a small patch test on a small area of skin to check for any allergic reactions or sensitivities.
11. Be Mindful of Ingredients: Some people may be sensitive to certain ingredients in sunscreen oils. If you have sensitive skin or allergies, opt for products that are labeled as hypoallergenic or made for sensitive skin.
12. Remove Thoroughly: At the end of the day, make sure to properly cleanse your skin to remove any residue of the sunscreen oil. This is particularly important if you have oily or acne-prone skin.
Remember, sunscreen is a crucial part of your skincare routine, helping to protect your skin from harmful UV rays, which can lead to premature aging and increase the risk of skin cancer.
Tanning lotion vs Sunscreen
| Tanning Lotion | Sunscreen |
|---|---|
| Purpose Enhances tanning by accelerating melanin production | Protects skin from UV radiation |
| Protection Level Low to none | High (varies with SPF) |
| UV Protection May contain low SPF but not primarily for UV protection | Blocks or absorbs UV radiation (both UVA and UVB) |
| Skin Types Suitable for those looking to tan | Suitable for all skin types |
| Active Ingredients Tyrosine, melanin, bronzers | Active Ingredients Zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, avobenzone, octocrylene |
| Application Frequency Reapply every 2-4 hours or as needed | Application Frequency Reapply every 2 hours or after swimming/sweating |
| Common Use Achieving a tan | Common Use Preventing sunburn and skin damage |
SPF Oil vs SPF Cream: Differences and Benefits

SPF Oil
- Texture: Lightweight and non-greasy.
- Application: Easy to spread, provides a glowing finish.
- Suitability: Ideal for dry skin due to its moisturizing properties.
- Absorption: Absorbs quickly into the skin.
- Protection: Offers broad-spectrum protection but may need more frequent reapplication, especially if it is water-resistant.
SPF Cream
- Texture: Thicker and more moisturizing.
- Application: May require more effort to spread evenly.
- Suitability: Suitable for all skin types, especially normal to dry skin.
- Absorption: Takes a bit longer to absorb but provides a protective barrier.
- Protection: Offers long-lasting protection, often includes additional skincare benefits like anti-aging ingredients.
Essential Benefits of Sunscreen Oil
- Sun Protection: Like traditional sunscreen lotions, sunscreen oil helps protect the skin from harmful UV rays, preventing sunburn, premature aging, and reducing the risk of skin cancer.
- Hydration: Many sunscreen oils contain moisturizing ingredients that help keep the skin hydrated, preventing it from drying out in the sun.
- Non-Greasy Feel: Sunscreen oils are typically lighter and less greasy than traditional creams, making them more comfortable to wear, especially in hot and humid conditions.
- Easy Application: The oil formulation allows for easy and smooth application, ensuring even coverage over the skin.
- Enhanced Tanning: Some sunscreen oils contain ingredients like bronzers or tanning accelerators, which can help achieve a natural-looking tan while still providing sun protection.
- Multipurpose Use: Some sunscreen oils are designed for use on both the body and hair, offering a convenient, all-in-one solution for sun protection.
- Suitable for Sensitive Skin: Many sunscreen oils are formulated to be hypoallergenic and are free from common skin irritants, making them suitable for individuals with sensitive skin.
- Water Resistance: Some sunscreen oils are water-resistant, providing extended protection even when swimming or sweating.
- Natural Ingredients: Some brands offer sunscreen oils made from natural and organic ingredients, providing an eco-friendly option for sun protection.
Sunscreen Lotion, Application and how it works
Sunscreen lotion, often simply referred to as sunscreen, is a topical product designed to protect the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. It works by absorbing, reflecting, or scattering the sun’s rays.
The two main types of UV radiation that sunscreen protects against are UVA and UVB:
- UVA rays can prematurely age your skin and are linked to skin cancer. They can pass through glass and are present with relatively equal intensity during all daylight hours throughout the year.
- UVB rays are the primary cause of sunburn and play a key role in the development of skin cancer. They are most intense between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. and their intensity varies by season and location.
Sunscreen usually contains organic (chemical) or inorganic (physical) compounds (or a combination of both) that absorb, reflect, or scatter the sun’s rays. Organic sunscreens contain chemicals that absorb UV radiation, while inorganic sunscreens contain minerals that reflect it.
How Sunscreen lotion Work
There are two main types of UV radiation that reach the Earth’s surface, UVA and UVB that causes damages to our collagen and elastin fibers in the skin, which leads to loss of elasticity and firmness. Sunscreen is a topical product designed to protect the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. It works by absorbing, reflecting, or scattering the sun’s rays . These are the way in which sunscreen work.
- Chemical Filters:
- Chemical sunscreen contains organic (carbon-based) compounds that absorb UV radiation. These compounds include molecules like avobenzone, Oxybenzone, Octinoxate, and Octisalate.
- When UV rays hit the skin, these chemicals absorb the energy and transform it into a less damaging form, usually heat. This prevents the UV radiation from penetrating the deeper layers of the skin.
- Physical or Mineral Filters:
- Physical sunscreen contains inorganic compounds, usually zinc oxide or titanium dioxide. These minerals work by sitting on top of the skin and reflecting UV rays away from the skin.
- They form a physical barrier that doesn’t get absorbed into the skin. This is why they are often called “physical blockers.”
- Broad-Spectrum Protection:
- Many sunscreens are labeled as “broad-spectrum,” which means they protect against both UVA and UVB rays. This is important because both types of radiation can cause skin damage and increase the risk of skin cancer.
- SPF (Sun Protection Factor):
- SPF is a measure of how effectively a sunscreen protects against UVB rays. It indicates how much longer you can stay in the sun without getting sunburned compared to not wearing sunscreen. For example, SPF 30 means you can stay in the sun 30 times longer than if you were not wearing sunscreen.
- It’s important to note that higher SPF values offer more protection but the increase is not linear. SPF 30 filters out about 97% of UVB rays, while SPF 50 filters out about 98%.
- Water-Resistant Sunscreens:
- If you’ll be swimming or sweating, it’s advisale to use a water-resistant sunscreen. These formulas adhere better to the skin even when wet, but they still need to be reapplied after a certain period of time.
- Additional Protection:
- Sunscreen is an important part of sun protection, but it’s not the only measure you should take. Wearing protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses, seeking shade during peak sun hours, and avoiding excessive sun exposure all contribute to a comprehensive sun protection plan.
Remember, using sunscreen is crucial in preventing sunburn, premature aging, and reducing the risk of skin cancer. It’s a key component of a healthy skincare routine, especially if you spend time outdoors.

smear sunscreen
Application and Reapplication of Sunscreen lotion.
- Sunscreen should be applied generously to all exposed skin, including face, neck, ears, and any other areas not covered by clothing.
- It should be applied about 15-30 minutes before going out into the sun, and then reapplied every 2 hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
- Apply generously: Use enough sunscreen to cover all exposed skin. For most adults, this is about an ounce (30 milliliters), which is enough to fill a shot glass.
- Apply early: Put on sunscreen 15 to 30 minutes before going out in the sun.
- Reapply often: Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more often if you’re sweating or swimming.
- Use it every day: UV rays can cause damage even on cloudy or overcast days, so it’s a good idea to use sunscreen daily.
- Cover all exposed skin: This includes areas like your face, neck, arms, and legs. Don’t forget your ears, lips, and the top of your feet.
7 Health Benefits Of Sunscreen you must know
Sunscreen offers several important benefits for skin health:
- UV Protection: Shields the skin from harmful UV rays, preventing sunburn and reducing the risk of skin cancer.
- Prevents Premature Aging: Helps maintain youthful-looking skin by guarding against wrinkles and age spots caused by sun exposure.
- Maintains Even Skin Tone: Reduces pigmentation and redness, contributing to a more consistent complexion.
- Preserves Collagen and Elastin: Protects essential skin proteins, preventing sagging and loss of elasticity.
- Supports Post-Procedure Healing: Aids in the healing process after dermatological treatments by providing a protective barrier.
- Appropriate for All Skin Types: Available in various formulations for different skin types and activities.
- Overall Health Benefits: Beyond cosmetic advantages, it helps prevent serious conditions like skin cancer, emphasizing its importance for overall health.
Differences Between Tanning Oil, Sunscreen Oil and Sunscreen Lotion
TANNING OIL

1.Primarily designed to enhance and accelerate the tanning process, usually by attracting and intensifying UV rays.
2. May or may not contain SPF. If it does, the level is usually lower than typical sunscreens, as the primary purpose is to encourage tanning.
3.Often a lightweight, non-greasy oil that absorbs quickly into the skin, sometimes leaving a slight sheen.
4.May contain natural oils (e.g., coconut oil, carrot oil) and sometimes low levels of SPF, but the emphasis is on ingredients that attract and intensify UV rays for tanning.
5.If it contains SPF, it will offer some level of protection against UVB rays. However, it’s not designed for extended sun exposure without additional protection.
6. Enhances tanning by attracting and intensifying UV rays, potentially giving a deeper and faster tan.
7. Intended for individuals who are already tan and want to deepen their color or for those who want to accelerate the tanning process. Caution should be taken to avoid overexposure.
SUNSCREEN LOTION

1. Also designed for sun protection, but it’s typically a cream or liquid that is absorbed into the skin to form a protective layer.
2. Contains SPF, indicating its ability to protect against UVB rays.
3.Creamy or liquid texture that absorbs into the skin but might leave a slightly heavier feel compared to oil.
5. Contains similar active ingredients to sunscreen oil but is often mixed with various other moisturizing agents, antioxidants, and sometimes anti-inflammatory ingredients.
5. Offers protection against both UVA and UVB rays.
6. Provides sun protection while also offering moisturization and potentially additional skin benefits (depending on the formulation).
7. Suitable for those who want comprehensive sun protection with added skincare benefits and a variety of texture options (e.g., lotions, creams, sprays).
SUNSCREEN OIL

1. Primarily designed to provide sun protection by creating a barrier on the skin that absorbs or reflects UV rays.
2. Contains SPF, which indicates the level of protection against UVB rays.
3.Typically lightweight, non-greasy, and absorbs quickly into the skin.
4. Contains active ingredients like chemical or physical UV filters (e.g., avobenzone, titanium dioxide, zinc oxide) along with emollients or carrier oils.
5. Offers protection against both UVA and UVB rays
6. Provides sun protection while often giving a light, dewy finish. Some also offer additional skincare benefits like hydration.
7. Ideal for those who prefer a lighter texture and want both sun protection and a slight sheen on the skin.

photo of the sunset, beach Oil, Lotion
Key Considerations When Purchasing Sunscreen
- Opt for a broad-spectrum sunscreen safeguarding against both UV-A and UV-B rays, with an SPF of at least 15.SPF, or Sun Protection Factor, indicates the sunscreen’s effectiveness in guarding against UVB-induced sunburn. For instance, if you typically start to burn after 10 minutes of sun exposure, SPF 15 extends that duration by a factor of 15, allowing you approximately 150 minutes before experiencing sunburn.

- SPF 15 suffices for the majority of individuals. However, those with extremely fair skin, a familial predisposition to skin cancer, or conditions such as lupus that heighten sun sensitivity should opt for SPF 30 or higher. It’s important to note that as the SPF value increases, the added protection becomes incrementally smaller.
- Surprisingly, SPF 30 isn’t twice as potent as SPF 15. While SPF 15 shields against 93% of UVB, SPF 30 filters out 97%, representing only a marginal enhancement.
- Examine product labels and choose a waterproof variant for activities involving sweating or swimming.
- Select a non-irritating product or one specially designed for facial application.
- If you’re sensitive to para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), opt for a brand without this ingredient.
- Experiment with sunscreens containing different active chemicals if your skin reacts negatively to your current choice; formulations vary.
- For those with oily or acne-prone skin, opt for a water-based sunscreen.
- Recognize that a higher price tag doesn’t necessarily equate to superior performance; costlier brands may offer enhanced fragrance or texture but not necessarily better protection.
- Pay attention to the expiration date, as certain sunscreen components may degrade over time.
you’ll want a sunscreen with broad-spectrum or multi-spectrum protection for both UVB and UVA. Ingredients with broad-spectrum protection include benzophenones (oxybenzone), cinnamates (octylmethyl cinnamate and cinoxate), sulisobenzone, salicylates, titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, avobenzone (Parsol 1789) and ecamsule (Mexoryl SX- known as ecamsule, has been accessible in Europe and Canada since 1993. In the United States, L’Oreal now offers products containing ecamsule under the brand Anthelios SX)this make it more costly.
Sunscreen That is better for kids
Choose sunscreens that are free from para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) and benzephenones like dioxybenzone, oxybenzone, or sulisobenzone. Children’s sunscreens employ gentler ingredients, such as titanium dioxide and zinc oxide, which are less likely to cause skin irritation. Unlike chemical components, these substances safeguard infants’ skin without absorption.
For children aged 6 months and above, seek out a sunscreen specially formulated for them with a Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of 15 or higher. The American Academy of Pediatrics advises keeping babies under 6 months of age completely out of direct sunlight.
13 Sunscreens without PABA and benzophenones:
Here is a table of sunscreens without PABA and benzophenones:
| Sunscreen | Ingredients |
|---|---|
| Blue Lizard Australian Sunscreen | Zinc Oxide, Titanium Dioxide |
| Badger Balm Sunscreen | Zinc Oxide |
| EltaMD UV Physical Broad-Spectrum SPF 41 | Zinc Oxide, Titanium Dioxide |
| Neutrogena Sheer Zinc Dry-Touch Sunscreen SPF 50 | Zinc Oxide |
| Thinkbaby Safe Sunscreen SPF 50+ | Zinc Oxide |
| La Roche-Posay Anthelios Melt-in Milk Sunscreen SPF 100 | Homosalate, Octisalate, Avobenzone, Octocrylene |
| Neutrogena Hydro Boost Water Gel Lotion SPF 30/50 | Avobenzone, Homosalate, Octisalate, Octocrylene |
| Coppertone Pure and Simple SPF 50 | Zinc Oxide |
| Supergoop! Unseen Sunscreen SPF 40 | Avobenzone, Homosalate, Octisalate, Octocrylene |
| CeraVe Hydrating Mineral Sunscreen SPF 30/50 | Titanium Dioxide, Zinc Oxide |
| Australian Gold Botanical Sunscreen SPF 50 | Titanium Dioxide, Zinc Oxide |
| Bare Republic Mineral Sunscreen Gel-Lotion SPF 30 | Zinc Oxide |
| Alba Botanica Sensitive Mineral Sunscreen SPF 30 | Titanium Dioxide, Zinc Oxide |
Sunscreen recall due to Benzene

This was Recall by FDA due to containing benzene According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), signs a person is suffering from a high level of benzene include drowsiness, dizziness, rapid or irregular heartbeat, headaches, tremors, confusion, unconsciousness and in severe cases, death. Contact your physician or healthcare provider if you believe you are experiencing any medical problem caused by benzene exposure.
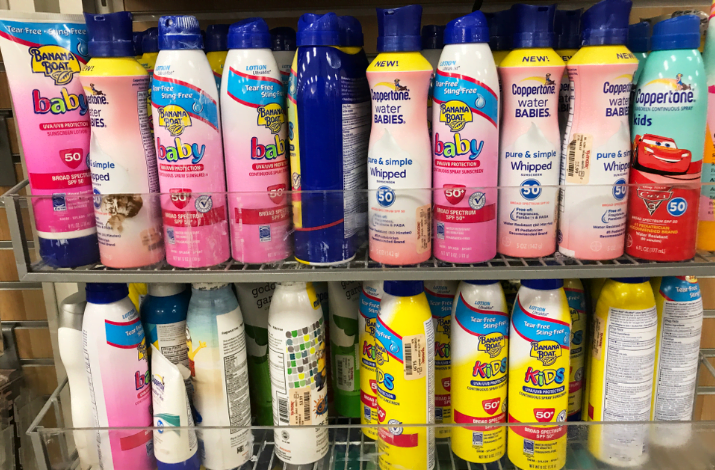

Recall Sunscreen by FDA,The affected Coppertone products were all manufactured between January 10 and June 15 and sold across the country. They include specific lots of five Coppertone aerosol sunscreen spray products: Coppertone’s Pure & Simple SPF 50 Spray, Pure & Simple Kids SPF 50 Spray, Pure & Simple Baby SPF 50 Spray, Sport Mineral SPF 50 Spray and travel-size Coppertone Sport Spray SPF 50. According to the American Cancer Society, based on evidence from studies in both people and lab animals, benzene has been linked with causing cancer, most often leukemia and other cancers of blood cells.
The Food & Drug Administration recently announced the recall of more Banana Boat Hair & Scalp Sunscreen Spray SPF 30 because it contained benzene, a cancer-causing chemical.
The manufacturer issued the Jan.27 voluntary recall after a July ,29,2022 recall warned that a propellant that sprays the product out of the can had traces of benzene. Here is a list of both Johnson & Johnson and Coppertone aerosol products recalled in 2021.
- Neutrogena Beach Defense
- Neutrogena Cool Dry Sport
- Neutrogena Invisible Daily Defense
- Neutrogena Ultra Sheer
- Aveeno Protect + Refresh
- CoppertonePure & Simple SPF 50
- Coppertone Pure & Simple Kids SPF 50
- Coppertone Pure & Simple Baby SPF 50
- Coppertone Sport Mineral SPF 50
- Coppertone, Travel-size Sport Spray SPF 50
For more information about the recall, you can call (888) 921-1537.
Resources
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/risk-prevention/chemicals/benzene.html
https://www.webmd.com/beauty/features/whats-best-sunscreen
https://www.webmd.com/beauty/features/high-spf-sunscreens-are-they-better