Adherus and Duraseal are two dural sealants for neurosurgical procedures, particularly for preventing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks. Adherus features a two-component hydrogel that forms a watertight seal over the dura mater, which is absorbed over approximately 90 days with longer absorption period. DuraSeal also uses a hydrogel composed of polyethylene glycol (PEG) but is known for a quicker absorption rate, typically within 4 to 8 weeks. DuraSeal is not powered, which means it relies on manual application, potentially making it less convenient in complex surgical settings compared to Adherus.
| Adherus | DuraSeal |
|---|---|
| Application: Battery-powered, auto-spray | Application: Manual application |
| Absorption Time~90 days | Absorption Time: 4-8 weeks |
| Sealant Composition: Two-component hydrogel | Sealant Composition: PEG-based hydrogel |
| Swelling Potential: Up to 13% in size, 46% by volume | Swelling Potential: Up to 50% in size |
| FDA Approval: 2019 | FDA Approval: 2005 |
| Use Cases: Longer-term protection | Use Cases: Faster healing, shorter procedures |
While both Adherus and Dura-seal excel in their respective domains, their unique attributes and targeted applications set them apart, prompting a thorough examination of their strengths and limitations. This comparative analysis aims to shed light on the key features and optimal use cases of these adhesive technologies, ultimately assisting industries in making informed choices for their specific requirements.
Adherus and DuraSeal

What is Adherus?
Adherus is an Auto-Spray battery powered Dural Sealant is a specialized medical tool utilized in neurosurgical procedures. Its primary purpose is to effectively close Dural incisions, safeguarding the delicate covering of the brain and spinal cord, thereby minimizing the risk of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks.
This device is package sterile and is a disposable design, and can be open on a sterile surgical field. It has an internal system components that provide air flow to aid in the delivery of a synthetic , absorbable, two-component hydrogel sealant system and allow delivery to be interrupted without clogging.
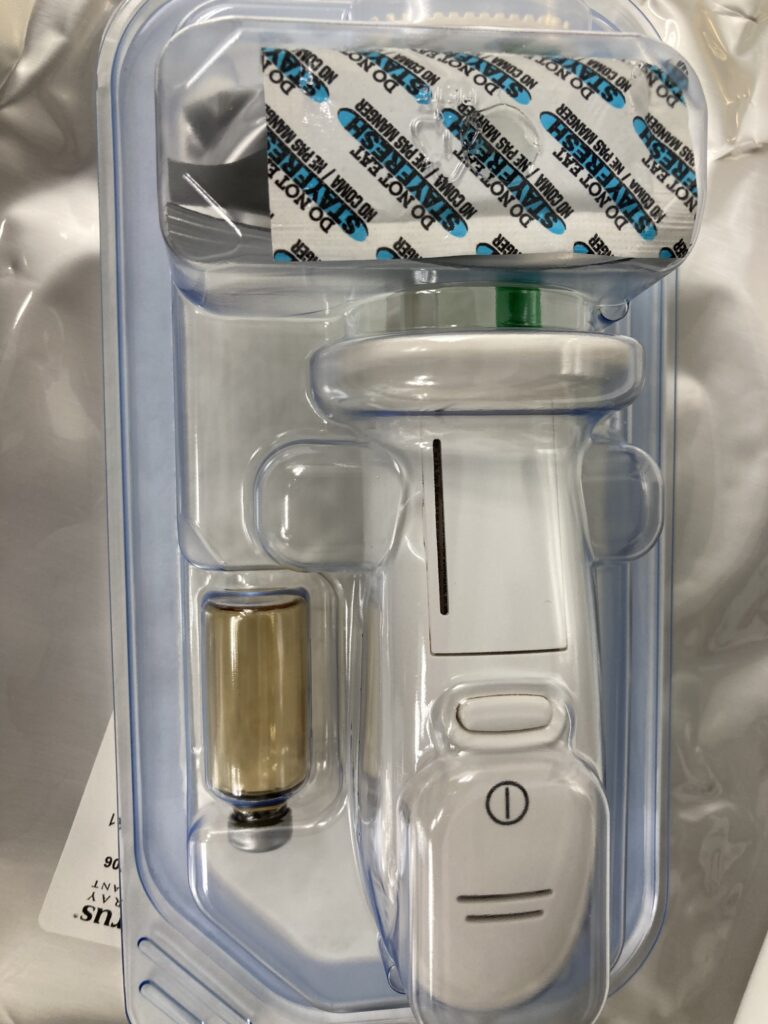
The device is supplied as a pre-assembled applicator and two separate glass vials, one of which is package within a foil pouch. The two glass vials contain either an active polyethylene glycol (PEG) ester powder or a polyethyleneimine (PEI) dissolve sterile water.
How it works the solution immediately crosslinks to form a hydrogel sealant which is absorbed over approximately 90days , sufficient time to allow for healing.
What is dural sealant ?
A dural sealant is a medical product used to create a watertight seal on the dura mater, which is the tough outer membrane covering the brain and spinal cord.
This sealant is typically used during neurosurgical procedures, particularly when the dura mater has been cut or torn, to prevent cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from leaking.
Dural sealants are often made from materials that can adhere to the wet surface of the dura and form a flexible, impermeable barrier.
These sealants may be natural (derived from human or animal proteins) or synthetic, and they are designed to be biocompatible and gradually absorbed by the body over time. Examples are Adherus and DuraSeal.
The use of a dural sealant can help reduce the risk of post-operative complications such as CSF leaks, which can lead to issues like infection, headaches, and neurological problems. The application of the sealant is usually done after the primary surgical repair of the dura, as an additional measure to ensure a complete seal.
Indication for use Of Adherus
Adherus Auto-Spray Dural Sealant is indicated for use in patients who are 13yrs old and older .Instead of standard methods of Dural repair, such as sutures, to provide watertight closure during cranial procedures.
Contraindications Of Adherus
Adherus Auto-Spray Dural Sealant should not be use in Confined anatomical spaces where nerve compression is of concern. The hydrogel may swell up to 13% of it size in any dimension or 46% by volume after application.
Here is a list of conditions and situations where Adherus AutoSpray Dural Sealant has not been studied or is not recommended for use:
- Paients who require a procedure involving a Translabyrinthine, Transsphenoidal, or transoral approach, or any procedure that penetrates the air sinus or mastoid air cells.
- Patients whose dural edge gaps are larger than 2 mm.
- Patients with severely altered renal or hepatic function.
- Patients with an active infection present at the surgical site.
- Patients who have treated or untreated hydrocephalus (e.g., those with devices designed to evacuate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or altered CSF dynamics).
- Patients who have an underlying medical co-morbidity or are on a medication known to interfere with wound healing (e.g., those with previous intracranial neurosurgical procedure in the same anatomical location, radiation and chemotherapy treatment, known malignancy, diabetes, steroid toxicity and chronic corticosteroid use, compromised immune system, or on an anticoagulant agent, aspirin or non-steroid anti-inflammatory agent).
- Patients with a known allergy to FD&C Blue #1 Dye or FD&C Yellow #5 Dye.
- Patients who are pregnant or lactating.
9 basic Precaution to follow when using Adherus Autospray
1. The Adherus AutoSpray Dural Sealant pouch is provided in a sterile condition. If the pouch appears damaged or has been opened, do not use it. Avoid re-sterilization.
2. The Adherus AutoSpray Dural Sealant package is designed for single-patient use exclusively. Properly dispose of any unused or opened product. Reusing the device may lead to potential cross-contamination, posing risks to patient safety.
3. Store the product away from direct sunlight. Refrain from using if the PEG ester powder does not flow freely.
4. Apply the Adherus AutoSpray Dural Sealant within two hours after reconstituting the crosslinking components. Extensive testing has shown that samples reconstituted for longer periods, such as 8 hours, exhibited a small but statistically significant increase in swelling compared to those reconstituted for 1, 2, or 4 hours.
5. The applicator system has an operational battery life of approximately two hours when used continuously.
6. Before applying the Adherus hydrogel, ensure that there is no active fluid outflow (such as cerebrospinal fluid or blood).
7. Avoid using the Adherus AutoSpray Dural Sealant in conjunction with flammable anesthetics or anesthetics that contain oxidants.
8. Keep the Adherus AutoSpray Dural Sealant device away from powerful magnetic fields to prevent potential interference with RF communication. Magnetic resonance equipment may generate disruptions in pump operations.
9. Only open the system covers as needed for battery replacement; do not remove any other covers.
DuraSeal Sealant System
The DuraSeal Dural Sealant System is a medical device used in neurosurgery. It is designed to help prevent cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage following certain surgical procedures on the brain and spinal cord.
CSF leakage can be a complication of neurosurgery, and it’s important to prevent it to avoid potential complications and infections.
The DuraSeal system provides a sealant that is applied to the dura mater, which is the outermost layer covering the brain and spinal cord. This sealant helps create a watertight barrier, reducing the risk of CSF leakage.
The sealant is composed of two solutions, a polyethylene glycol(PEG) ester solution a trilysineamine solution(referred to as the blue and clear precursors, respectively).precursor crosslink when mixed together to form hydrogel sealant.
The hydrogel implant is absorbed in approximately 4 to 8 weeks, sufficient time to allow for healing.
DuraSeal dural sealant was approved by the FDA in 2005 for use during brain surgery. DuraSeal spinal sealant was originally approved by FDA in September 2009.

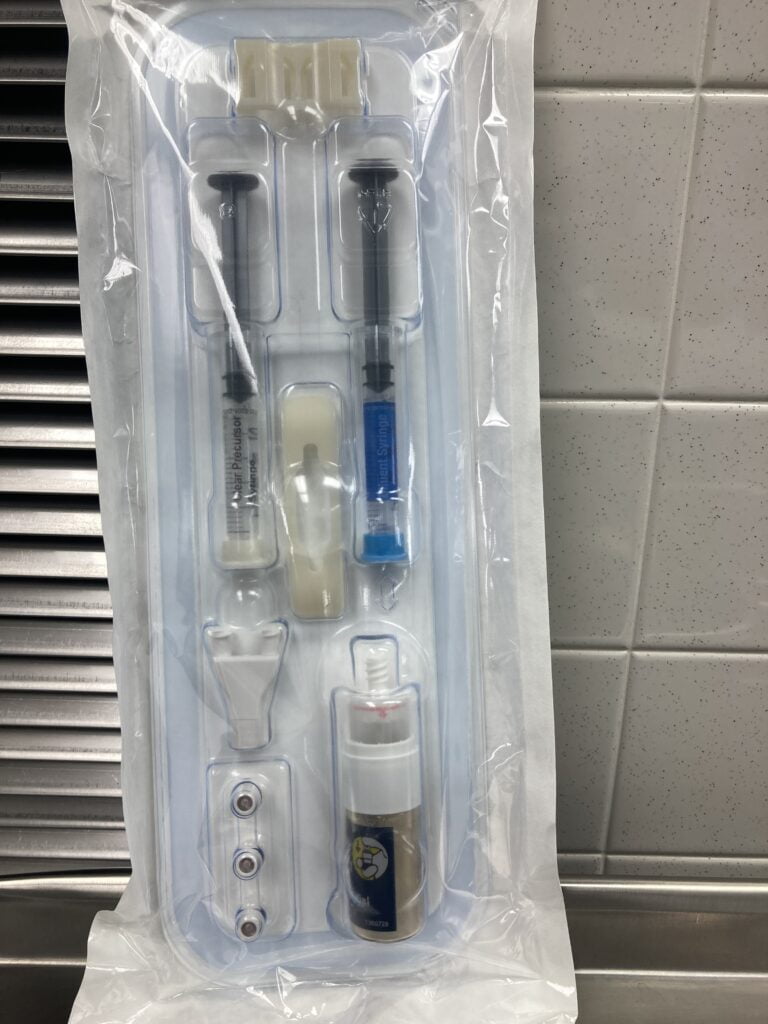
DuraSeal
What is the shelf life of Adherus
The shelf life of Adherus, as approved by the FDA, is typically 24 months (2 years) when stored under recommended conditions.
This information is based on the stability studies that are required for FDA approval, ensuring that the product remains effective and safe for use within this period.
Always refer to the specific packaging and product insert for the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding the shelf life of Adherus, as it may vary slightly depending on the specific formulation and storage conditions.
Indication for use of DuraSeal
The DuraSeal Dural Sealant System is intended for use as an adjunct to sutured Dural repair during cranial surgery to provide watertight closure.
- Closure of dural defects during neurosurgery, including:
- Craniotomy procedures
- Spinal cord surgeries
- Decompressive surgeries for conditions like tumors or hematomas
- Prevention of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks:
- Especially important in procedures involving the skull base or spine where CSF leakage can lead to complications such as meningitis or pseudomeningocele formation
- Management of dural tears or defects caused by trauma:
- DuraSeal can be used to seal traumatic injuries to the dura mater, providing a protective barrier and facilitating healing
- Reduction of postoperative complications:
- By promoting a watertight seal and supporting tissue healing, DuraSeal may help reduce the risk of complications such as infections or recurrent CSF leaks after surgery
- Adjunct to sutures or staples:
- DuraSeal can be used in conjunction with traditional closure techniques to enhance the integrity of the dural closure and minimize the risk of leaks or herniation
- Facilitation of tissue healing:
- DuraSeal’s biocompatible formulation supports tissue regeneration and healing at the surgical site, aiding in the recovery process following neurosurgical procedures.
Types of duraSeal
There are a few different variations or formulations of DuraSeal that cater to specific surgical needs:
1. DuraSeal Xact: This formulation is designed specifically for use in spinal surgeries. It provides a watertight closure of the dura to prevent cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks in the spine. DuraSeal Xact has a slightly lower viscosity, making it easier to apply in confined spinal spaces.
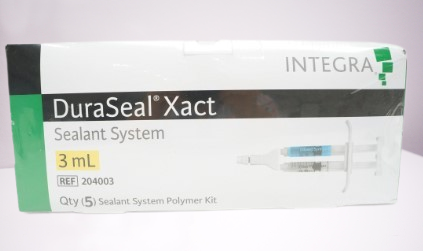
2. DuraSeal Exact Spine Sealant System: This is another variant for spinal surgeries, designed to be used in procedures where precise application is necessary.
It comes with an applicator that allows for better control during application, which is particularly useful in complex spinal surgeries.
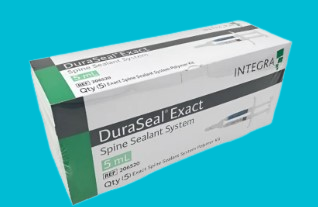
3. DuraSeal Dural Sealant System: This is the original formulation designed for use in cranial procedures. It is used to seal the dura mater after neurosurgical operations on the brain to prevent CSF leaks.

4. DuraSeal Plus: This variant includes an additional hemostatic agent, which not only seals the dura but also helps to control bleeding at the surgical site.
This is particularly useful in surgeries where both a sealant and hemostatic control are needed.
5. DuraSeal Exact Cranial Sealant System: Similar to the spinal variant, this version is designed for cranial procedures, providing a more precise application and better control during surgery.
6. DuraSeal QuickCoat Penetrating Stain: This premium wood stain is designed for finishing and staining wood surfaces, providing a durable and aesthetically pleasing finish while enhancing the natural beauty of the wood.
Ideal for DIY enthusiasts and professionals alike, DuraSeal QuickCoat offers a rich, deep color that lasts.
Note: This product is specifically formulated for wood surfaces and should not be confused with medical products. Always use in a well-ventilated area and follow safety instructions on the label. Keep out of reach of children.

Contraindications of DuraSeal
Do not apply to confined bony structures where nerves are present since neural compression may result due to hydrogel swelling
The hydrogel may swell up to 50% of its size in any direction.
- Infection at the Application Site: DuraSeal should not be used in areas where there is an active infection, as this could exacerbate the condition or lead to further complications.
- Hypersensitivity or Allergies: Patients with known hypersensitivity or allergies to any components of DuraSeal should avoid its use to prevent severe allergic reactions.
- Spinal Cord Compression: It is contraindicated to use DuraSeal in situations where there is evidence of spinal cord compression, as it may worsen the condition.
- Cranial Procedures Near Optic Nerve: Avoid using DuraSeal in cranial procedures where the sealant might come into contact with the optic nerve, as it could cause damage or impair vision.
- Pregnancy and Lactation: The safety of DuraSeal in pregnant or breastfeeding women has not been established, so its use should be carefully considered and possibly avoided in these cases.
- Closed Body Cavities: DuraSeal is not recommended for use in closed body cavities where swelling from the sealant could cause pressure-related complications.
These contraindications are important to consider to ensure the safe and effective use of DuraSeal in surgical settings. Always consult the specific product labeling and medical guidelines for detailed contraindication information.
Shelf Life of DuraSeal (per FDA)
A 12-month shelf life was established based on results from real-time (53 weeks) test.https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf4/P040034b.pdf
evaluations for 3 DuraSeal product lots. The devices were tested for the following
attributes following real-time and accelerated aging:
- Visual assessment
- Hydrogel performance
- Packaging assessment
DEVICE DESCRIPTION
The DuraSeal Dural Sealant System consists of components for preparation of an
absorbable polyethylene glycol (PEG) hydrogel sealant and a delivery system (i.e.,
applicator, spray tips and plunger cap) packaged in a sterile single use kit. The sealant is
composed of two solutions, a PEG ester solution and a trilysine amine solution which are
referred to as the “blue” and “clear” precursors, respectively. When mixed together, the
precursors rapidly polymerize in-situ to form the hydrogel sealant.
DuraSeal compare to Adherus
| DURASEAL | ADHERUS |
| 1. Not powered ,so thus has no on and off button. | 1. Auto-Spray battery powered, has ON/OFF button |
| 2.System has 2 syringes one with blue label one with the diluent | 2. has 2 Glass vials with active polyethylene glycol(PEG)ester powder |
| 3. A product of Integra ,for Dural repair | 3. A product Stryker, for Dural repair. |
| 4. Use within 1 hour of preparation. | 4. Use within 2 hours of preparation |
| 5. Hydrogel implant is absorbed in approximately 4-8 weeks | 5.Hydrogel sealant absorbed in approximately 90 days |
| 6.Hydrogel swell up 50% in all directions | 6.Hydrogel swells up 13% of it size in any direction |
| 7. Package sterile and consist of polyethylene glycol(PEG) | 7.Package sterile and consist of polyethylene glycol(PEG) |
| 8. Consist of Trilysineamine solution a product of l-lysine synthesis | 8.Consist of Polyethyleneimine dissolve sterile water synthetic water . |
| 9. Dose not need batteries . | 9. Battery operated compartments are glued shut to prevent them from opening and contaminating the sterile field during procedures. |
Adherus vs DuraSeal Cost
| Adherus | DuraSeal |
|---|---|
| Dural Sealant | Dural Sealant |
| $500 – $700 per unit | $450 – $650 per unit |
| 5 mL, 10 mL | 3 mL, 5 mL, 10 mL |
| $50 – $70 per mL | $45 – $65 per mL |
| 1-2 years | 1-2 years |
| Single-use kits | Single-use kits |
| May include specialized applicators | May include specialized applicators |
| Available through medical suppliers | Available through medical suppliers |
What are the common allergens present in Adherus and DuraSeal?
Both products have specific formulations, and while they are generally designed to minimize allergic reactions, some components may act as allergens in sensitive individuals.
Adherus:
Adherus is a synthetic, polyethylene glycol (PEG)-based hydrogel. The common allergens that may be present or involved in reactions include:
- Polyethylene Glycol (PEG): While PEG itself is generally considered hypoallergenic, some individuals may have an allergic reaction to it.
- Polypropylene Glycol (PPG): This can also be a sensitizer for some individuals, though it is rare.
- Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate (HEMA): Used in some formulations as a crosslinker, this compound can be a contact allergen, though not typically in Adherus.
DuraSeal:
DuraSeal is also a PEG-based hydrogel, with some additional components that may contribute to allergic reactions:
- Polyethylene Glycol (PEG): Similar to Adherus, PEG is the main component and can cause reactions in sensitive individuals.
- FD&C Blue No. 1 (Brilliant Blue FCF): Used as a colorant, this dye has been known to cause allergic reactions in rare cases.
- Human Serum Albumin (HSA): Although not present in every formulation, when included, it can cause allergic reactions in individuals allergic to human proteins.
Key Points:
- Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) is the most common potential allergen in both Adherus and DuraSeal.
- DuraSeal has an added risk with FD&C Blue No. 1, which can be an allergen for some people.
- Human Serum Albumin in certain formulations of DuraSeal may also be a concern for individuals with specific allergies.
It’s crucial to assess the patient’s allergy history before using these products in a clinical setting.
What emergency measures should be taken if an allergic reaction occurs during the use of Adherus or DuraSeal?
If an allergic reaction occurs during the use of Adherus or DuraSeal (which are surgical sealants used in procedures involving the dura mater), the following emergency measures should be taken:
- Immediately Discontinue Use:
- Stop the application of the sealant immediately if an allergic reaction is suspected.
- Assess the Patient:
- Quickly assess the patient’s condition, looking for signs of an allergic reaction such as hives, swelling, difficulty breathing, low blood pressure, or anaphylaxis.
- Administer Antihistamines:
- Administer antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) to help alleviate mild allergic reactions like hives or itching.
- Administer Epinephrine:
- If the patient shows signs of anaphylaxis (e.g., severe swelling, difficulty breathing, drop in blood pressure), immediately administer epinephrine. This is typically done through an intramuscular injection (e.g., an EpiPen).
- Provide Oxygen Support:
- Administer supplemental oxygen if the patient is having difficulty breathing or shows signs of respiratory distress.
- Initiate Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) if Necessary:
- If the patient’s condition deteriorates rapidly, and they experience respiratory or cardiac arrest, begin CPR immediately and follow advanced cardiovascular life support (ACLS) protocols.
- Notify the Surgical Team:
- Ensure that all members of the surgical team are aware of the situation so that they can assist in managing the reaction and adjust the surgical plan if necessary.
- Prepare for Potential Intubation:
- If the patient’s airway is compromised, be prepared to intubate the patient to secure the airway and ensure adequate ventilation.
- Administer Corticosteroids:
- Administer corticosteroids such as methylprednisolone to help reduce inflammation and prevent a delayed or prolonged allergic reaction.
- Monitor Vital Signs:
- Continuously monitor the patient’s vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation, to assess their response to treatment.
- Transfer to ICU if Necessary:
- If the reaction is severe and requires ongoing critical care, arrange for the patient to be transferred to an intensive care unit (ICU) for further monitoring and treatment.
- Document the Reaction:
- Document the allergic reaction in the patient’s medical records, including the symptoms, treatment administered, and the patient’s response to the treatment.
- Report the Incident:
- Report the allergic reaction to the appropriate medical authorities, such as the hospital’s adverse event reporting system or the FDA’s MedWatch, as this information may be critical for future patient safety and product assessment.
These steps are essential to ensure the safety and well-being of the patient during and after the occurrence of an allergic reaction to Adherus or DuraSeal.
Overview of Human Studies and research on polyethylene glycol (PEG) Sealants
- umber of Studies: 9 studies, including 2 systematic reviews, 5 randomized controlled trials (RCTs), 1 nonrandomized comparative study, and 1 single-arm study.
- Areas of Use: Sealants were analyzed in various anatomical areas: ocular, pleural (lung), vascular, gynecological, spinal/cranial, and rectal.
- Patient Follow-Up: Ranged from immediate postoperative to 60 months, involving 66 to 347 patients. One study focused on pediatric patients.
Local Responses/Device Events
- Ocular Sealants: Higher immediate postoperative eye pressure and pain were reported with ReSure compared to other methods. OcuSeal had fewer issues like astigmatism and foreign body sensation compared to sutured closure.
- Pleural Sealants: The most common issue was pneumothorax (collapsed lung), with rates ranging from 8.1% to 40.5%. Other issues included bronchopleural fistula, emphysema, and pain, but these were less common.
- Vascular Sealants: A small number of patients experienced pericardial effusion (fluid around the heart) with Tridyne sealant.
- Gynecological Sealants: Patients reported abdominal pain, ovarian cysts, and uterine issues, similar to the control group.
- Spinal/Cranial Sealants: Issues included cerebrospinal fluid leaks, neurological complications, and in rare cases, meningitis.
- Rectal Sealants: Complications like gastrointestinal (GI) toxicities were reported, ranging from mild to severe, including cases of fistulas and proctitis.
Systemic Responses
- Pleural Study: Similar complication rates between PEG sealants and control groups.
- Vascular Study: Both PEG and non-PEG groups reported similar issues like stroke and kidney-related problems.
- Gynecological Study: Side effects like headache and skin rash were reported, similar to the control group.
- Spinal/Cranial Study: Serious adverse events were mild to moderate, with most resolving by 120 days.
Overall Quality of Evidence
- Local Responses/Events: Evidence quality was generally low due to inconsistencies across studies.
- Systemic Responses: The quality of evidence was also low, with only some consistent findings, such as migration issues in aneurysm treatments.
Aneurysm Sealants
- Studies: 3 human studies, including 2 systematic reviews.
- Local Responses: Issues like endoleaks, aneurysm ruptures, and device migration were reported.
- Systemic Responses: Included mortality, respiratory failure, stroke, and postimplantation syndrome (PIS).
Adhesion Barrier
- Studies: 4 human studies, including 1 systematic review.
- Local Responses/Device Events: Some adverse events were noted with PEG devices, though they were generally similar to control groups. One study reported issues like abscesses and fistulas with another non-PEG barrier device.
In summary, while PEG sealants and barriers have been used across various medical fields, the evidence of their safety and efficacy is generally low due to inconsistencies and a lack of high-quality studies. Some local and systemic complications were reported, but many were similar to those seen with other methods.
for further information on the research visit https://www.fda.gov/media/155398/download
Resources
Work experience and training and education from product company vendors.
https://www.fda.gov/media/155398/download
https://cmf.stryker.com/assets/files/74/cmf-fl-93_rev.-2_19251-adherus-et-flyer.pdf