Explore the differences between obsidian blades and steel blades. Learn about their sharpness, durability, and best uses in various applications to find out which blade suits your needs best.
Obsidian blades are crafted from volcanic glass by flintknapping, where as steel blade is a metal alloy primarily composed of iron and carbon, with varying amounts of other elements like chromium, nickel, and more. Steel blades are formed through processes like forging, grinding, and heat-treating. This allows for a wide range of hardness, sharpness, and durability depending on the specific alloy and heat treatment used.
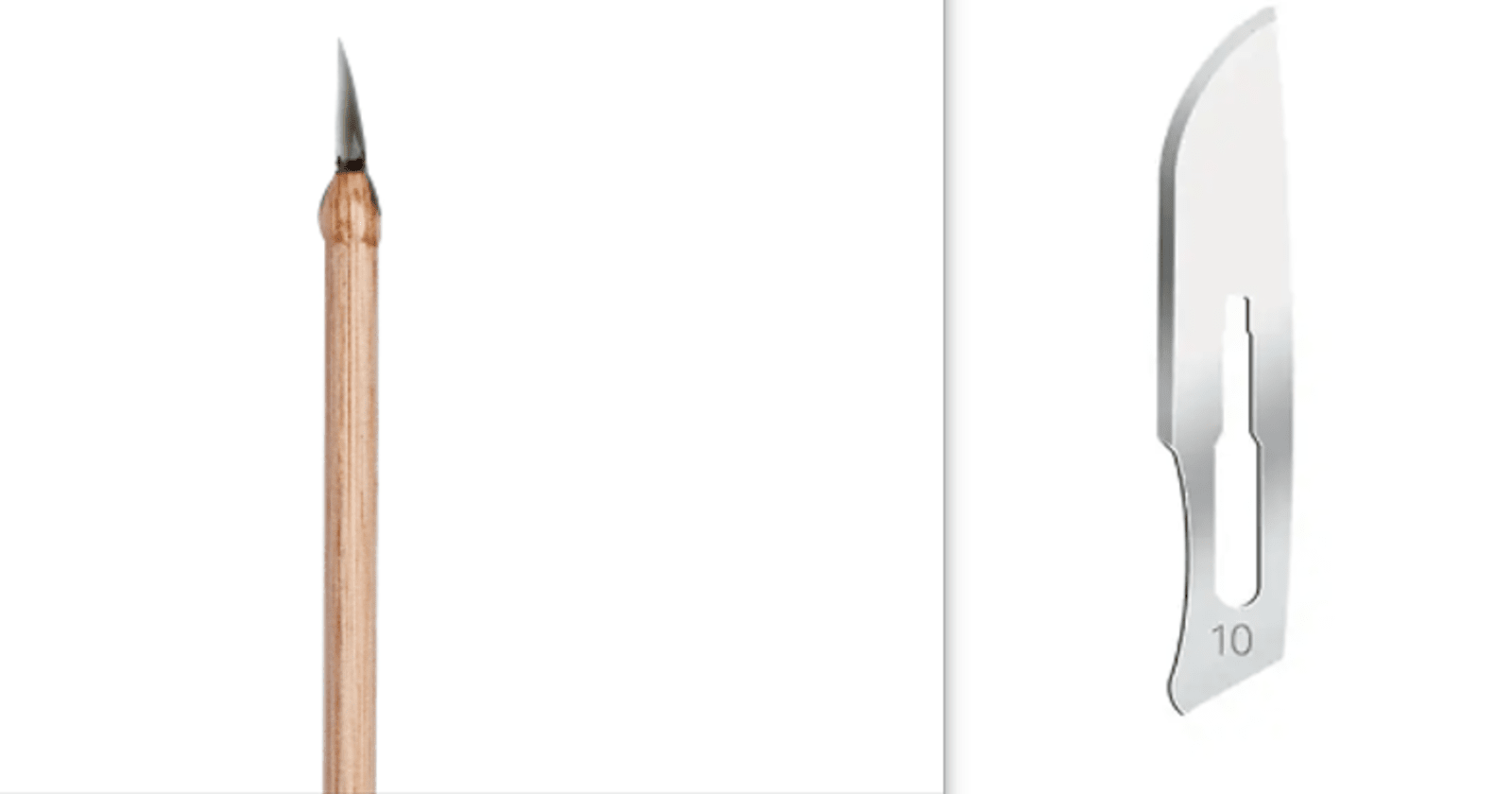
Obsidian is a type of natural glass that forms from rapidly cooled lava. It is a hard and brittle material. Obsidian blades are crafted from this volcanic glass through a process called flintknapping, where skilled artisans shape and sharpen it into a cutting tool. Obsidian blades are known for their exceptional sharpness and fine edge, making them suitable for tasks that require precision.
Obsidian Surgical Blade
Obsidian blades are renowned for their exceptional sharpness and edge retention, making them prized tools throughout history. This type of natural glass is formed when molten lava from a volcanic eruption cools rapidly, often due to contact with water or air. The rapid cooling prevents the formation of crystalline structures, resulting in a smooth, non-crystalline material known as glass.
Obsidian is typically dark in color, ranging from black to dark brown, and sometimes even exhibits hints of red or green, depending on impurities and mineral inclusions. Its appearance can be glossy and smooth, with a glassy luster that gives it a distinctive and attractive aesthetic.


Because of its composition, obsidian is notoriously brittle and lacks the durability of metals like steel. However, its sharpness and ability to maintain a keen edge make it invaluable for various purposes, particularly in cutting and slicing applications.
To create obsidian blades, skilled artisans would carefully shape and flake the raw obsidian material using techniques such as pressure flaking, percussion flaking, or abrading. This process required precision and expertise, as mishandling could lead to fractures or irregularities in the blade’s edge.
Despite its brittleness, obsidian blades have found enduring use in specialized fields such as surgery, where an extremely sharp edge is crucial for precise incisions. Additionally, obsidian blades have been utilized in niche applications like archaeological excavations, where their sharpness and fine edges are beneficial for delicate tasks.
In modern times, obsidian blades continue to be appreciated for their sharpness and are sometimes used for tasks like crafting custom knives, surgical instruments, and artistic creations. While they may not replace the ubiquity of steel in many applications, obsidian blades remain a testament to the enduring appeal and utility of this unique natural material.
Steel Surgical Blade

Steel surgical blades can be extremely sharp and are commonly used in medical procedures. They are made from high-quality stainless steel that is carefully manufactured and sharpened to a fine edge. However, compared to obsidian, which has a unique molecular structure that allows it to achieve an exceptionally sharp edge, steel blades may not achieve the same level of edge refinement.
Obsidian is a naturally occurring volcanic glass that has been used for thousands of years by various cultures for cutting tools and weapons. Its sharpness is a result of its microstructure, which consists of very fine, uniform crystals. This allows obsidian blades to achieve an incredibly sharp edge, sometimes even finer than what can be achieved with steel.
That being said, steel surgical blades are still highly effective and widely used in medical settings due to their durability, corrosion resistance, and overall reliability. They are designed to meet the specific requirements of surgical procedures, and they undergo rigorous quality control processes to ensure their effectiveness and safety.
Unique Differences between Obsidian Blade and Steel Blade
| Obsidian Blade | Steel Blade |
|---|---|
Material Composition: Obsidian, a volcanic glass, forms rapidly from lava cooling and is mostly silicon dioxide. Blades are crafted by shaping and flaking this raw material. Hardness: Obsidian is extremely hard and brittle. It has a hardness of around 5.5 on the Mohs scale, which is comparable to window glass. Toughness: While obsidian is very hard, it is also extremely brittle. This means that it can fracture or chip easily if subjected to lateral stress or impact. Edge Retention: Obsidian blades can achieve an incredibly sharp edge due to their fine crystalline structure. However, this edge can dull relatively quickly due to the brittleness of the material. Maintenance: Obsidian blades require special care and handling to prevent chipping or damage. They should not be used for heavy-duty tasks and may need re-sharpening more frequently. Applications: Obsidian blades were historically used by various ancient cultures for cutting, slicing, and performing surgical procedures. They were also used for ceremonial and ritualistic purposes. Cultural Significance: Obsidian blades have cultural and historical significance in various indigenous cultures around the world, including Mesoamerican civilizations like the Aztecs and Maya | Material Composition: Steel is an alloy composed primarily of iron with varying amounts of carbon and other elements. It is manufactured through a process involving smelting and refining iron ore. Hardness: The hardness of steel can vary widely depending on the specific type of steel and its heat treatment. High-quality steel used for blades is typically hardened to a much higher level than obsidian. Toughness: Steel is tougher and more resilient compared to obsidian. It can flex and absorb impacts without breaking. Edge Retention: High-quality steel blades can also achieve a sharp edge, and they tend to retain their edge for longer periods of time compared to obsidian. Maintenance: Steel blades are more versatile and durable. They require regular maintenance like cleaning, oiling, and occasional sharpening, but they can handle a wider range of tasks. Applications: Steel blades are used in a wide range of applications, including kitchen knives, hunting and survival knives, swords, tools, and industrial equipment. Cultural Significance: Steel blades have played a crucial role in human history, from the early development of blades to modern industrial applications. |
Key Limitations of Obsidian blade and Steel Blade
Obsidian Surgical Blade:
- Fragility: Obsidian is a naturally occurring volcanic glass, which makes it inherently more fragile compared to steel. It can chip or break if not handled carefully.
- Durability: Obsidian blades tend to wear down faster than steel blades. This means they may need to be replaced more frequently, which can increase costs over time.
- Limited Applications: Obsidian blades are primarily used in procedures requiring very precise and fine incisions, such as ophthalmic surgery or certain types of cosmetic surgery. They may not be suitable for all surgical procedures.
- Sterilization: Obsidian blades may require special care in sterilization processes. They can be more sensitive to certain sterilization methods compared to steel.
- Availability: Obtaining high-quality obsidian and crafting surgical blades from it can be more challenging and less standardized compared to mass-produced steel blades. This may result in variations in quality and availability.
Steel Surgical Blade:
- Less Sharpness: While steel surgical blades are extremely sharp, they may not be able to achieve the same level of sharpness as obsidian blades. This can be a consideration for procedures requiring the utmost precision.
- Risk of Corrosion: Steel blades can corrode over time if not properly cared for. This may be a concern if they are exposed to certain chemicals or not cleaned and stored correctly.
- Allergies and Sensitivities: Some individuals may have allergies or sensitivities to certain metals used in steel surgical blades. This can lead to skin irritation or other adverse reactions.
- Weight: Steel blades are typically heavier than obsidian blades. While this may not be a significant issue for many procedures, it could potentially be a factor in cases where the weight of the instrument matters.
- Cost: High-quality surgical steel can be expensive, and the cost of steel blades may be higher compared to obsidian blades. Additionally, they can be more costly to manufacture and maintain.
It’s important to note that the choice between using an obsidian or steel surgical blade depends on the specific requirements of the surgical procedure and the preferences of the surgeon. Additionally, advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques may lead to improvements and innovations in both types of blades in the future.
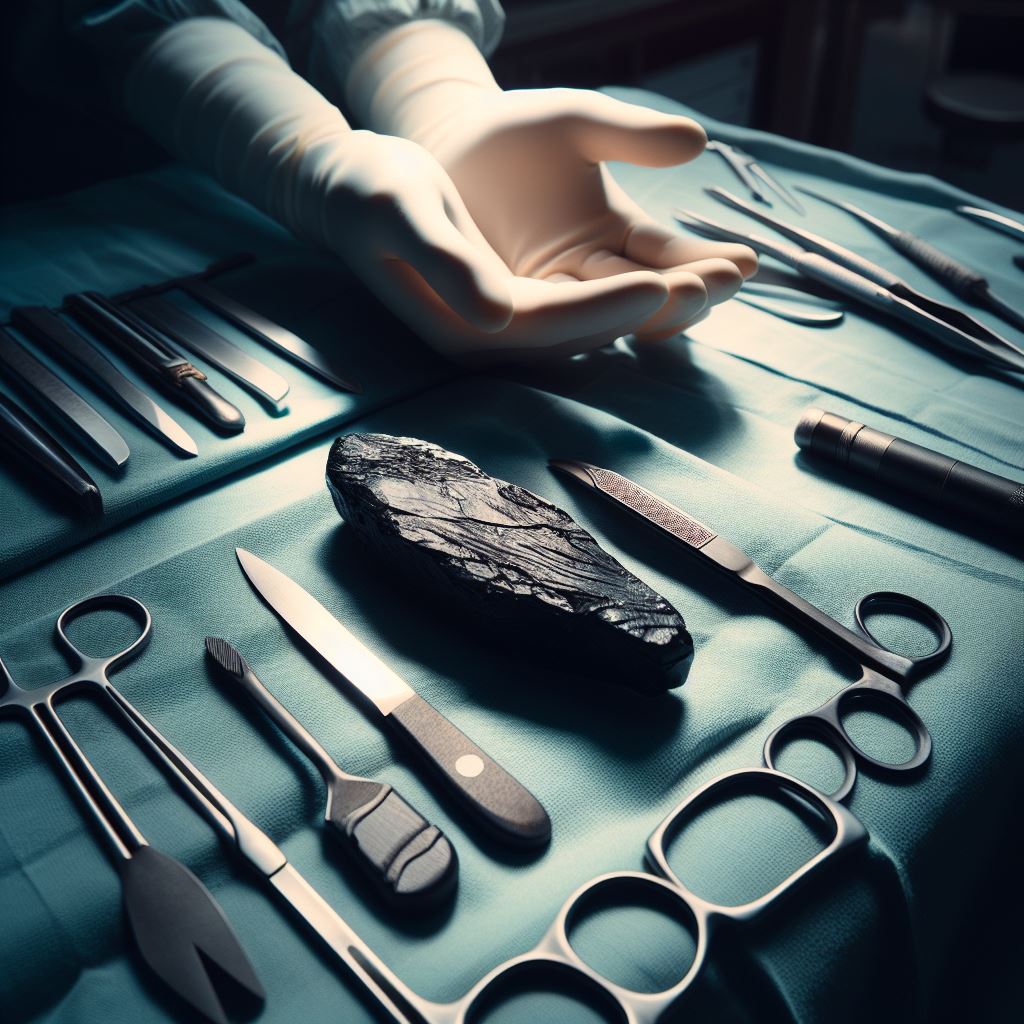
Advantages of Obsidian blades compared to steel blades in microsurgical procedures:
Obsidian blades are advantageous in performing surgery on very thin skin such as the eyelids or genital area. These blades have been used in various surgical procedures, including microsurgery, due to their exceptional sharpness and precision. Here are some advantages of obsidian blades compared to steel blades in microsurgical procedures:
- Sharpness: Obsidian blades are incredibly sharp, with edges that can be honed to a level finer than even the sharpest steel blades. This allows for cleaner and more precise cuts, which is crucial in microsurgery where delicate tissues and small blood vessels are involved.
- Minimal Tissue Damage: The sharpness of obsidian blades means that they can make extremely fine incisions with minimal tissue damage. This is essential in microsurgery, where preserving healthy tissue and minimizing trauma to surrounding structures is critical for successful outcomes.
- Reduced Tissue Trauma: Due to their sharpness, obsidian blades can cut through tissues with less resistance compared to steel blades. This reduces the amount of force required to perform a surgical procedure, minimizing the risk of damaging delicate tissues and structures.
- Precision in Dissection: Microsurgery often involves intricate dissection of small structures like blood vessels and nerves. The precision of obsidian blades allows surgeons to navigate through these structures with a high degree of accuracy, reducing the risk of inadvertent damage.
- Improved Healing: Because obsidian blades create clean, precise incisions, they can lead to better wound healing. Clean edges promote faster tissue regeneration and reduce the likelihood of complications such as infections.
- Reduced Scarring: The fine cuts made by obsidian blades can result in smaller, less noticeable scars compared to those made with steel blades. This is particularly important in cosmetic or reconstructive microsurgery, where minimizing visible scarring is a priority.
- Less Post-operative Pain: Due to the reduced tissue trauma and finer incisions, patients operated on with obsidian blades may experience less post-operative pain and discomfort. This can lead to quicker recovery times and improved overall patient satisfaction.
- Less Blood Loss: The sharpness of obsidian blades allows for more precise control over bleeding during surgery. This can be especially important in microsurgery where small blood vessels are involved, as minimizing blood loss is crucial for a successful outcome.
- Reduced Risk of Tissue Necrosis: Because of their sharpness and precision, obsidian blades can help minimize the risk of tissue necrosis (death of tissue) often associated with imprecise or traumatic surgical techniques.
- Lower Risk of Complications: Overall, the advantages of obsidian blades in microsurgery contribute to a lower risk of complications during and after the surgical procedure. This can lead to better outcomes and higher success rates.
While obsidian blades offer significant advantages in microsurgical procedures, it’s important to note that they require specialized training and care in handling and sterilization. Additionally, they may not be suitable for all types of surgeries or situations, and their use should be carefully considered on a case-by-case basis.
Advantages of Steel blades compare to Obsidian surgical blade:
Steel blades and obsidian blades each have their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Here are some of the advantages of a steel blade over an obsidian blade:
- Durability: Steel blades are generally more durable than obsidian blades. They can withstand more impact and are less likely to chip or break during use.
- Versatility: Steel blades can be used for a wider range of tasks. They can be sharpened to different edge geometries for cutting, slicing, chopping, and other purposes. Obsidian blades are more specialized and are primarily used for cutting.
- Ease of Sharpening: While obsidian blades can be incredibly sharp, they can also be fragile and require more skill and care to sharpen properly. Steel blades, on the other hand, can be easily sharpened using various tools and techniques.
- Corrosion Resistance: Steel blades can be made with various alloys and coatings that provide resistance to rust and corrosion. Obsidian is naturally resistant to corrosion, but it can become damaged or worn over time with use.
- Availability: Steel is a widely available and commonly used material for blades. It can be easily sourced and manufactured in a variety of forms and sizes.
- Adaptability to Different Environments: Steel blades can be used effectively in a wider range of environments, including wet or humid conditions, without significant degradation.
- Customizability: Steel blades can be crafted with a wide range of designs, shapes, and features to suit specific purposes or user preferences. This includes variations in the type of steel used, blade shape, handle material, and more.
- Maintenance: Steel blades generally require less maintenance compared to obsidian blades. They can be cleaned, oiled, and stored with relative ease.
- Availability of Accessories: There are a wide range of accessories available for steel blades, such as sheaths, sharpening tools, and other maintenance equipment.
It’s worth noting that the choice between a steel blade and an obsidian blade depends on the specific use case, personal preference, and the intended environment of use. Obsidian blades, for example, excel in certain applications due to their exceptional sharpness, but they are also more fragile and may require more care and maintenance.
Tissue Interaction Of Obsidian blade compared to Steel blade:
Obsidian and steel blades have distinct properties that affect their interaction with human tissues during surgical procedures. Here, I will compare the tissue interaction of obsidian and steel blades based on factors like tissue trauma, healing time, and post-operative outcomes.
- Tissue Trauma:
- Obsidian Blade: Obsidian blades are known for their exceptional sharpness. They can create very fine incisions with minimal tissue trauma due to their micro-serrated edges. This reduces the amount of collateral damage to surrounding tissues.
- Steel Blade: Steel blades are also sharp, but they tend to be less sharp than obsidian. However, modern surgical steel blades are designed to be very precise and minimize tissue trauma.
- Healing Time:
- Obsidian Blade: Because obsidian blades create very fine incisions, they may result in faster initial wound healing. The fine edges allow for cleaner cuts, which can lead to quicker surface healing.
- Steel Blade: Steel blades may result in slightly longer healing times compared to obsidian due to the potential for more tissue trauma. However, modern surgical steel is designed to minimize this effect.
- Post-operative Outcomes:
- Obsidian Blade: The reduced tissue trauma caused by obsidian blades may lead to less post-operative pain and inflammation. Additionally, patients may experience reduced scarring due to the fine incisions.
- Steel Blade: While steel blades are also effective, there may be slightly more post-operative pain and swelling compared to obsidian blades. However, with proper surgical technique, the difference in outcomes may not be significant.
- Material Durability:
- Obsidian Blade: Obsidian is a naturally occurring volcanic glass and is relatively brittle compared to steel. It can chip or break if not handled carefully.
- Steel Blade: Surgical steel is known for its durability and ability to maintain its sharpness over time. It can withstand the rigors of surgical procedures and can be easily sterilized for reuse.
- Sterilization:
- Obsidian Blade: Obsidian blades are generally single-use due to their fragile nature and difficulty in sterilizing them effectively for reuse.
- Steel Blade: Steel blades can be easily sterilized and reused multiple times, making them more cost-effective in the long run.
- Specialized Uses:
- Obsidian Blade: Obsidian blades are sometimes preferred in specific surgical procedures that require exceptionally precise and clean cuts, such as certain types of eye surgeries or cosmetic procedures.
- Steel Blade: Steel blades are versatile and are used in a wide range of surgical procedures across various medical specialties.
In conclusion, while obsidian blades offer advantages in terms of reduced tissue trauma and potentially faster initial healing, modern surgical steel blades have been engineered to provide excellent surgical outcomes with the added benefits of durability, reusability, and versatility. The choice between the two will ultimately depend on the specific surgical procedure, surgeon preference, and the need for specialized cutting properties. It’s important to note that regardless of blade material, proper surgical technique and aseptic practices are crucial for successful outcomes.
Cost and Accessibility of Obsidian Blade vs Steel blade
Obsidian Blades:
- Cost: Obsidian blades can vary widely in price depending on factors such as size, craftsmanship, and where they are sourced. Handcrafted obsidian blades made by skilled artisans can be quite expensive, ranging from tens to hundreds of dollars. Some rare or particularly finely crafted pieces can be even more expensive.
- Accessibility: While obsidian is relatively abundant in certain parts of the world, obtaining high-quality obsidian and crafting it into blades requires skill and expertise. There are artisans and workshops that specialize in creating obsidian blades, and you can find them in regions known for their volcanic activity, such as parts of Mexico and the United States.
Steel Blades:
- Cost: The cost of steel blades can also vary widely depending on factors like the type of steel, the manufacturing process, the design, and the brand. Mass-produced steel blades, like those found in many kitchen knives, can be quite affordable, ranging from a few dollars to a few hundred dollars. High-end, custom-made steel blades or collectible blades can cost thousands or even tens of thousands of dollars.
- Accessibility: Steel blades are highly accessible in most parts of the world. They are manufactured on a large scale and are readily available in stores, both physical and online. The variety and quality of steel blades you can find will depend on your location and access to specialized retailers.
Remember, when choosing a blade, it’s important to consider its intended use, quality, and the reputation of the manufacturer or artisan. Additionally, factors like maintenance, sharpness, and durability should also be taken into account. Always buy from reputable sources to ensure you’re getting a quality product.
Advancements in Blade Technology of Obsidian and steel blade:
Obsidian Blade Technology:
- Nano-blades: Researchers have been exploring the potential of creating extremely sharp obsidian blades at the nanoscale. This involves manipulating individual atoms to create edges with unprecedented sharpness.
- Surface Treatments: Just like with steel blades, surface treatments for obsidian have been investigated. These treatments can enhance the blade’s performance, including its resistance to chipping and wear.
- Composite Materials: Combining obsidian with other materials in a composite structure has been explored to create blades with improved properties. For example, adding a reinforcing material to obsidian could potentially enhance its toughness without sacrificing its sharpness.
- 3D Printing: While not specific to obsidian, 3D printing technology has been applied to the fabrication of blades. This allows for precise control over the blade’s geometry and composition, potentially leading to advancements in obsidian blade technology as well.
- Laser Cutting and Etching: Advanced laser cutting and etching techniques can be used to shape and refine obsidian blades, allowing for intricate designs and precise edge geometries.
Steel Blade Technology:
a. Super Alloys: Advancements in metallurgy have led to the development of super alloys, which are specialized steel alloys with enhanced properties like strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. These alloys are often used in high-performance blades.
b. Powder Metallurgy: Powder metallurgy techniques involve the blending of fine metal powders, which are then compacted and sintered to create a solid metal structure. This process allows for precise control over the alloy composition and can lead to blades with improved performance.
c. Nanostructured Materials: Researchers have been experimenting with nanostructured materials, which involve manipulating materials at the nanoscale to enhance their mechanical properties. This technology has the potential to create blades with exceptional strength and sharpness.
d. Heat Treatment: Advances in heat treatment processes have allowed for better control over the hardness, toughness, and overall performance of steel blades. This can result in blades that are more resistant to wear and deformation.
e. Ceramic Coatings: Ceramic coatings applied to steel blades can significantly improve their hardness, corrosion resistance, and overall durability. These coatings are often used in high-end knives and cutting tools
Resources
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Obsidian#
https://www.finescience.com/en-US/Products/Scalpels-Blades/Micro-Knives/Obsidian-Scalpels









