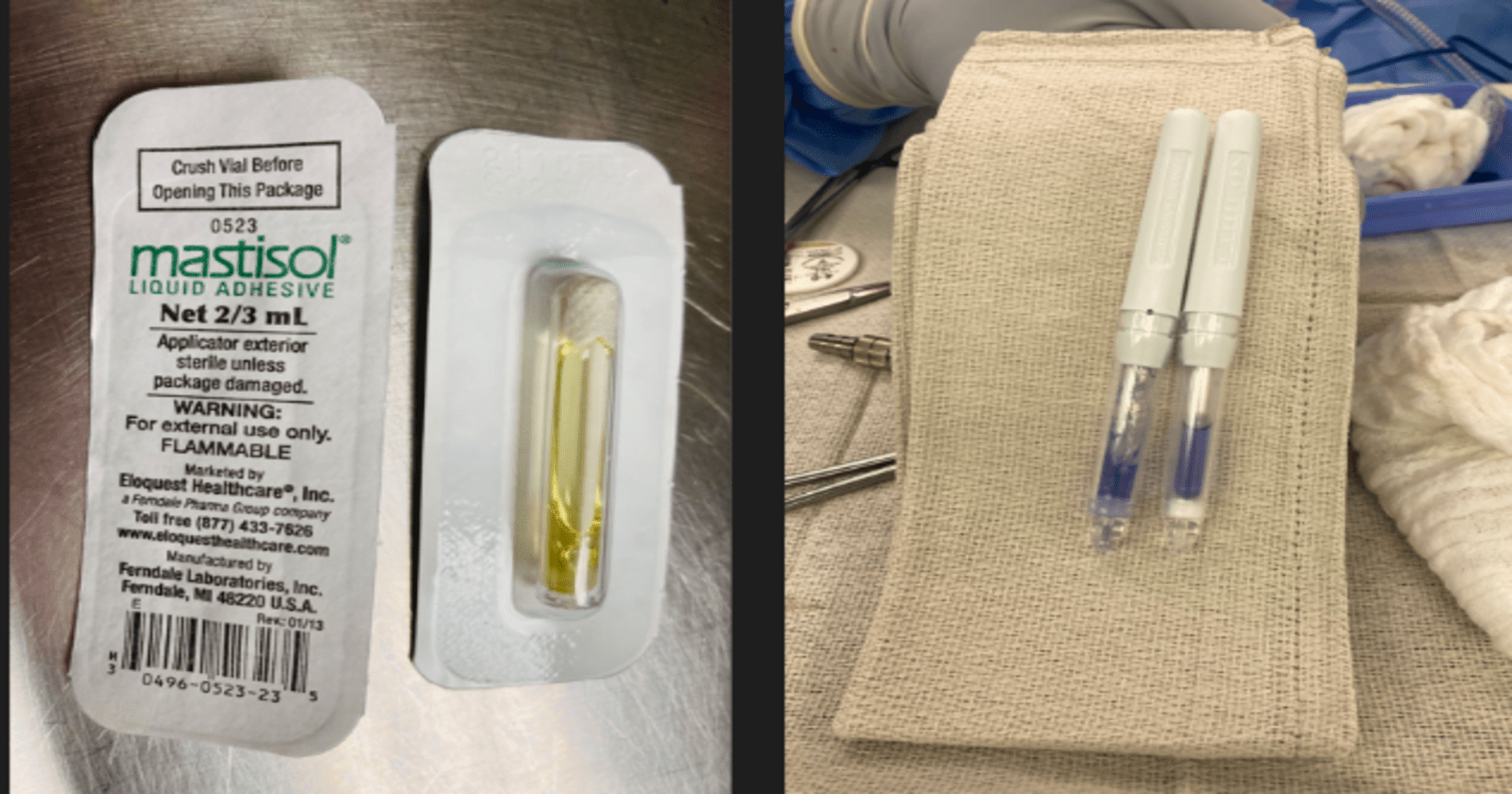
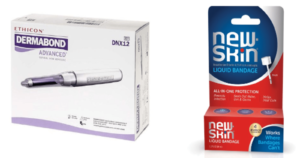
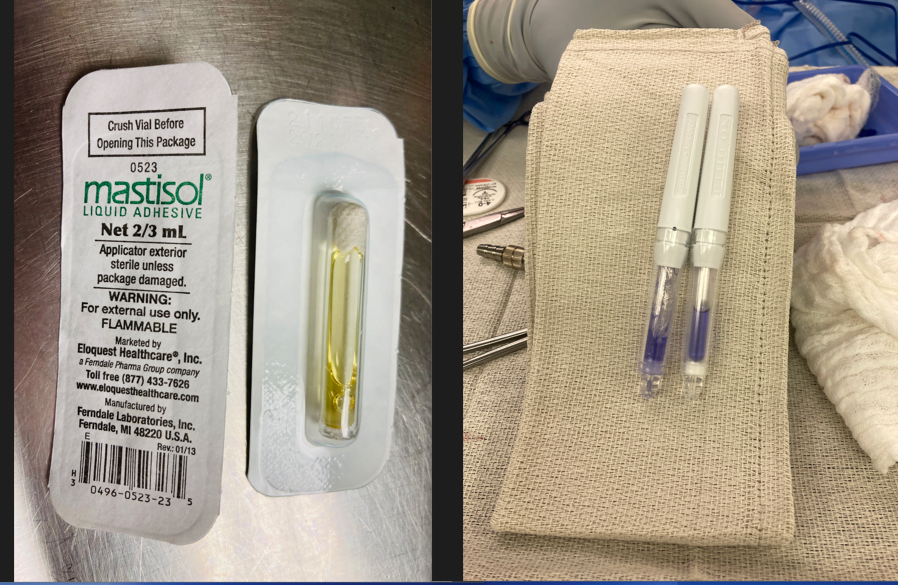
Both Mastisol and Dermabond are liquid adhesive solutions used in medical settings to secure wound closures and provide a protective barrier over the skin. While they serve similar purposes, they have distinct properties and applications.
Mastisol and Dermabond are two essential medical products that play pivotal roles in wound closure and skin adhesion within the field of healthcare.
Mastisol, a liquid adhesive, is renowned for its strong and reliable bonding capabilities.
It is often utilized as a skin adhesive for surgical incisions, wound dressings, and medical devices.

On the other hand, Dermabond is a topical skin adhesive that offers a convenient alternative to traditional sutures or staples.
It is composed of a monomeric liquid adhesive that polymerizes when exposed to moisture, effectively sealing wounds with out the need for invasive procedures.
Together, these two products have revolutionized wound closure techniques, providing medical professionals with efficient and reliable options for securing wounds and facilitating the healing process.
In this discussion, we will delve into the distinct features, applications, and benefits of both Mastisol and Dermabond, shedding light on their critical roles in modern healthcare practices.
What is Mastisol Adhesive
Mastisol is a clear, non-irritating liquid adhesive that is primarily used to enhance the adhesion of medical tapes, dressings, and certain devices to the skin.
It is often used in situations where a strong and long-lasting bond is required, such as in surgical procedures.
Several Freatures of Mastisol Skin Adhesive
- Clear and Colorless: Mastisol is usually clear and colorless when applied. This makes it aesthetically pleasing and allows for easy monitoring of the underlying skin.
- Quick Drying: It dries rapidly after application, forming a strong, flexible bond between the skin and the medical material.
- Strong Adhesion: Mastisol provides a strong, secure adhesion that helps to keep dressings, tapes, and medical devices in place, even in areas prone to movement or moisture.
- Water-Resistant: It is water-resistant, meaning it maintains its adhesion even when exposed to moisture or sweat. This is particularly important in situations where the patient may be active or in environments with high humidity.
- Low Irritation: Mastisol is formulated to be gentle on the skin. It is hypoallergenic and designed to minimize skin irritation, making it suitable for a wide range of patients, including those with sensitive skin.
- Non-Stinging: It is non-stinging, which means it doesn’t cause a burning or stinging sensation when applied to the skin. This helps to enhance patient comfort during application.

- Latex-Free: Mastisol is typically latex-free, which reduces the risk of allergic reactions for individuals who are sensitive or allergic to latex.
- Versatility: It can be used with a variety of medical materials, including dressings, tapes, adhesive strips, and medical devices. This versatility makes it a valuable tool in a healthcare setting.
- Long-Lasting: Once applied, Mastisol provides long-lasting adhesion, reducing the need for frequent re-application of dressings or medical devices.
- Easy to Remove: While Mastisol provides strong adhesion, it can be easily removed using a suitable adhesive remover. This helps to minimize skin trauma during dressing changes.
- Sterile Packaging: It is typically available in sterile packaging to ensure aseptic application, reducing the risk of infection.
Key points about Mastisol:
- Composition: Mastisol is primarily composed of gum mastic, a resin obtained from the trunk of the mastic tree (Pistacia lentiscus). It is mixed with a solvent to create a liquid adhesive.
- Application: It is applied topically to the skin. The liquid is usually brushed or swabbed onto the area where the dressing or tape will be applied.
- Quick Drying: Mastisol dries quickly, forming a strong bond within seconds to minutes.
- Waterproof: Once dry, Mastisol is generally waterproof and resistant to moisture, making it suitable for use in various clinical settings.
- Removal: It can be removed using an adhesive remover, which is specifically designed to break down the adhesive without causing harm to the skin.
- Uses:
- Surgical Settings: Mastisol is commonly used in surgical procedures to secure drapes, dressings, and wound closure devices.
- Wound Care: It is used to help keep wound dressings in place, particularly in areas where traditional tape might not be as effective.
- Medical Device Attachment: Mastisol can be used to secure medical devices like catheters or tubing to the skin.

7. Precautions:
- Mastisol should be used according to manufacturer instructions and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- It should be used with caution on patients with sensitive or compromised skin, as it may cause irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals.
8. Availability: Mastisol is typically available in healthcare facilities and is not generally available for direct consumer purchase.
Remember, if you have any specific concerns or questions about the use of Mastisol in a particular medical situation, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional who can provide personalized advice based on the individual’s circumstances.
It’s important to note that while Mastisol has many benefits, it may not be suitable for every individual or situation. Healthcare professionals should assess each patient’s specific needs and consider any allergies or sensitivities before using Mastisol or any other adhesive product.
Considerations when using Mastisol
When considering the use of Mastisol or any medical adhesive, there are several important factors that healthcare professionals should take into account to ensure its safe and effective application. Here are some key considerations:
- Patient Sensitivity and Allergies:
- Determine if the patient has any known allergies or sensitivities to adhesive products, including latex allergies.
- Perform a skin sensitivity test if there is uncertainty about the patient’s reaction.
- Skin Condition:
- Assess the condition of the patient’s skin, particularly if it is fragile, compromised, or has underlying dermatological conditions.
- Avoid applying Mastisol to areas with open wounds, ulcers, or irritated skin.
- Site of Application:
- Consider the location on the body where Mastisol will be applied. Some areas may have more sensitive or delicate skin.
- Purpose of Adhesion:
- Understand the specific purpose of using Mastisol (e.g., securing dressings, tapes, or medical devices) and ensure it is appropriate for that purpose.
- Duration of Use:
- Determine how long the adhesion needs to last. This will help in selecting the appropriate type and amount of adhesive to use.
- Moisture Levels:
- Consider the moisture levels at the application site. Mastisol is water-resistant, but excessive moisture or sweating may affect adhesion.
- Compatibility with Materials:
- Ensure that Mastisol is compatible with the materials it will be adhering (e.g., dressings, tapes, medical devices). Some adhesives may not work well with certain materials.
- Application Technique:
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for application, including proper cleaning and preparation of the skin.
- Apply a thin, even layer of Mastisol to ensure effective adhesion.
- Adhesive Remover:
- Have an appropriate adhesive remover available for use during dressing changes. This helps to minimize skin trauma.
- Patient Comfort:
- Consider the comfort and well-being of the patient. Mastisol is non-stinging and hypoallergenic, but ensure the patient does not experience any discomfort during application.
- Documentation and Communication:
- Document the use of Mastisol in the patient’s medical record, including the location of application and any observed reactions.
- Communicate with the patient about the use of Mastisol, addressing any concerns or questions they may have.
- Storage and Expiry:
- Ensure that Mastisol is stored according to manufacturer guidelines and is within its expiration date to maintain its effectiveness.
- Adverse Reactions and Follow-Up:
- Monitor the patient for any signs of adverse reactions, such as skin irritation or allergic responses.
- Follow up with the patient to ensure that the adhesive is well-tolerated and effective.
By carefully considering these factors, healthcare professionals can use Mastisol or any adhesive product in a manner that maximizes its benefits while minimizing potential risks or discomfort for the patient.
Limitation of Mastisol
Not for Deep Wounds: It is not intended for use on deep wounds or puncture wounds where there may be a risk of internal bleeding or infection.
Instructions for Use of Mastisol Adhesive
1. Crack: Place an individual vial blister pack on a sturdy surface, ensuring the label is facing downwards. Gently exert pressure on the vial through the blister pack to crush the inner ampule and release Mastisol.
2. Peel: Carefully peel back the lid of the blister pack and extract the vial using aseptic technique.
3. Apply: Invert the vial to dispense Mastisol onto the skin in a half-inch wide line. Ensure that you apply Mastisol to the outer perimeter of the area where the dressing will be affixed, avoiding the immediate vicinity of the catheter insertion site. Allow Mastisol to thoroughly air dry, typically taking about 20–30 seconds.
4. Dress: Adhere to the facility’s established protocol and affix the dressing to the skin, making sure that the edges come into contact with the previously applied Mastisol.
For optimal results during removal, utilize Detachol Adhesive Remover.
Mastisol ingredients
Mastisol is a liquid adhesive used to secure dressings and medical devices to the skin. Its primary ingredients include:
- Mastic Gum: A resin obtained from the mastic tree, which provides adhesive properties.
- Styrax: A natural resin used for its adhesive qualities.
- Alcohol: Often used as a solvent to help the adhesive components mix and apply easily.
- Methyl Salicylate: An ester of salicylic acid, used for its soothing properties and also as a fragrance.

Additional components may be present depending on the specific formulation, but these are the main active ingredients. If someone has known allergies to any of these ingredients, they should avoid using Mastisol and consult with a healthcare provider for alternatives.
Mastisol Allergies
Mastisol, a liquid adhesive used in medical settings, can cause allergic reactions in some individuals. Those who might be allergic to Mastisol typically include:
- Individuals with a history of adhesive allergies: People who have had allergic reactions to other medical adhesives or tapes are at higher risk.
- Individuals with sensitive skin: Those with skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or other dermatological sensitivities may be more prone to reactions.
- Individuals with a history of contact dermatitis: People who have experienced contact dermatitis from other substances may react similarly to Mastisol.
- Individuals with specific ingredient allergies: Mastisol contains several ingredients that can be allergens. If someone is allergic to any of these components, they may experience a reaction. Common allergens include:
- Gum mastic (from which the product gets its name)
- Gum rosin
- Alcohol
- Fragrances
Symptoms of an allergic reaction to Mastisol may include redness, itching, swelling, blistering, or rash at the site of application. In severe cases, a more widespread or systemic allergic reaction could occur, though this is rare.
If someone suspects they have an allergy to Mastisol, they should discontinue its use and consult a healthcare provider for appropriate testing and alternative options.
The Pros and Cons of Mastisol
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Strong adhesive properties | May cause allergic reactions in some individuals |
| Prolongs the adherence of dressings | Can be difficult to remove without a specific remover |
| Reduces the need for frequent dressing changes | Potential for residue build-up on the skin |
| Effective for securing medical devices | More expensive compared to some other adhesives |
| Minimizes skin irritation | Requires proper storage conditions |
| Widely used and trusted in medical settings | May not be suitable for all skin types |
| Quick drying time |
What is Dermabond liquid adhesive
Dermabond is a cyanoacrylate-based adhesive that is specifically formulated for skin closure. It is used as an alternative to traditional sutures (stitches) for certain types of wounds, providing a quick and convenient method for closing minor cuts and lacerations. Dermabond creates a flexible, waterproof seal that helps protect the wound from bacteria and other contaminants.
Several features of Dermabond skin adhesive
- Quick Application: Dermabond is applied topically and dries quickly, which can save time in wound closure compared to traditional sutures.
- No Need for Removal: Unlike sutures or staples, Dermabond does not need to be removed. It sloughs off naturally as the wound heals.
- Reduced Scarring: The use of Dermabond can result in less noticeable scarring, as it provides a smooth, even surface for the wound to heal.
- Waterproof: Once it’s fully cured, Dermabond is water-resistant. This allows patients to shower or bathe without worrying about the adhesive becoming compromised.
- Bacterial Barrier: It creates a protective barrier over the wound, helping to reduce the risk of infection.

- Flexibility: Dermabond is flexible and moves with the skin, which can be particularly beneficial for wounds in areas prone to movement.
- Transparent: It dries to a clear finish, allowing healthcare professionals to monitor the wound without having to remove any dressings.
- Minimal Tissue Trauma: Dermabond is gentle on the skin and causes minimal tissue trauma, which can lead to less discomfort for the patient.
- Precision Application: It is applied in a controlled manner with a specialized applicator, allowing for precise placement on the wound.

- Versatility: Dermabond can be used on a variety of wound types and sizes, from small cuts to larger incisions.
- Hypoallergenic: It is formulated to be hypoallergenic, reducing the risk of allergic reactions in patients.
- Cost-Efficient: While the upfront cost of Dermabond might be higher than traditional sutures, it can potentially save money in the long run due to reduced follow-up care and removal procedures.
The pros and cons of Dermabond, a topical skin adhesive
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Quick and easy to apply | May cause an allergic reaction in some patients |
| Eliminates the need for sutures | Not suitable for all types of wounds (e.g., heavily contaminated or high-tension areas) |
| Reduces the risk of needle-stick injuries | Can cause skin irritation or burning sensation |
| Creates a waterproof barrier | Risk of dehiscence (wound reopening) in areas of high movement or stress |
| Good cosmetic results with minimal scarring | May not adhere well to moist or oily skin |
| Less painful than sutures | Limited shelf life and must be stored properly |
| Lower risk of infection compared to sutures | Higher cost compared to traditional sutures |
| No need for follow-up visits for removal | Can be accidentally peeled off if not properly protected |
| Faster wound closure time | Not recommended for deep or jagged wounds |
Consideration When using Dermabond
- Wound Type and Size: Dermabond is best suited for small, clean, and straight-edged wounds. It may not be appropriate for wounds with irregular edges or high tension.
- Wound Location: Consider the location of the wound. Dermabond may not be suitable for areas of high tension or where there is a lot of movement, such as joints.
- Patient Factors:
- Allergies: Check for any known allergies to cyanoacrylate compounds, as this is the primary ingredient in Dermabond.
- Skin Condition: Consider the overall health of the patient’s skin. Dermabond may not adhere as well to areas with excessive moisture or oily skin.
- Cleanliness: The wound must be thoroughly cleaned and dried before applying Dermabond. Contaminants or excess moisture can affect its adhesion.
- Hemostasis: Ensure that bleeding from the wound has been adequately controlled before applying Dermabond. Active bleeding can prevent proper adhesion.
- Tissue Approximation: Dermabond works best when the wound edges can be easily approximated (brought together). It may not be suitable for wounds with significant tissue loss.
- Skill and Experience: Proper application of Dermabond requires skill and training. Ensure that the healthcare provider applying it is familiar with the technique.
- Follow-Up Care: Advise the patient on proper wound care and let them know what signs of infection or complications they should watch for.
- Cosmetic Considerations: Dermabond can provide good cosmetic results, but it may not be suitable for wounds in highly visible or cosmetically sensitive areas.
- Cost and Availability: Consider the cost of Dermabond compared to other wound closure methods. It may be more expensive than traditional sutures.
- Sterility: Ensure that the Dermabond applicator and the surrounding area are sterile to minimize the risk of infection.
- Adverse Reactions: While rare, some individuals may experience adverse reactions to Dermabond. Monitor for signs of irritation or allergic reactions.
How to Apply Dermabond

- Clean the Wound: Ensure the wound is thoroughly cleaned and bleeding is controlled.
- Apply the Adhesive: After aligning the wound edges, the Dermabond vial is crushed, and the adhesive is brushed over the wound in thin layers. Typically, three layers are applied for optimal strength.
- Drying Time: The adhesive takes about 2.5 to 3 minutes to reach maximum strength. During this time, it’s essential to avoid disturbing the wound (Elite Learning) (AAFP).
Post-application care of dermabond includes
- Keeping the wound dry and avoiding direct application of creams or ointments.
- Monitoring for signs of infection and seeking medical advice if necessary.
- Allowing the adhesive to peel off naturally within 5 to 10 days (USA Medical Surgical) (AAFP).
Dermabond is particularly useful for facial wounds and in pediatric cases where traditional sutures might cause more distress. However, it should be avoided in areas with high tension or where precise alignment of wound edges is challenging, as sutures might be more appropriate in such cases
Clinical Outcomes of Dermabond
In a randomized trial comparing topical skin adhesives and sutures in the management of lacerations, DERMABOND Adhesive was
- Associated with short procedure time (3.6 minutes vs. 12.4 minutes; P <0.001)
- Associated with less patient pain (visual analog pain scores, 7.2 mm vs. 18.0 mm; P<0.001)
Always consult a healthcare professional for specific medical advice and treatment options. This list is not exhaustive, and individual patient circumstances may require additional considerations.
Economic Outcomes of Dermabond
In retrospective analyses, DERMABOND ADVANCED was associated with:
- Reduction in 25% length of stay for sternal closure patients in cardiac surgery
- Dermabond 7 (D7) demonstrates a notable $500 reduction in overall hospital costs for Cesarean section procedures when compared to the expenses associated with staples and sutures.
It’s important to note that while Dermabond is a versatile and effective wound closure option, it may not be suitable for all types of wounds or patients. The choice of wound closure method should be determined by a healthcare professional based on the specific characteristics of the wound and the patient’s medical history.
While both Mastisol and Dermabond are liquid adhesive solutions, Mastisol is primarily used to enhance the adhesion of medical tapes and dressings, where as Dermabond is specifically designed for skin closure and wound sealing, often replacing the need for sutures.
General Tips for Using Medical Adhesives
- Clean the Area: Ensure the skin around the wound is clean and dry before applying any adhesive. Use an antiseptic solution to cleanse the area and remove any oils, dirt, or moisture.
- Read Instructions: Always read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the specific adhesive product you are using.
- Test for Allergies: Perform a patch test on a small area of skin if using the adhesive for the first time to check for any allergic reactions.
- Proper Application: Apply the adhesive evenly and in the appropriate amount. Too much adhesive can cause skin irritation, while too little may not secure the dressing or wound edges effectively.
Tips for Using Mastisol
- Application Area: Apply Mastisol to the edges of the dressing or tape rather than directly on the wound. Avoid contact with the wound itself.
- Allow Drying Time: Let Mastisol dry for a few seconds before applying the dressing or tape to ensure optimal adhesion.
- Avoid Overuse: Use sparingly to avoid excessive buildup on the skin, which can be difficult to remove and may cause irritation.
- Removal: Use a medical adhesive remover or an alcohol pad to gently remove Mastisol from the skin. Avoid pulling the skin, which can cause irritation or damage.
Tips for Using Dermabond
- Wound Preparation: Ensure the wound edges are clean and dry. Control bleeding before applying Dermabond, as excessive bleeding can interfere with adhesion.
- Positioning the Wound Edges: Bring the wound edges together manually or with forceps before applying Dermabond. Hold the edges together until the adhesive sets.
- Application Technique: Apply a thin layer of Dermabond over the wound edges. Avoid getting the adhesive into the wound itself, as it should only be on the surface.
- Drying Time: Allow the adhesive to dry completely. This usually takes about 60 seconds. Protect the area from moisture and friction while it dries.
- Protection: Keep the wound dry and avoid submerging it in water. Showering is usually permitted, but avoid scrubbing the area.
- Monitor for Complications: Watch for signs of infection or allergic reactions, such as redness, swelling, or increased pain. Seek medical attention if any of these occur.
Additional Considerations
- Patient Comfort: Consider the patient’s comfort and skin sensitivity when applying and removing adhesives.
- Environment: Ensure you are working in a clean environment to prevent contamination.
- Training: Healthcare providers should be trained in the proper use of medical adhesives to avoid misuse and ensure patient safety.
- Storage: Store adhesives as per the manufacturer’s recommendations to maintain their effectiveness.
Mastisol vs Dermabond Innovations in Wound Care Adhesives
Recent innovations in wound care adhesives, including Mastisol and Dermabond, focus on improving the effectiveness, safety, and comfort of wound treatment. These innovations include:
- Bioengineered Adhesives: Development of adhesives that mimic natural biological processes to enhance healing and reduce complications.
- Advanced Polymer Formulations: Use of advanced polymers that provide better flexibility, strength, and biocompatibility.
- Smart Adhesives: Incorporation of smart technology in adhesives that can monitor wound healing and release medications as needed.
- Eco-Friendly Options: Development of environmentally friendly adhesives that are biodegradable and reduce environmental impact.
Mastisol and Dermabond represent significant advancements in wound care, each serving distinct purposes. Mastisol enhances the adhesion of dressings, while Dermabond provides a needle-free option for wound closure with excellent cosmetic outcomes. Ongoing innovations continue to improve the functionality and safety of these adhesives, offering better options for wound management.
FAQs and Common Questions Mastisol vs Dermabond
Common Questions about Mastisol
Q1: What is Mastisol? A1: Mastisol is a liquid medical adhesive used to secure wound dressings, medical tapes, and certain types of medical devices to the skin. It helps prevent dressings from becoming loose or dislodged, which can be critical for maintaining the integrity of wound care.
Q2: How is Mastisol applied? A2: Mastisol is typically applied using an applicator stick or spray. The skin area where the adhesive is needed is first cleaned and dried. Mastisol is then applied in a thin layer to the area, and the dressing or medical device is pressed onto the skin, allowing the adhesive to bond.
Q3: Is Mastisol safe for all skin types? A3: Mastisol is generally safe for most skin types. However, individuals with sensitive skin or known allergies to adhesives should use it with caution. A patch test can help determine if Mastisol will cause any adverse reactions.
Q4: How do I remove Mastisol? A4: Mastisol can be removed using an adhesive remover or a gentle solvent like alcohol. It’s important to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer to avoid skin irritation or damage.
Q5: Can Mastisol be used on open wounds? A5: Mastisol should not be applied directly to open wounds. It is designed for use on intact skin to secure wound dressings and medical devices.
Common Questions about Dermabond
Q1: What is Dermabond? A1: Dermabond is a topical skin adhesive used to close small cuts and wounds. It is a type of medical glue that bonds the edges of the wound together, facilitating healing without the need for stitches in some cases.
Q2: How is Dermabond applied? A2: Dermabond is applied by first cleaning the wound and ensuring it is dry. The adhesive is then applied along the edges of the wound, holding them together for about 60 seconds until the adhesive sets.
Q3: Is Dermabond waterproof? A3: Yes, Dermabond is waterproof. However, it is advisable to avoid soaking the area in water for extended periods to ensure the adhesive remains effective and the wound heals properly.
Q4: How long does Dermabond last? A4: Dermabond typically lasts for about 5 to 10 days. It naturally sloughs off as the skin underneath heals.
Q5: Can Dermabond be used on all types of wounds? A5: Dermabond is suitable for small, clean cuts and surgical incisions. It should not be used on infected, deep, or large wounds, or on areas with high tension, such as over joints.
Mastisol vs. Dermabond FAQ
Q1: What is the main difference between Mastisol and Dermabond? A1: Mastisol is primarily used to secure dressings and medical devices to the skin, whereas Dermabond is used to close small wounds and cuts.
Q2: Can Mastisol and Dermabond be used together? A2: Yes, Mastisol can be used to secure dressings that cover wounds closed with Dermabond. However, they are generally used for different purposes.
Q3: Which one is better for wound closure, Mastisol or Dermabond? A3: Dermabond is better suited for wound closure as it is specifically designed for that purpose. Mastisol is not intended for closing wounds but for securing dressings.
Q4: Is there a risk of allergic reaction with either product? A4: Both products can potentially cause allergic reactions, especially in individuals with sensitive skin or known allergies to adhesives. A patch test or consultation with a healthcare provider is recommended if there are concerns.
Q5: Are there any special storage requirements for Mastisol or Dermabond? A5: Both products should be stored at room temperature and kept away from excessive heat or cold. Ensure they are sealed properly to maintain their effectiveness.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or medical equipment. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.