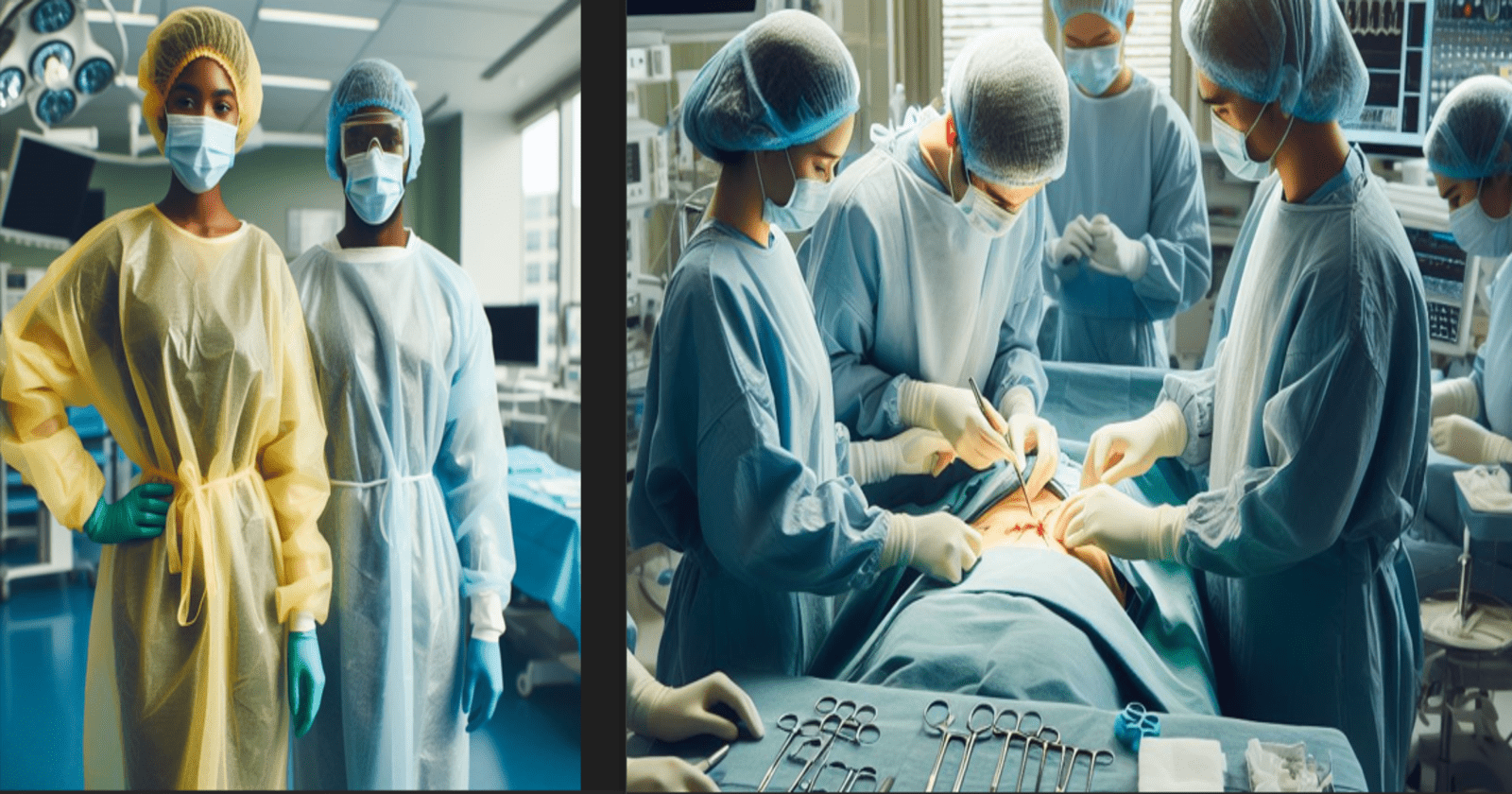
An isolation gown is a personal protective equipment (PPE) worn by healthcare professionals to protect themselves and patients from the transfer of microorganisms, body fluids, and particulate matter versus a surgical gown which is a specialized garment worn by healthcare professionals during surgical procedures to provide a barrier between the surgeon or other healthcare workers and the patient during surgery or surgical procedures.
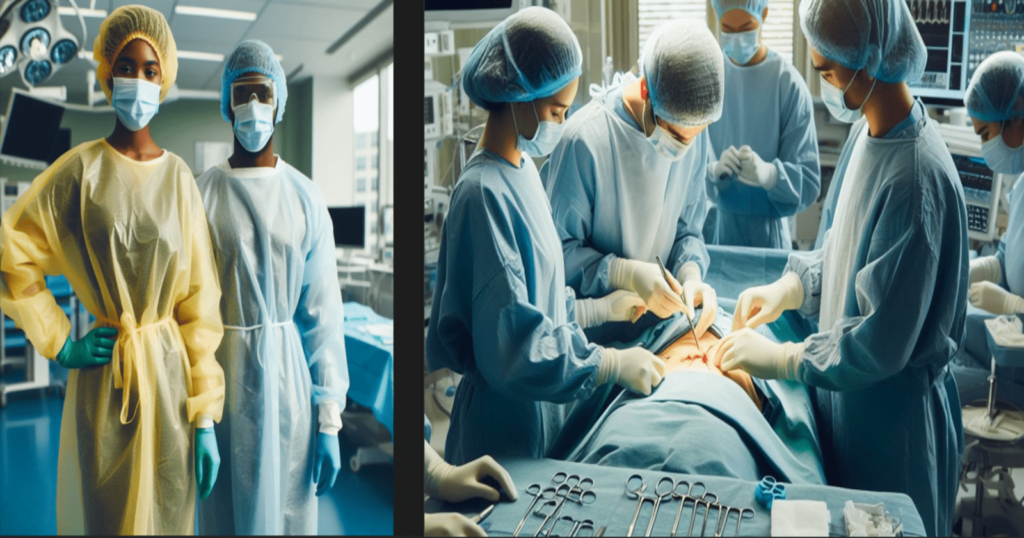
Isolation Gown

An isolation gown is a type of personal protective equipment (PPE) worn by healthcare professionals or individuals in certain settings to protect themselves from potential exposure to infectious agents and chemicals spill. It is typically used in healthcare settings, laboratories, and other environments where there is a risk of contamination.
Isolation gowns are designed to cover the front and back of the body and provide full coverage from the neck to the knees and wrists. They are made of various materials, including non-woven fabrics, and are often disposable. The purpose of the isolation gown is to prevent the transfer of microorganisms, body fluids, chemicals, and particulate matter between the wearer and the surrounding environment.
These gowns are an essential component in infection control measures, especially in situations where there is a need to protect against the spread of infectious diseases or contaminants.
Surgical Gowns

A surgical gown is a protective garment worn by healthcare professionals during surgical procedures to prevent the transmission of infections and maintain a sterile environment. These gowns are typically made of fabric that has barrier properties to resist the penetration of liquids and microorganisms. Surgical gowns cover the healthcare worker’s body and arms, providing a physical barrier between the surgical team and the patient to reduce the risk of contamination. They are an essential part of the personal protective equipment (PPE) used in healthcare settings to ensure the safety of both patients and medical personnel.
Basic Differences between an Isolation gown vs Surgical gown
| Isolation gown | Surgical gown |
|---|---|
| Isolation gowns are typically non-sterile and may be disposable or reusable, depending on the material and design. | Surgical gowns are always sterile to maintain aseptic conditions in the operating room. They undergo a sterilization process before use. |
| Designed for general patient care, isolation gowns are used to protect healthcare workers and patients from the transfer of microorganisms and body fluids. | Specifically designed for use during surgical procedures, surgical gowns provide a higher level of protection against bloodborne pathogens and other infectious agents. |
| Offers a basic level of protection and is suitable for low-risk situations where the risk of exposure to blood or bodily fluids is minimal. | Provides a higher level of protection, meeting more stringent requirements to ensure the safety of healthcare workers during surgical procedures. |
| Typically made of lightweight, breathable materials such as polypropylene. They may have an open back design. | Constructed from materials that provide a barrier against fluids and microorganisms. Surgical gowns often have a closed-back design and may be reinforced in critical areas. |
| Generally complies with basic infection control guidelines but may not meet the same rigorous standards as surgical gowns. | Must meet specific regulatory standards and guidelines for surgical attire, ensuring a higher level of protection during surgical procedures. |
| May have simple design features and closures, such as ties at the neck and waist. | Designed with features like adjustable closures, reinforced areas, and sometimes extra layers or barriers for added protection |
| Isolation gowns may have a looser fit to allow for comfortable movement during routine patient care activities. | The sleeves of surgical gowns are often longer and have elastic cuffs to provide additional protection for the arms. |
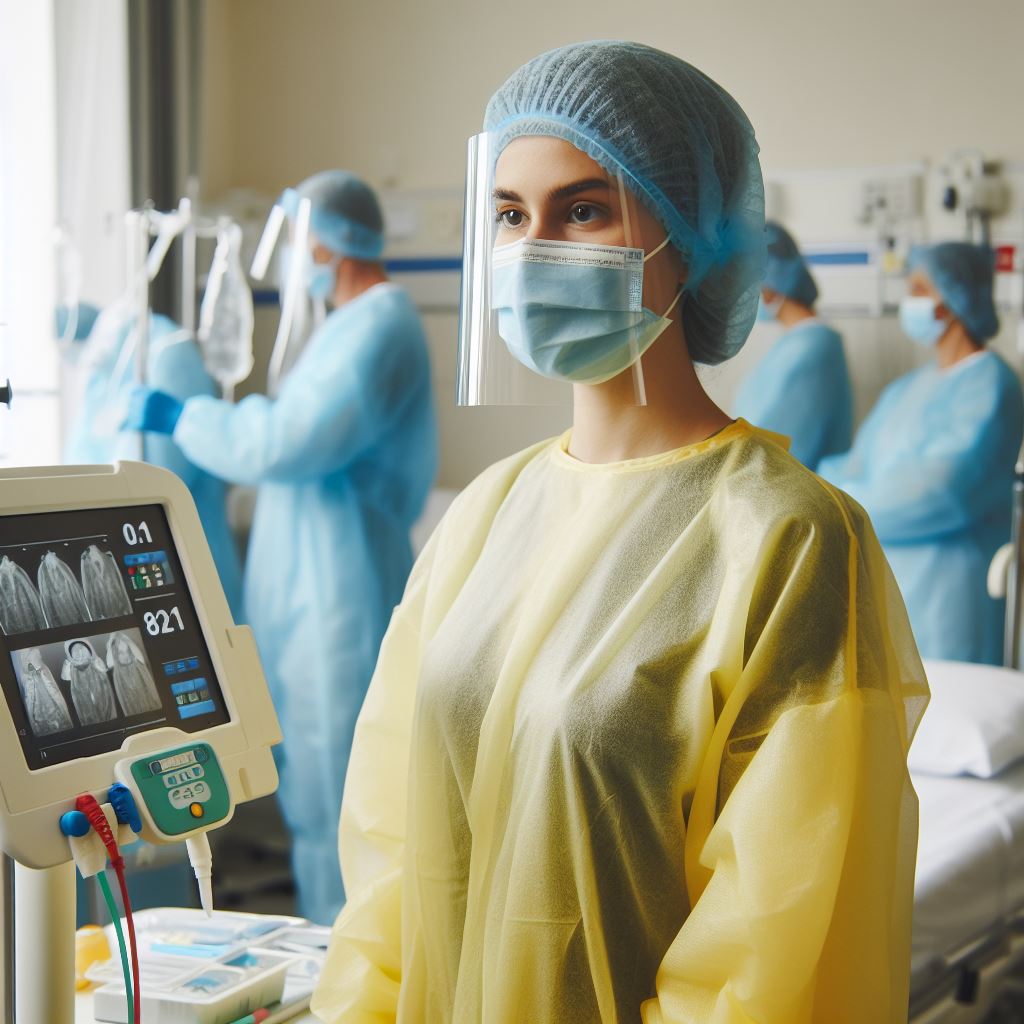
While both isolation gowns and surgical gowns are essential in healthcare settings, isolation gowns focus on general barrier protection, whereas surgical gowns are specifically designed for sterile environments during surgical procedures, offering a higher level of protection.
3 Easy and important use of an Isolation gown vs use of a Surgical gown
Isolation gown
- Barrier Protection: Isolation gowns are primarily designed to provide a barrier against the transfer of microorganisms and other contaminants. They are used to protect healthcare workers and patients from potential sources of infection.
- General Use: Isolation gowns are suitable for general patient care, isolation, and basic procedures where a low to moderate level of protection is required.
- Fluid Resistance: They are designed to resist the penetration of liquids, such as blood and bodily fluids, to prevent contamination.
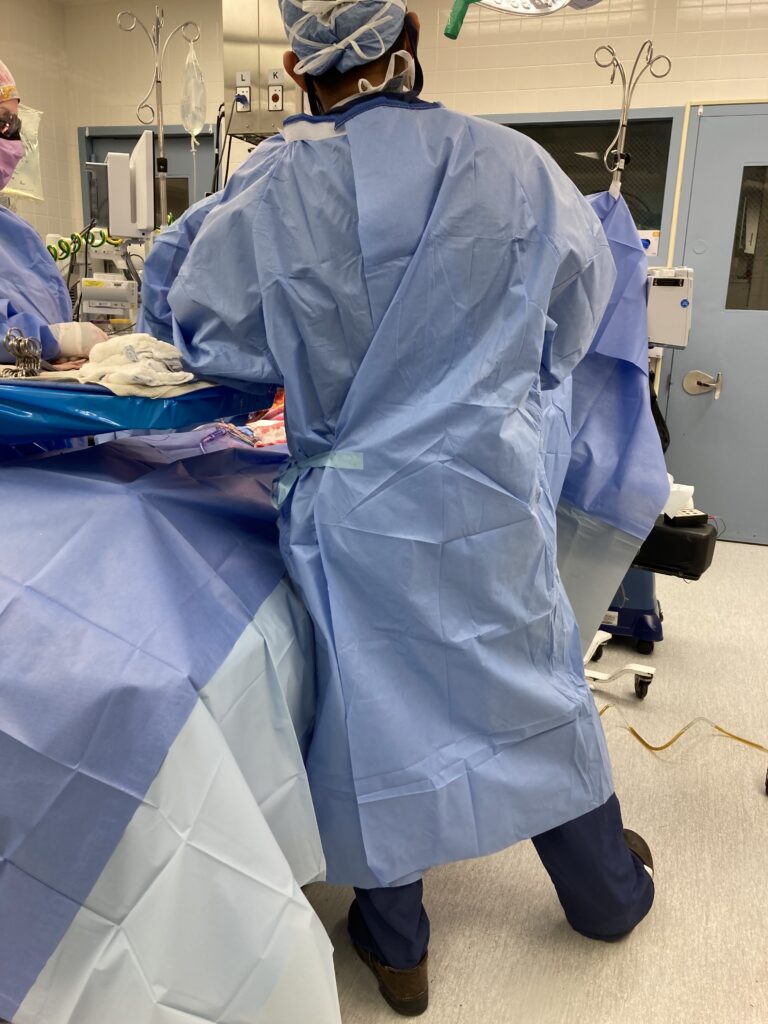
Surgical gown
- Sterile Environment: Surgical gowns are intended for use in sterile environments, particularly during surgical procedures. They provide a sterile barrier to prevent the transmission of pathogens between the surgical team and the patient.
- Higher Level of Protection: Surgical gowns offer a higher level of protection compared to isolation gowns. They are designed to withstand exposure to blood, body fluids, and other potentially infectious materials.
- Critical Procedures: Surgical gowns are used during invasive and critical medical procedures where maintaining a sterile field is crucial.
Important Role of an Isolation gown vs Surgical gown of Barrier Protection in Healthcare Settings

- Infection Control:
- Barrier protection is critical in preventing the transmission of infectious agents, including bacteria and viruses, between healthcare workers and patients. This is especially crucial in settings where patients may have compromised immune systems.
- Surgical Procedures:
- During surgical procedures, both isolation and surgical gowns play a pivotal role in maintaining a sterile environment. Surgical gowns, with their higher level of protection, are often preferred in the operating room.
- Patient Care and Safety:
- Barrier protection contributes to patient safety by minimizing the risk of contamination. Healthcare workers wearing appropriate gowns can provide care confidently, knowing they are protected from potential hazards.
- Compliance with Standards:
- Healthcare facilities are required to adhere to standards and guidelines that mandate the use of appropriate barrier protection. This ensures a safe environment for both healthcare providers and patients.
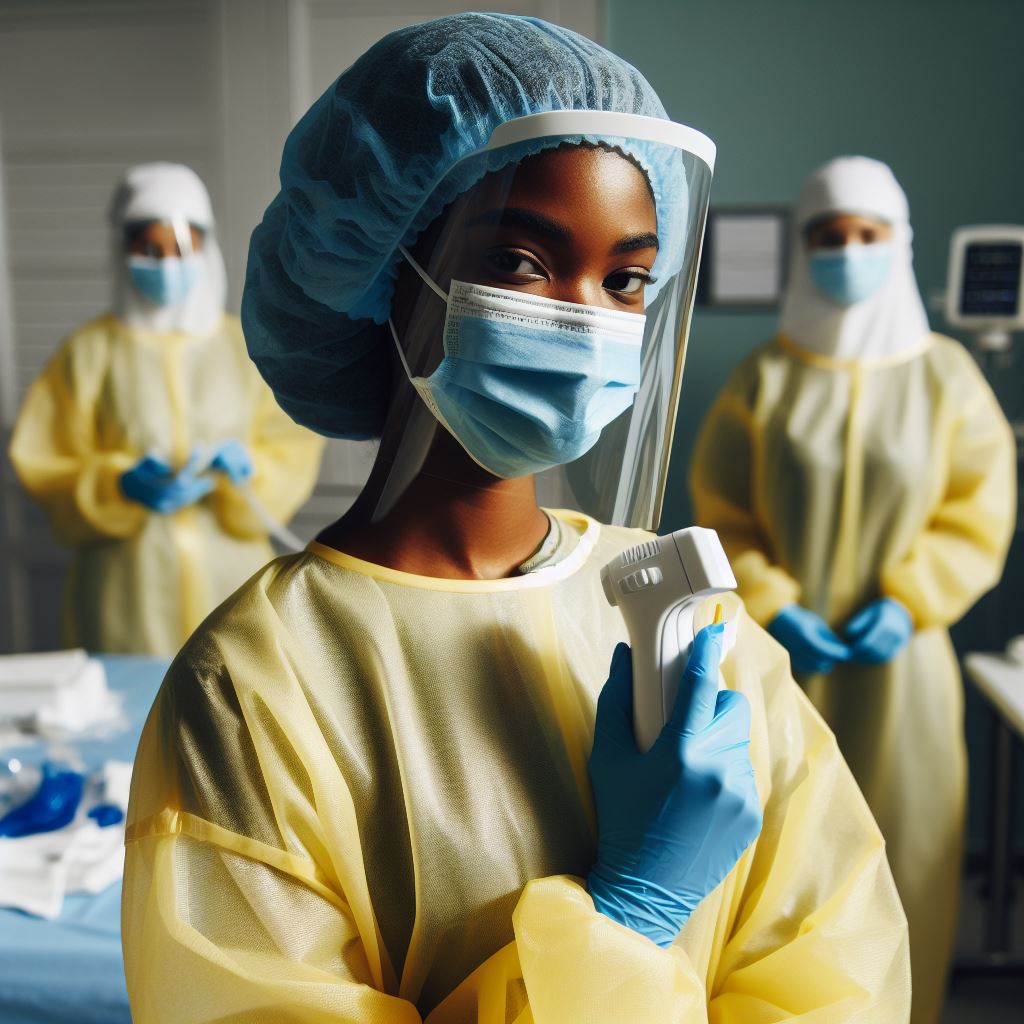
Both isolation gowns and surgical gowns serve basic essential functions in providing barrier protection. The choice between them depends on the specific requirements of different healthcare settings, with surgical gowns having an advantage, being preferred in environments where a higher level of protection is necessary, such as during surgical procedures.
7 Simple step when removing an Isolation Gown
- Remove Gloves: If you are wearing gloves, remove them first. Grasp the outside of one glove at the wrist and peel it off, turning the glove inside out. Hold the removed glove in the gloved hand. Slip two fingers of the ungloved hand under the remaining glove at the wrist and peel it off, turning it inside out. Dispose of the gloves in the trash.
2. Untie or Unfasten Gown:
- Untie or unfasten the gown at the neck and waist. Avoid touching the front of the gown.
3. Remove Gown:
- Remove the gown by pulling it away from your body, taking care to avoid touching the outside surface. Roll or fold the gown inside out as it is removed.
4. Dispose of Gown:
- Dispose of the gown in the designated receptacle for contaminated waste.
5. Perform Hand Hygiene Again:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
6. Inspect for Contamination:
- After removing the gown, visually inspect yourself to ensure there is no contamination on your clothing or skin.
7. Don New Gloves (if needed):
- If you need to continue with any tasks requiring gloves, put on a new pair.
Aurelius Hospital Nilai Official
6 Easy steps when putting on a Surgical gown
- Pick up the gown clutch/grab the single fold below the neck.

2. Position your fingers on either hand beneath the lateral flaps of the arm openings.

3. Open gown laterally and Allow the body of the gown to fall open. Extend arms into the sleeves
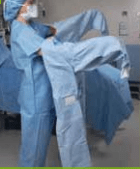
4. Have the circulator should secure the inner rear waist ties first, and then fasten the neck closure.
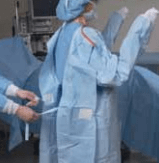
5. Hold the upper section of the transfer card using the right hand, and untie the left side with the left hand.
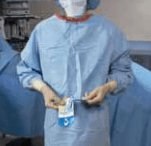
6. Hand the bottom portion of the transfer card to assistant. then turn to the left, pulling the waist tie from the transfer card held by assistant. Tie the waist ties at the left side of the gown.
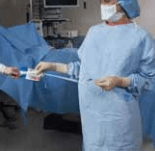
Key important Levels of Surgical gowns
Surgical gowns are classified into different levels based on their level of protection. These levels are typically determined by the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) and are designated as Level 1, Level 2, Level 3, and Level 4.
- Level 1: Minimal Risk
- Used for basic care, standard isolatin, or in a standard medical unit.
- Provides a minimal barrier to fluid penetration.
- Level 2: Low Risk
- Used in procedures where there is a low risk of fluid exposure.
- Provides a low level of fluid resistance.
- Level 3: Moderate Risk
- Used in areas where there is a moderate risk of fluid exposure.
- Provides a moderate level of fluid resistance.
- Level 4: High Risk
- Used in high-risk situations, such as during major surgical procedures.
- Provides the highest level of fluid resistance.
These levels help healthcare professionals choose the appropriate gown for specific procedures or environments based on the potential risk of fluid exposure.
Key points to Consider when using an Isolation gown vs a surgical gown
- Material Quality:
- Surgical gowns often require higher quality materials to meet specific standards for use in sterile environments. These materials can be more expensive than those used in isolation gowns.
- Manufacturing Standards:
- Surgical gowns are subject to more stringent manufacturing standards, involving additional processes and quality control measures. Meeting these standards contributes to higher production costs.
- Level of Protection:
- Surgical gowns are designed for a higher level of protection in sterile settings such as operating rooms. The additional features, such as reinforcement in critical areas, contribute to the higher cost compared to isolation gowns.
- Disposable vs. Reusable:
- The choice between disposable and reusable options can impact costs. Reusable surgical gowns, if designed to meet the necessary standards for sterilization and reuse, may have a higher upfront cost but can be more cost-effective over time.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Ensuring compliance with health and safety regulations adds to the production costs. Surgical gowns must adhere to specific standards, requiring additional testing and certification.
- Volume of Production:
- Economies of scale can influence costs. Manufacturers producing larger quantities may be able to offer more competitive prices, but the overall cost may still be higher for surgical gowns due to their specialized nature.
Disadvantages and Limitations of an Isolation gown
Isolation gowns, like any protective clothing, have limitations and disadvantages that users should be aware of.
- Limited Protection Against Punctures and Tears: Isolation gowns are designed to provide a barrier against bodily fluids and contaminants, but they may not offer strong protection against punctures or tears. Sharp objects can potentially penetrate the material.
2. Not airtight: Isolation gowns are not designed to be airtight, and they do not provide respiratory protection. If there are airborne contaminants, additional respiratory protection may be needed.
3.. Limited Coverage: While isolation gowns cover a significant portion of the body, they may not provide full-body coverage. Gaps or openings can exist, particularly in the back, and may compromise protection.
4. Single-Use or Limited Reusability: Many isolation gowns are designed for single-use, and their effectiveness may diminish with repeated use or after being laundered. Reusable gowns often have a limited number of wash cycles before their protective properties are compromised.
5. Variability in Standards: There may be variability in the standards and specifications for isolation gowns. Different materials and designs may offer varying levels of protection, and users should be aware of the specific standards applicable to the gowns they are using.
6. Dependence on Proper Usage: The effectiveness of isolation gowns depends on proper usage, including correct donning and doffing procedures. If these procedures are not followed correctly, the protective capabilities of the gown may be compromised.
7. Not a Substitute for Other Precautions: Isolation gowns are part of a comprehensive infection control strategy, but they are not a substitute for other precautions such as hand hygiene, environmental cleaning, and the use of other personal protective equipment (PPE).
Basic limitations and disadvantages of a Surgical Gown
- Limited Protection: Surgical gowns may not provide complete protection against all types of contaminants. They are designed to protect against blood and bodily fluids, but they may not be impervious to certain chemicals or microorganisms.
2. Not Waterproof: While surgical gowns are fluid-resistant, they are not completely waterproof. In situations where there is a high risk of exposure to liquids, additional protective measures may be necessary.
3. Limited Durability: Surgical gowns are typically disposable, and their durability is limited. They are designed for single-use, and repeated use can compromise their protective capabilities.
4. Comfort and Mobility: Some healthcare professionals may find surgical gowns less comfortable compared to other protective clothing options. The design and material of the gown can affect mobility and may cause discomfort during prolonged use.
5. Environmental Impact: Disposable surgical gowns contribute to medical waste, which can have environmental implications. The production, use, and disposal of disposable gowns may contribute to landfill waste and other environmental concerns.
6. Potential for Contamination during Removal: Proper doffing procedures are crucial to prevent contamination when removing a surgical gown. If not done carefully, there is a risk of self-contamination during the removal process.
7. Cost: Disposable surgical gowns can contribute to the overall cost of healthcare. While they are necessary for infection control, the cost of purchasing and disposing of large quantities of gowns adds to healthcare expenses.
8. Variability in Protection Levels: Different surgical gowns offer varying levels of protection. The choice of gown depends on the specific procedure and the potential risks involved. Inconsistent use or selection of gowns may lead to inadequate protection.
Resources
As an RN I have had my experiences using both gowns.
https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/personal-protective-equipment-infection-control/medical-gowns#g2
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7572274/
https://www.halyardhealth.com/wp-content/uploads/C15847-Surgical-Gown-Donning-Guide.pdf