In the heart of every kitchen lies a choice that can shape the very essence of a dish. the selection between a clove head, garlic clove and a garlic head. These small, unassuming bulbs hold a world of flavor within their papery layers, yet their characteristics diverge in intriguing ways.

left to right garlic head, in the middle garlic clove and three clove head
Garlic Head Explained
Garlic is a plant in the Allium (onion) family, scientifically known as Allium sativum. It is native to Central Asia and has been cultivated for thousands of years for both culinary and medicinal purposes.
The most commonly used part of the garlic plant is the bulb, often referred to as a “garlic head” or “garlic bulb”. This bulb is composed of multiple individual cloves enclosed in a papery skin. Each clove has a distinct, pungent flavor and aroma when crushed or minced.
Identifying Garlic Clove
A garlic clove is one of the individual segments that make up a bulb of garlic. Each bulb of garlic typically contains multiple cloves, and each clove is covered by a thin papery skin. When you peel away this outer layer, you reveal the firm, white or pale yellowish interior of the clove.
Tips to identify the differences between Garlic Head vs Garlic Clove
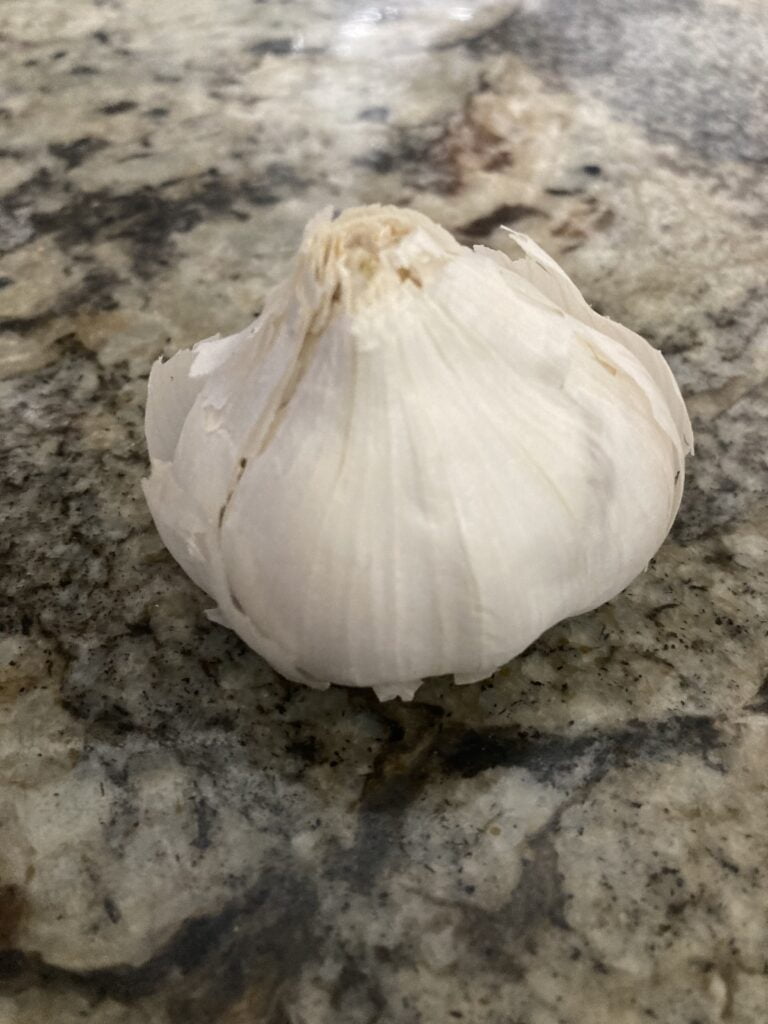

GARLIC HEAD
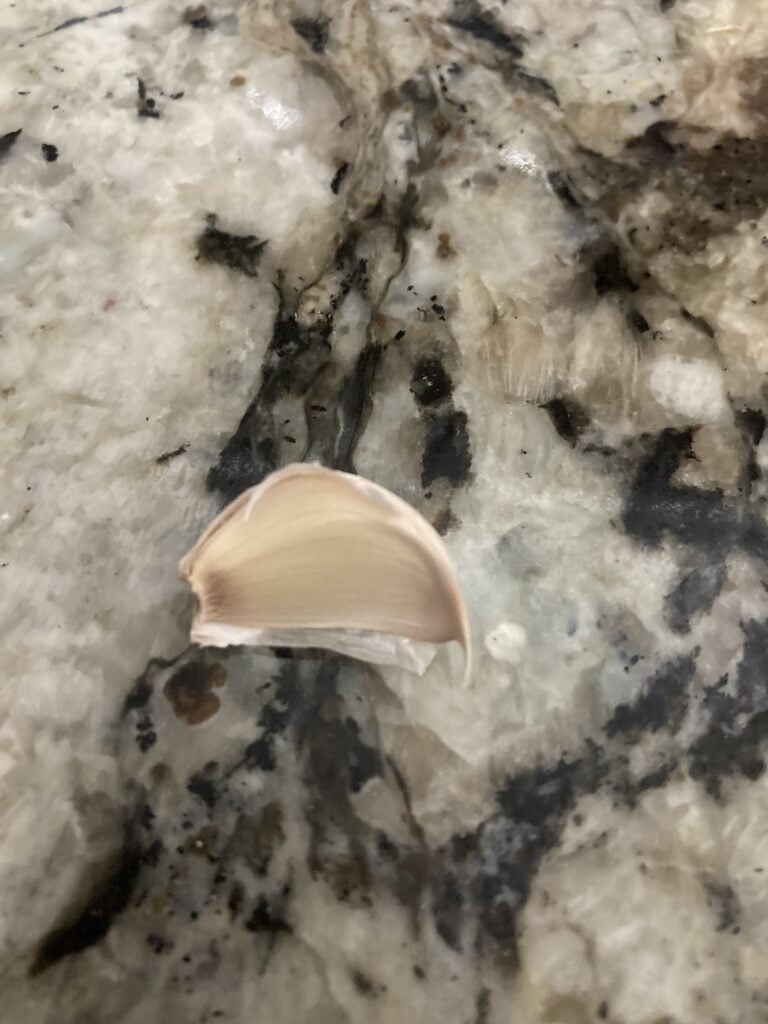
GARLIC CLOVE
A garlic head, also known as a bulb of garlic or garlic bulb, is the whole, multi-segmented structure that contains individual cloves of garlic. Each clove is covered in a papery skin and is attached to a central stalk. When you break apart a garlic head, you’ll find several cloves clustered together.
The garlic head typically consists of multiple cloves, which are the smaller, individual segments that make up the bulb. These cloves are arranged in a circular pattern, each wrapped in a thin, papery membrane. The outer layer of the garlic head is usually a white or off-white papery skin that helps protect the cloves inside.
When you break apart the garlic head, you can separate the cloves, which can then be further peeled and used in cooking. Each clove has a distinct, pungent aroma and a strong, spicy flavor when crushed or minced.

Brief History Of Garlic
Garlic has a rich history dating back thousands of years. Originating in Central Asia, it was cultivated by ancient civilizations like the Egyptians, who valued it for its culinary and medicinal properties. In ancient Greece and Rome, it was popular among soldiers and athletes. Garlic played a vital role in medieval Europe, both as a flavoring agent and a medicinal remedy. It made its way to Asia via trade routes, becoming a staple in many Asian cuisines. After being introduced to the Americas post-1492, it quickly integrated into both indigenous and European culinary traditions. Today, garlic is a ubiquitous ingredient worldwide, known for its diverse culinary applications and potential health benefits.
5 Secret Superstitions and Folklore Of Garlic head and garlic clove
1. Garlic can be used in banishing. Hang a braid of twelve heads of garlic over your door to banish jealous people and thieves.
2. Craft your bulbs into a wreath and add salt and mustard seeds sewn into a small pouch, then add other lucky charms and hang over your business door for protection and to draw in more customers.
3. Add your garlic peels and some brown sugar to a mortar and pestle and grind into a powder. Burn this on a charcoal disc for smoke cleansing. If you want to cleanse someone else’s negative energy, place a crushed clove of garlic under their bed or chair, then remove and burn it 24 hours later.
4. To create some passion with a touch of domination, puncture two cloves with a steel nail to hold them together, one on top of the other. Your clove is on top, so be sure to keep it there. Hide this in a dark, private place until the target becomes interested in you.
5. Vampires and Folklore: Garlic has a long-standing reputation as a ward against vampires and evil spirits in folklore and mythology, particularly in European traditions. It was believed that garlic’s strong odor could repel vampires and protect against their attacks.

garlic head with plant
Use Of Garlic Head and Garlic Clove
Garlic heads, also known as bulbs, are versatile ingredients that can be used in various culinary and non-culinary applications. Here’s a list of some common uses for garlic heads:
- Cooking:
- Flavoring: Garlic is a fundamental flavoring agent in many cuisines around the world. It can be used in a wide range of dishes, including soups, stews, sauces, marinades, and more.
- Roasting: Roasting whole garlic bulbs brings out a sweeter, milder flavor. The cloves can be squeezed out and spread on bread or used in cooking.
- Sautéing: Sliced or minced garlic can be sautéed in oil or butter to add flavor to dishes like stir-fries, pasta, and vegetables.
- Spreads and Dips:
- Garlic Butter: Mashed garlic mixed with butter creates a delicious spread for bread, seafood, or vegetables.
- Aioli: A garlic-infused mayonnaise, commonly used as a dip or condiment.
- Condiments:
- Garlic Paste: Crushed garlic cloves can be mixed with salt to form a paste, which can be used as a base for various recipes.
- Garlic Oil: Infusing oil with garlic imparts its flavor and aroma. This can be used in dressings, marinades, or for sautéing.
- Preservation:
- Fermentation: Garlic can be fermented to create products like black garlic, which has a sweeter, umami-rich flavor.
- Health and Wellness:
- Medicinal Uses: Garlic has been used traditionally for its potential health benefits, such as its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and cardiovascular benefits. It’s often consumed raw or in supplement form.
- Gardening:
- Planting: Individual cloves from a garlic head can be planted to grow new garlic plants.
- Pest Control:
- Natural Pesticide: Garlic extracts or sprays can be used in organic gardening as a natural deterrent for certain pests.
- Home Remedies:
- Soothing Sore Throat: Garlic has been used for its potential antibacterial properties in home remedies for throat discomfort. Crushed garlic can be mixed with honey and consumed.
- Aromatherapy:
- Scented Sachets: Dried garlic bulbs can be used in sachets for their pungent aroma, which can help repel pests.

Garlic: Nature’s Superhero – Discover the Secrets Behind Its Health benefits and Powers
Garlic is not only a flavorful culinary ingredient but also has a range of potential health benefits. Here are some of the well-documented health benefits of consuming garlic:

- Cardiovascular Health:
- Garlic has been associated with potential benefits for heart health. It may help:
- Lower blood pressure levels.
- Reduce cholesterol levels, especially LDL cholesterol.
- Improve circulation and prevent the formation of blood clots.
- Garlic has been associated with potential benefits for heart health. It may help:
- Antimicrobial Properties:
- Garlic contains compounds like allicin, which have potent antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral properties. It may help in fighting off infections.
- Immune System Support:
- Garlic is rich in antioxidants that can help strengthen the immune system. It may also stimulate immune cell activity.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects:
- Compounds in garlic may help reduce inflammation in the body, which is linked to chronic diseases like arthritis and certain types of cancer.
- Cancer Prevention:
- Some studies suggest that garlic consumption may be associated with a reduced risk of certain types of cancer, particularly those of the digestive system (e.g., stomach, colon).
- Digestive Health:
- Garlic may aid in digestion by promoting the production of digestive enzymes. It can also help regulate the gut flora.
- Antioxidant Properties:
- Garlic is rich in antioxidants like selenium and allicin, which can help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- Improved Athletic Performance:
- Some studies suggest that garlic supplements may enhance physical performance and reduce exercise-induced fatigue.
- Regulation of Blood Sugar:
- Garlic may help regulate blood sugar levels, which is important for individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance.
- Bone Health:
- Garlic contains nutrients like manganese, vitamin B6, and vitamin C, which are important for bone health and may help prevent osteoporosis.
- Respiratory Health:
- Garlic has been used traditionally to help alleviate respiratory conditions like coughs, colds, and bronchitis.
- Weight Management:
- Some research suggests that garlic may help regulate metabolism and assist in weight management.

3 Things to Consider when using Garlic head and garlic clove
- Cautions:
- Allergies and Sensitivities: Some individuals may be allergic or sensitive to garlic. It’s important to be cautious if you or someone you’re cooking for has such sensitivities.
- Breath Odor: Garlic can lead to strong breath odor. Chewing parsley or mint can help mitigate this effect.
- Storage:
- Store garlic bulbs in a cool, dry place. Once the bulb is broken, use the cloves within ten days. Avoid storing garlic bulbs in the refrigerator, as it can encourage sprouting.
- Cultural Considerations:
- Garlic is a significant ingredient in many cultural cuisines, including Italian, Mediterranean, Asian, and Middle Eastern. It’s used in various forms and plays a crucial role in defining the flavors of these cuisines.

garlic bulb with sprouts.
Remember, the intensity of garlic flavor can vary based on factors like the variety of garlic, its age, and how it’s prepared. Adjusting the amount of garlic used in a recipe can help you achieve the desired flavor profile.
Explaining what Clove Head really is
A clove head typically refers to a single bud of the clove plant (Syzygium aromaticum). Cloves are aromatic flower buds that grow on a tree native to Indonesia the Caribbean and other tropical islands .They are commonly used as a spice in cooking, particularly in Asian, African, Caribbean and Middle Eastern cuisines. Cloves have a strong, pungent flavor and are used in both sweet and savory dishes.

Clove trees thrive in humid tropical or subtropical climates. They necessitate consistent temperatures above 50 degrees Fahrenheit, with the optimal range falling between 70 and 85 degrees Fahrenheit.
Descriptions of Clove Head
A clove head is a small, dark-brown, dried flower bud that comes from the clove tree, These buds are harvested before they open into flowers. They are distinctive in appearance, with a tapered shape and a nail-like projection at the top, which gives them their name.

clove tree with young clove buds.
The term “clove” is derived from the Latin word “clavus,” which translates to “nail.” This association stems from the similarity in appearance between the shaft and head of the clove bud and that of a nail.
The flower buds start off with a subtle, light hue, which then transforms into a vibrant green before finally adopting a brilliant red shade, indicating they are ripe for harvest. Cloves are collected when they reach a length of 1.5–2 centimeters (5⁄8–3⁄4 inches). They comprise an elongated calyx that ends in four outward-spreading sepals, surrounding four petals that remain closed, forming a compact central sphere.

Young Clove Bud.
History of Clove
Cloves come from the flower buds of an evergreen tree that is native to the North Moluccas Islands in Indonesia.
Prior to the colonial era, cloves were exclusively found on a handful of islands in the Moluccas, historically referred to as the Spice Islands. These include Bacan , Makian, Moti, Ternate, and Tidore.
The first notable instance of contemporary clove cultivation emerged along the eastern coast of Madagascar. This cultivation takes place through three distinct methods: monoculture, agricultural parklands, and agroforestry systems.
In the colonial period, cloves were a highly sought-after commodity, comparable in value to oil, and their exportation was strictly regulated. The Dutch East India Company, in its efforts to dominate the spice trade during the 17th century, aimed to establish a similar monopoly over cloves as it had with nutmeg.
However, unlike nutmeg and mace, which were limited to the minute Bandas clove trees grew all over the Moluccas, and the trade in cloves was beyond the limited policing powers of the corporation.
Clove Head in Culture, Rituals and Beliefs
cloves have a rich history in Caribbean folklore and spiritual practices. They are often used in various forms of magic, including spells and rituals. Cloves are believed to possess protective and healing properties, and they are sometimes used in rituals related to love, prosperity, and banishing negative energies. In some traditions, cloves are also associated with enhancing psychic abilities and promoting spiritual insight. Keep in mind that these beliefs and practices vary widely across different cultures and individual practitioners, so it’s important to approach them with respect and cultural sensitivity.

CLOVE ESSENTIAL OIL
11 ways in which cloves are associated with spirituality
- Purification and Protection: Cloves are sometimes used in spiritual practices to purify and protect spaces, objects, and individuals from negative energies or entities. They are believed to have the ability to ward off harmful influences.
- Enhancing Psychic Abilities: In some belief systems, cloves are thought to have the power to enhance psychic abilities, intuition, and spiritual insight. They may be used in rituals or ceremonies to open up channels of spiritual communication.
- Anointing and Blessings: Cloves are sometimes used in anointing oils or incense blends during ceremonial or ritualistic practices. They are believed to impart blessings, amplify intentions, and facilitate a deeper connection to the divine.
- Symbolism: In certain cultures and belief systems, cloves are used as symbols of protection, love, and abundance. They may be incorporated into rituals, charms, or spells for these purposes.
- Meditation and Spiritual Awareness: Some people believe that the aroma of cloves can help create a conducive environment for meditation and spiritual contemplation. The scent is thought to aid in focusing the mind and promoting a sense of calm and centeredness.
- Healing Properties: Cloves have been used in traditional medicine for their various health benefits, and in some spiritual practices, they are believed to possess healing properties that extend to the spiritual and energetic realms.
- Aromatherapy: In aromatherapy, the scent of cloves is often used to alleviate stress, anxiety, and promote relaxation. This can facilitate a state of mind conducive to spiritual practices.
- Offerings and Devotion: Cloves, like many other herbs and spices, are sometimes used as offerings in devotional practices. They can symbolize gratitude, reverence, and a desire for spiritual connection.
- Hinduism: Cloves are often used in religious ceremonies and rituals in Hindu temples. They can be offered to deities as a form of devotion.
- Buddhism: Cloves may be used as an offering in Buddhist ceremonies and rituals. They can be part of incense blends or placed on altars.
- Traditional Chinese Medicine: Cloves are used in traditional Chinese medicine to address digestive issues, respiratory problems, and as a warming spice.
It’s important to note that the significance of cloves in spirituality can vary widely depending on the specific tradition, culture, or belief system.
Use of Clove Head
Clove head is a versatile spice that has been used for various culinary, medicinal, aromatic purposes for centuries, making spices, making teas, pickling and preserving, mulled beverages, aromatherapy.
Culinary Purposes of Clove
- Seasoning: Cloves are used to add flavor and aroma to various dishes, particularly in Asian, African, and Middle Eastern cuisines. They are commonly used in both sweet and savory dishes.

ground clove you by McCormick
- Spice Blends: Cloves are a key ingredient in many spice blends, such as garam masala (used in Indian cuisine) and Chinese five-spice powder. They contribute to the complex flavor profiles of these blend.
- Desserts: Cloves can be used in dessert recipes, especially those that incorporate fruits like apples or pears. They can also be used in custards and puddings for added warmth and depth of flavor.
- Infused Oils and Vinegars: Cloves can be used to infuse oils or vinegars, which can then be used in salad dressings, marinades, or as a finishing touch to dishes.
- Tea and Infusions: Clove tea, made by steeping cloves in hot water, is popular in some cultures. It’s believed to have various health benefits and is consumed for its soothing properties.

Cup of clove tea
- Baking: Ground cloves are commonly used in baking, particularly in recipes for gingerbread, pumpkin pie, and other spiced desserts. They complement the flavors of cinnamon, nutmeg, and ginger.

ground clove
- Mulled Beverages: Whole cloves are often used in mulled beverages like spiced cider, mulled wine, and chai tea. They impart a warm, aromatic quality to the drink.
- Curries and Stews: Ground cloves are used in many curry recipes, adding depth and complexity to the flavor profile. They are also used in hearty stews and soups.
- Pickling and Preserving: Cloves are used in pickling brines and marinades. They help add flavor and act as a natural preservative..
- Garnish food: They are use to garnish bake Christmas pork.

baked pork garnish with clove

pork rib roast with clove
Explore Clove journey from the kitchen Medicinal Uses
- Dental Health: Cloves are known for their natural analgesic and antiseptic properties. They have been used for centuries in various cultures to alleviate toothaches and gum pain. Clove oil or powder can be applied directly to the affected area.
- Digestive Health: Cloves can help with digestive issues like bloating, gas, and indigestion. They stimulate the production of digestive enzymes.
- Respiratory Health: Cloves can be used in remedies for coughs, colds, and sinusitis. Clove oil or tea can be helpful in soothing respiratory discomfort.
- Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties: Cloves contain compounds like eugenol that have antimicrobial properties, which can help in fighting infections.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: They may help in reducing inflammation in the body, which can be useful in conditions like arthritis.
Clove Oil: The Ultimate Natural Powerhouse for Health, Wellness, and Oral use.
- Essential Oils: Clove essential oil is used in aromatherapy for its warm, spicy scent. It’s believed to have a stimulating and revitalizing effect.

clove heads and clove oil
- Antimicrobial Properties: Clove oil is known for its potent antimicrobial properties. It can help kill or inhibit the growth of harmful microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
- Pain Relief: Clove oil contains eugenol, a natural compound with analgesic (pain-relieving) properties. It can be used topically (diluted with a carrier oil) to alleviate muscle aches, joint pain, and headaches.
- Oral Health: Clove oil is often used in dental care products due to its ability to fight bacteria that cause gum disease and tooth decay. It can also provide relief from toothaches.
- Respiratory Benefits: Inhaling the aroma of clove oil may help alleviate respiratory issues like coughs, colds, and sinusitis. Its expectorant properties can help clear mucus and improve breathing.
- Stress Relief: The aroma of clove oil is believed to have calming and stress-relieving effects. It is used in aromatherapy practices to promote relaxation and reduce anxiety.
5 secrets of Clove power in Pest Control:
- Natural Insect Repellent: Cloves have a strong, pungent odor that many insects find unpleasant. Placing cloves or clove oil in areas where pests are a problem can help deter them. This can be especially useful for repelling moths, ants, and flies.
- Insecticidal Properties: Clove oil contains compounds like eugenol, which has insecticidal properties. It can be mixed with water and used as a natural insecticide for certain pests.
- Rodent Control: Some people use cloves to deter rodents like mice and rats. They can be placed in areas where these pests are active.
- Clove Oil for Garden Pests: Clove oil can be used in gardening to repel certain pests that might harm plants. It’s important to note that this should be used with caution, as it can also affect beneficial insects.
- Insect Bite Relief: Clove oil can be applied to insect bites to alleviate itching and discomfort.
Clove: Nature’s Preservative! Unveiling the Art of Food Preservation with this Aromatic Spice
- Food Preservation: Cloves have natural antimicrobial and antifungal properties due to the presence of compounds like eugenol. In some cultures, cloves have been used traditionally to preserve food. They can be added to pickles, jams, and chutneys to extend their shelf life.

- In the art of food preservation, clove can be employed in various forms. One popular method is to include whole cloves in pickling solutions or brines, where they help to prevent the growth of spoilage microorganisms, thus extending the shelf life of pickled foods. Additionally, powdered clove can be used as a seasoning or incorporated into spice blends for curing meats, imparting both flavor and preservation benefits.
- Historically, clove played a crucial role in preserving food during long voyages and in regions where refrigeration was not readily available. Sailors often carried cloves on their journeys to prevent the spoilage of food supplies, particularly meats and grains.
- Moreover, beyond its preservative properties, clove offers numerous health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. It has been used in traditional medicine for centuries to alleviate various ailments, from toothaches to digestive issues.
Clove as a Flavoring Agents:
- Liquors and Beverages: Cloves are used to flavor certain liquors and beverages, including mulled wine and spiced cider.
Industrial and Cosmetic Uses of Clove
- Topical Applications: Clove oil is sometimes used topically for its pain-relieving properties. However, it should be used with caution and diluted properly as it can be quite potent.
- Perfumes and Cosmetics: Clove oil is used in some perfumes, soaps, and cosmetics for its aromatic qualities.
Health Benefits of clove head
Cloves have been used for centuries in traditional medicine, and they offer a range of potential health benefits:
- Rich in Nutrients: Cloves are a good source of nutrients like fiber, vitamins (especially vitamin K), and minerals (such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium).
- Antioxidant Properties: Cloves are high in antioxidants, including eugenol, which can help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. This can potentially reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Anti-Inflammatory: Eugenol, a compound found in cloves, has anti-inflammatory properties. This can be helpful in reducing inflammation in the body, which is associated with various chronic conditions.
- Anti-Microbial Properties: Cloves have natural antimicrobial properties. They can help inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi, and viruses, which can be beneficial for oral health and fighting infections.
- Oral Health: Eugenol, the primary component of clove oil, is used in dentistry for its analgesic and antiseptic properties. It can help alleviate toothaches and is used in some toothpaste and mouthwash formulations.
- Digestive Health: Cloves may aid digestion by increasing the production of digestive enzymes. They can also help reduce gas and bloating. Raw garlic has a laxative effects. Eat it mixed with onion, raw or cooked and with milk or yogurt for best results.
- Blood Sugar Control: Some studies suggest that compounds in cloves may help regulate blood sugar levels. This can be particularly important for individuals with diabetes.
- Bone Health: Cloves contain a significant amount of manganese, which is essential for maintaining healthy bones and preventing conditions like osteoporosis.
- Cancer Prevention: Some studies have shown that the eugenol in cloves may have anti-cancer properties. However, more research is needed to fully understand its potential in cancer prevention.
- Respiratory Health: Cloves have been used traditionally to treat respiratory conditions like asthma and bronchitis. The eugenol in cloves may help to open up the airways.
- Pain Relief: Cloves have analgesic properties, which means they can help alleviate pain. This can be useful for headaches, muscle pain, and even arthritis.
- Weight Management: Some compounds in cloves may help boost metabolism, which could aid in weight management efforts.
key Considerations and warnings when using clove
However, there are several considerations and warnings associated with its use:
- Allergies: Some individuals may be allergic to cloves. If you have a known allergy to other spices or plants in the same family (such as eugenol-rich plants like basil, oregano, or bay leaf), you should exercise caution when using clove.
- Dental Sensitivity: Clove oil contains eugenol, which has a numbing effect. This is why it’s sometimes used for dental issues like toothaches. However, excessive use can lead to oral irritation or even damage to the tissues in your mouth.
- Blood-Thinning Properties: Cloves have blood-thinning properties due to their eugenol content. If you are already taking blood-thinning medications or have a bleeding disorder, you should consult a healthcare professional before using clove supplements or extracts.
- Digestive Issues: In large quantities, clove can cause digestive discomfort, including diarrhea or stomach cramps. It’s best to use it in moderation, especially if you have a sensitive stomach.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: While using cloves in culinary amounts is generally considered safe for pregnant and breastfeeding women, taking clove supplements or using concentrated clove oil is not recommended without consulting a healthcare professional.
- Interactions with Medications: Clove may interact with certain medications, including blood-thinning drugs, anticoagulants, and medications for high blood pressure. If you’re taking any medications, it’s important to consult your healthcare provider before using clove supplements.
- Skin Sensitivity: Applying clove oil directly to the skin can cause irritation in some individuals. It’s advisable to dilute it with a carrier oil before applying, and to do a patch test to check for any adverse reactions.
- Diabetes Management: Cloves may lower blood sugar levels, so if you have diabetes and are using medications to control your blood sugar, monitor your levels closely and consult your healthcare provider about incorporating cloves into your diet.
- Liver Health: There have been some reports of liver damage associated with high doses of clove or clove oil. If you have liver disease or are taking medications that affect the liver, it’s best to avoid concentrated forms of clove.
- Quality and Source: Ensure that you are using high-quality, organic cloves from a reputable source. Contaminated or poor-quality cloves may contain harmful substances or pathogens.
- Children and Infants: Clove oil should not be used on infants or young children, as their skin is more sensitive and they may be more susceptible to adverse reactions.
11 Types of clove that exist in different parts of the world.
- Madagascar Cloves: Madagascar is one of the largest producers of cloves in the world. Cloves from Madagascar are known for their rich, full flavor and strong aroma.
- Zanzibar Cloves: Zanzibar, an island off the coast of Tanzania, is renowned for producing high-quality cloves. Zanzibar cloves are considered to be some of the best due to their intense flavor and aroma.
- Indonesian Cloves: Indonesia is the largest producer of cloves globally. The country has several islands that produce cloves, including Sulawesi, Moluccas, and Sumatra. Indonesian cloves are known for their strong and pungent flavor.
- Brazilian Cloves: Brazil is also a significant producer of cloves. Brazilian cloves are known for their milder flavor compared to cloves from some other regions.
- Sri Lankan Cloves: Cloves from Sri Lanka are highly regarded for their distinctive, sweet flavor and aromatic qualities. They are often considered to be of high quality.
- Indian Cloves: India is a notable producer of cloves, especially in the states of Kerala and Tamil Nadu. Indian cloves tend to have a slightly milder flavor compared to cloves from other regions.
- Comorian Cloves: The Comoros Islands, located in the Indian Ocean, are known for producing cloves with a unique flavor profile. Comorian cloves are often described as having a sweet and fruity taste.
- Penang Cloves: Penang, an island in Malaysia, is known for producing high-quality cloves. Penang cloves are esteemed for their strong aroma and flavor.
- Mauritian Cloves: Mauritius, an island nation in the Indian Ocean, also produces cloves. Mauritian cloves are known for their rich, aromatic qualities.
- Tanzanian Cloves: Tanzania is a significant producer of cloves, with Zanzibar being the primary growing region. Tanzanian cloves are known for their bold and spicy flavor.
- Papua New Guinean Cloves: Papua New Guinea is a lesser-known producer of cloves. Cloves from this region may have a unique flavor profile influenced by local growing conditions.
It’s important to note that while cloves can offer these potential health benefits, they should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. If you have specific health concerns or conditions, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet or using them for medicinal purposes.
Differences between Garlic Head, Garlic Clove and Clove.
GARLIC HEAD

- The garlic head, also known as a bulb, is the entire structure of garlic, made up of multiple cloves.
- It is covered by a papery skin, which can be white or light purple depending on the variety.
- A garlic head contains multiple cloves, usually arranged in layers.
- It is the whole garlic plant’s storage unit, storing nutrients and energy for growth.
- A head of garlic can be broken apart into individual cloves.
GARLIC CLOVE

- A garlic clove is one of the individual segments that make up a garlic head.
- It is encased in its own papery skin, which is usually thin and easy to peel.
- Garlic cloves are the part of the garlic plant that can be used for cooking.
- When crushed, chopped, or minced, garlic cloves release their characteristic pungent flavor.
CLOVE

- A clove is a spices refers to the dried, unopened flower bud of the Syzygium aromaticum tree, native to Indonesia.
- Cloves are dark brown, nail-shaped, and have a distinctive, strong, sweet, and spicy flavor.
- They are commonly used in both savory and sweet dishes, as well as in various spice blends.
- Unlike garlic, cloves are not related to the allium family and have a different botanical origin.
Resources
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9271057/








