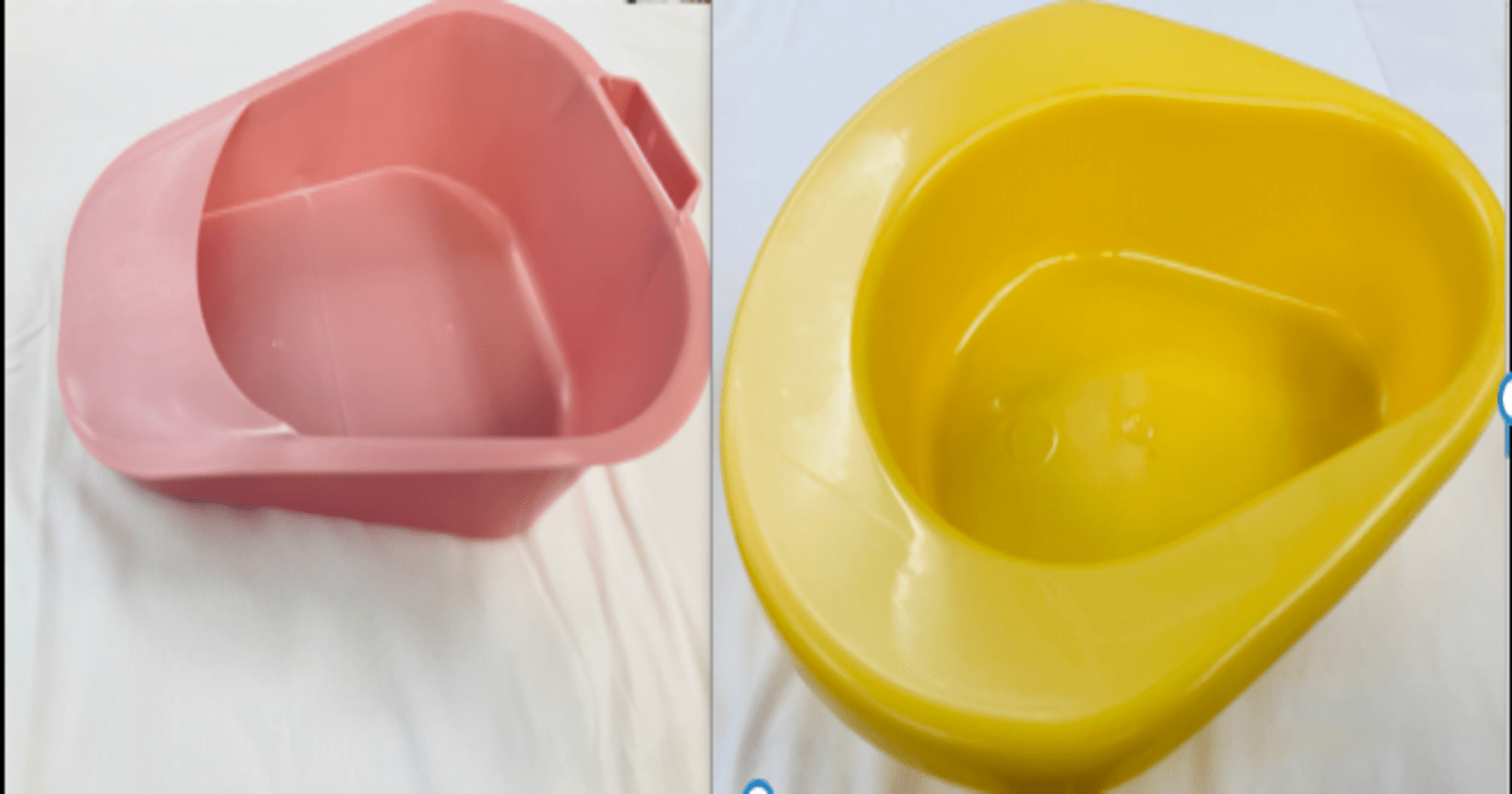
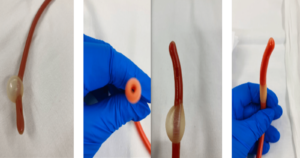
Fracture Bedpan is typically designed smaller, with a tapered end to make it easier to go under from the front diminishing the need to turn the patient, it is used for patients with limited mobility or those recovering from fractures to use without causing discomfort or exacerbating injuries. Regular Bedpan on the other hand has a more standard design, often with a flatter bottom, wide rim around the rear of the pan on which a patient can sit and this narrows as it comes around to the front of the container and is intended for general use.
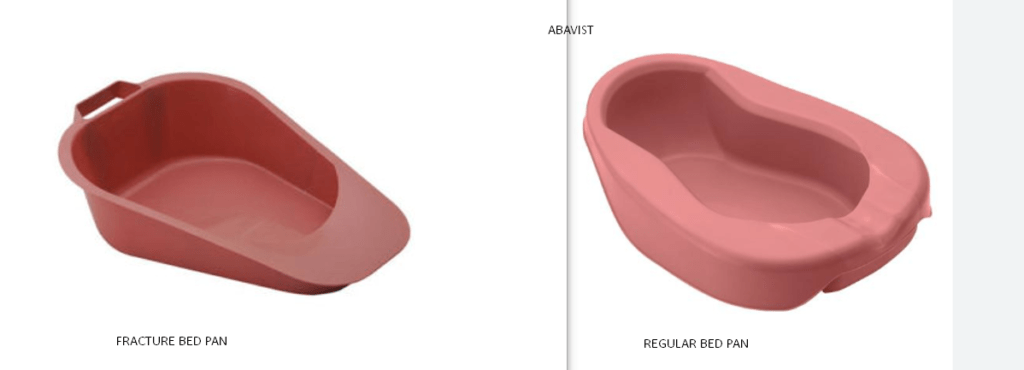
Types of fracture Bedpan
Fracture Bedpan may be made from lightweight, durable materials to ensure ease of use and handling for patients with fractures.
1.Plastic Fracture Bedpan

- Advantages: Lightweight, durable, easy to clean, and cost-effective.
- Disadvantages: May not be as robust as metal options.
2. Metal (such as stainless steel) Fracture Bedpan

- Advantages: Sturdy, durable, and resistant to damage.
- Disadvantages: Heavier than plastic, may be colder to the touch.
3.Composite Materials Fracture Bedpan

- Advantages: Can combine the benefits of different materials, such as being lightweight and durable.
- Disadvantages: Cost may be higher compared to some other materials.
Types of Regular Bedpan
- Plastic:
- Advantages: Lightweight, easy to clean, and cost-effective.
- Disadvantages: May not be as durable as metal options.

2. Metal (such as stainless steel):
- Advantages: Sturdy, durable, and resistant to damage.
- Disadvantages: Heavier than plastic, may be colder to the touch.

3. Disposable Materials (Cardboard or Paper Pulp):
- Advantages: Single-use, reduces infection risk, and eliminates the need for cleaning.
- Disadvantages: May not be suitable for all patients, cost considerations for long-term use.
4. Ceramic or Porcelain:
- Advantages: Durable, aesthetically pleasing, and may retain heat better.
- Disadvantages: Heavier, risk of breakage, and may be colder initially.

4. Composite Materials:
- Advantages: Can combine the benefits of different materials, such as being lightweight and durable.
- Disadvantages: Cost may be higher compared to some other materials.
When selecting the material for bedpans, considerations should be made based on the specific needs of the patients, ease of cleaning, durability, cost, and any potential preferences or requirements of healthcare facilities. It’s important to strike a balance between functionality, comfort, and practicality in the healthcare setting.
🔑Important Considerations when choosing a bedpan for a patient or Elderly person.

Choosing a bedpan may not be the most glamorous task, but it’s an important one for comfort and hygiene, especially for individuals who are bedridden or have limited mobility. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a bedpan.
- Choosing the right Material is important and depends on your patient preference.
- Plastic: Lightweight and easy to clean. Some have a contoured design for added comfort.
- Metal: Durable but may be colder and noisier than plastic.
- Size and Capacity plays a role when providing elimination care.
- Ensure the bedpan is the right size for the individual, providing enough support and coverage.
- Consider the weight capacity of the bedpan to ensure it can safely support the user.
- Design:
- Look for bedpans with a comfortable and ergonomic design that conforms to the body.
- Some bedpans have a tapered end for easier placement and removal.
- Splash Guard:
- A splash guard can help prevent spills and messes during use.
- Bedpans with Lid helps to maintain a patient dignity.
- Some bedpans come with a lid, providing discretion and reducing odors.
- Ease of Cleaning is a priority when providing care.
- Consider the ease of cleaning and sterilization. Look for bedpans that are dishwasher-safe or easy to wipe down.
- Disposable vs. Reusable:
- Disposable bedpans are convenient for one-time use and can be discarded.
- Reusable bedpans are more environmentally friendly but require thorough cleaning.
- Compatibility with Equipment:
- Ensure compatibility with any assistive equipment, such as bedpan racks or holders.
- Portability:
- If the bedpan needs to be moved frequently, consider its weight and portability.
- Patient Comfort:
- The comfort of the patient is crucial. Look for features like padding or a soft, contoured design.
- Healthcare Professional Recommendations:
- Consult healthcare professionals or caregivers for recommendations based on the specific needs and conditions of the individual.
- Cost can play a role in choice of bedpan for elderly and patients who is on a tight budget.
- Consider your budget, but prioritize the features that are most important for the user’s comfort and hygiene.
Always prioritize the user’s comfort and dignity when selecting a bedpan. Additionally, consulting with healthcare professionals or occupational therapists can provide valuable insights based on the individual’s specific requirements.
Differences Between Fracture bedpan and Regular bedpan.

Bedpan are created different to accommodate different situation. Here are some differences listed in table below.
| Fracture Bedpan | Regular Bedpan |
|---|---|
| Design: Designed with a tapered end to make it easier for patients with limited mobility or those recovering from fractures to use without causing discomfort or exacerbating injuries. | It has a more standard design, often with a flatter bottom, and is intended for general use. |
| Material: made from lightweight, durable materials to ensure ease of use and handling for patients with fractures. | Can be made from a variety of materials including plastic or metal, designed for general patient use. |
| Size: Have a smaller overall size to accommodate patients with limited movement or in awkward positions due to fractures. | Typically larger in size compared to a fracture bedpan, suitable for a broader range of patients. |
| Ease of Use: Specifically designed to be easy to use for patients with fractures, minimizing discomfort and the risk of exacerbating injuries. | Generally designed for standard use and may not take into account specific mobility issues associated with fractures. |
| Comfort: Emphasizes comfort, with features like a tapered design to accommodate patients with fractures without causing additional pain. | While designed for general comfort, it may not provide the same level of tailored support for patients with fractures. |
| Cleaning and Maintenance: Cleaning may be easier due to its design, with smooth surfaces and minimal crevices. | Typically more cost-effective due to its standard design and widespread use. |
| Versatility: Specialized for patients with fractures or limited mobility, may not be as versatile for general use. | Versatile and suitable for a wide range of patients, regardless of specific health conditions. |
| Cost: May be slightly more expensive due to the specialized design and materials used. | Typically more cost-effective due to its standard design and widespread use. |
Unique Features of a fracture Bedpan
These bedpans are unique in their design to make it more comfortable and practical for patients who may have difficulty using a regular bedpan due to their injury. Here are some features that make fracture bedpans unique:
- Low Profile:
- Fracture bedpans have a lower front and higher back compared to regular bedpans. This design allows individuals with lower extremity injuries, such as leg casts or splints, to position themselves more easily without causing discomfort.
- Extended Back:
- The higher back of a fracture bedpan provides additional support and helps maintain a comfortable position for individuals with back injuries or those who need to keep their upper body elevated.
- Tapered End:
- Many fracture bedpans have a tapered or contoured end, making it easier to slide the bedpan under the patient without causing unnecessary pressure or discomfort.
- Smooth Surface:
- The surface of fracture bedpans is typically smooth and contoured to provide comfort and prevent additional pressure on the injured area.
- Lightweight:
- Fracture bedpans are often lightweight to facilitate easy handling by both patients and caregivers.
- Material:
- They are commonly made from plastic, which is not only lightweight but also easy to clean and sterilize.
- Easy Placement and Removal:
- The design of fracture bedpans aims to make placement and removal as easy as possible for individuals with limited mobility or pain in the lower extremities.
- Non-Skid Base:
- Some fracture bedpans have a non-skid base to prevent slipping and provide stability when in use.
- Splash Guard:
- Similar to regular bedpans, fracture bedpans may have a built-in splash guard to prevent spills and maintain cleanliness.
🔑Key Physical Features of the Regular Bedpan.
Profile:
- The profile of a regular bedpan typically consists of a shallow, basin-like shape with a low front and higher sides. This design allows for easy positioning under a patient in a lying or semi-reclined position. The low profile aids in smooth insertion and removal, while the raised edges help prevent spillage. It’s resemblance is to the combination of a toilet seat and bowl.

Back:
- The back of the bedpan is the part that supports the patient’s lower back. It is designed to be comfortable and stable, providing a secure surface for the patient to lean against during use. The back is often contoured to follow the natural curve of the spine, enhancing support and minimizing discomfort.
Surface:
- The surface of the bedpan is smooth and non-porous, facilitating easy cleaning and sanitation. Materials commonly used for bedpans include plastic or stainless steel. The smooth surface also helps prevent discomfort for the patient and allows for straightforward waste removal.
- End:
- The end of the bedpan is where the patient’s buttocks rest. It is contoured to provide a comfortable seating area, and the design aims to distribute the patient’s weight evenly. This ensures that the patient can use the bedpan with minimal discomfort and reduces the risk of spills.
- Weight:
- The weight of a regular bedpan is carefully balanced to meet specific criteria. It should be light enough for easy handling by healthcare providers but sturdy enough to support the weight of the patient. Materials like lightweight plastics or durable metals contribute to achieving this balance, ensuring both usability and reliability.
6 Alarming Signs and Symptoms that may indicate a person needs a fracture bedpan
- Inability to Sit Up: If a person is unable to sit up due to a fracture or injury, a fracture bedpan may be necessary. This type of bedpan is designed to be used while the individual is lying down.
- Pain or Discomfort when Moving: Individuals with fractures may experience significant pain or discomfort when attempting to move, especially when trying to sit up. A fracture bedpan allows them to eliminate waste without exacerbating their injuries.
- Limited Mobility: If a person has limited mobility or is bedridden due to a fracture, a fracture bedpan can provide a more comfortable and convenient solution for toileting needs.
- Orthopedic Injuries: Fracture bedpans are commonly used for patients with orthopedic injuries such as hip fractures or lower extremity fractures, where movement is restricted to prevent further injury.
- Post-Surgery: After certain types of surgeries, individuals may have difficulty sitting up or moving, making a fracture bedpan a suitable option for managing their toileting needs during the recovery period.
- Spinal Cord Injuries: People with spinal cord injuries may also benefit from the use of a fracture bedpan, as it allows for toileting without the need to sit up or move.
8 Easy and Simple Steps for Placing a person on a regular bedpan
- Introduce yourself and verify patient identity, explain the procedure and address person’s requests.


2. Perform hand hygiene , wear gloves and ensure privacy and follow isolation precautions.

3. Lower the head of the bed and place an incontinence pad under the patient. You can dust bed pan with powder to ensure it dose not stick to user skin.

4. Position the bedpan beneath the patient by helping them roll onto their side, with their buttocks facing the healthcare provider. Position the bedpan beneath the patient based on the contour or shape of the bedpan, aligning the wider section towards the patient’s head and the narrower section towards their feet.

5. Ensure the buttocks are securely pressed against the bedpan, moving downward into the bed or mattress pad.
6. Use one hand to support the bedpan and the other to hold the patient’s hip while gently rolling them onto the bedpan. To prevent injury, refrain from forcefully positioning the pan under the buttocks. When using a bariatric bedpan, involve multiple people to ensure the safety of both person and patients.
7. Elevate the head of the stretcher or bed to a semi-Fowler position, with a minimum incline of thirty degrees. Place a pillow to enhance comfort in the lower lumbar area and provide a supportive base. Adjusting the bed’s head while the patient is utilizing it will aid in facilitating voiding or defecating.
8. If there are no contraindications, request the patient to bend their knees to facilitate a squatting motion. Additionally, instruct the person to using the bedpan to call when finish.
Essential Tips on removing a bedpan from under a patient.
- Ensure the person using the bedpan is finish then lower the bed head to make possible removal of the bed pan.
2. If the person can, ask them to raise their hips. Securely hold the bedpan and gently slide it out from beneath the patient. Provide assistance with cleansing the patient’s perineum as needed.
Brief History of the Bedpan
The bedpan has a long history, dating back to ancient times. Early civilizations, such as the Greeks and Romans, used various forms of chamber pots or containers for human waste. However, the bedpan as we know it today has more recent origins.
In the 18th century, with advancements in metalworking, bedpans began to take on a more recognizable form. They were typically made of materials like copper or pewter. As the Industrial Revolution progressed, manufacturing techniques improved, and bedpans became more widely available.
During the 19th and early 20th centuries, bedpans underwent further evolution, with the introduction of materials like enamel-coated metal and later, plastic. These developments aimed to enhance sanitation and ease of cleaning.
In the era of Florence Nightingale, bedpans were commonly referred to as utensils. This terminology is prominently featured in her renowned book, Notes on Nursing, where the term utensil is mentioned 15 times. Intriguingly, this designation for bedpans persisted beyond Nightingale’s time. For instance, in the cataloging efforts of George Washington’s belongings by his descendants, his bedpan found its place under the category of interesting utensils. Astonishingly, it was documented as a plate warmer, reflecting a curious historical perspective on the practical uses of such items in the past. This unconventional nomenclature offers a glimpse into the distinct cultural and linguistic nuances surrounding the mundane yet essential objects of daily life in different periods of history.
When is a Fracture Bedpan the choice for use?

- Lower Extremity Fracturhttps://abavistwellness.com/o-arm-imaging-device-vs-c-arm-imaging-device/es: Patients with fractures in the hip, pelvis, femur, or other lower extremities may find it challenging or painful to use a standard bedpan. The lower lip or flat end of the fracture bedpan can be positioned under the patient without requiring them to lift their injured leg. Using a fracture bed pan for patients with conditions such as Legg Calve Perthes Disease (LCPD) is ideal to alleviate pain and discomfort.
- Post-Surgery:
- After orthopedic surgeries, individuals may experience pain and reduced mobility, making a fracture bedpan more suitable for toileting.
- Spinal Injuries:
- Patients with spinal injuries, especially those affecting the lower back, may benefit from the use of a fracture bedpan.
- Musculoskeletal Injuries:
- Injuries to muscles, tendons, or ligaments in the lower body that restrict movement can make a fracture bedpan necessary.
- Immobility Issues:
- Patients who are temporarily or permanently bedridden may require a fracture bedpan when traditional bathroom facilities are not accessible.
- Rehabilitation:
- During the rehabilitation process, individuals may use fracture bedpans to maintain independence in daily activities while recovering from lower extremity injuries.
It’s important to note that the decision to use a fracture bedpan is typically made by healthcare professionals based on the specific needs and conditions of the patient.
Resources
As a nurse I work in a nursing home, hospitals and from time to time home care ,where I gain my knowledge and experiences on using both bedpans.
https://www.myamericannurse.com/bedpan-and-social-justice-during-pande