Filtered needles have filters used to trap particulates or matter. Blunt needles don’t have filters and are not used for skin or tissue infiltration. Regular needles don’t have filters and are used for skin and tissue penetration. Filtered hypodermic needles, blunt needles, and regular needles are three different types of needles commonly used in healthcare settings. Each type serves specific purposes and has unique characteristics.
The choice of needle type depends on the specific medical procedure and the goals of the healthcare provider. Regular needles are used for procedures that require precise puncturing of the skin and tissues. Blunt needles are employed in situations where skin penetration is not necessary, such as accessing IV lines. Filtered hypodermic needles have an added filter to reduce the risk of contamination during injections.

Key Comparison between Filtered Hypo-Needle, Blunt Needle and Regular Hypo-Needle
Filtered Hypodermic Needle:
- Filter: These needles are equipped with a filter designed to trap particulate matter and prevent it from entering the patient’s bloodstream during injections.
- Typical Use: They are used in situations where it is important to reduce the risk of contamination, such as during medication administration.
- Material: Like regular needles, they are typically made of stainless steel.
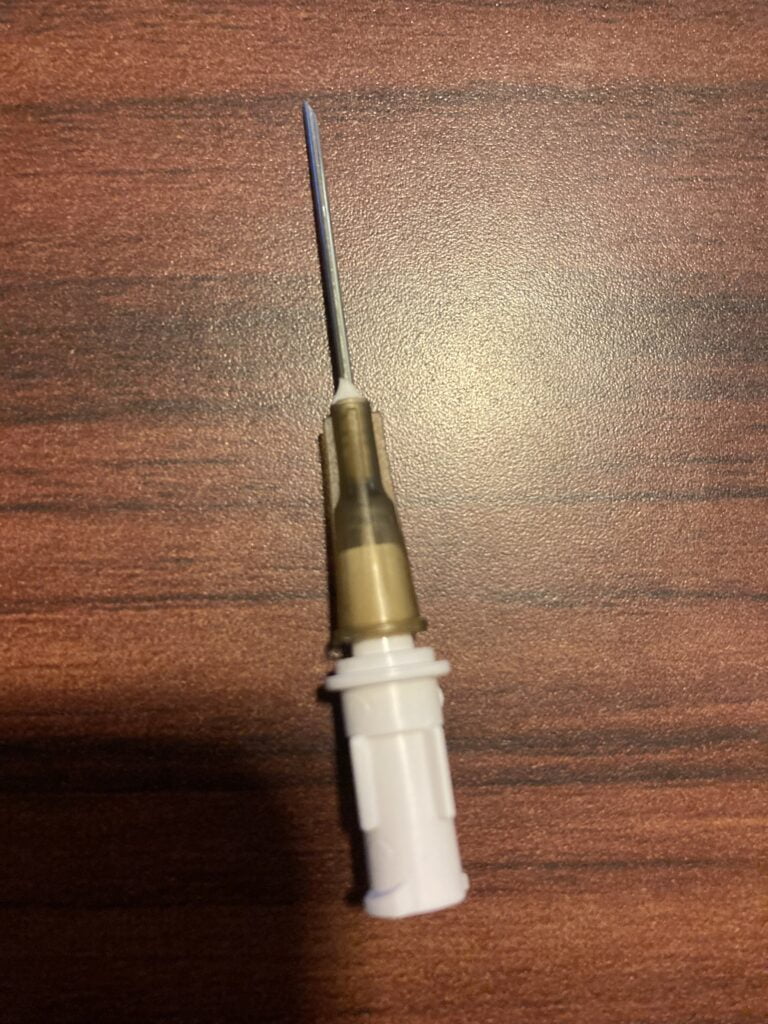
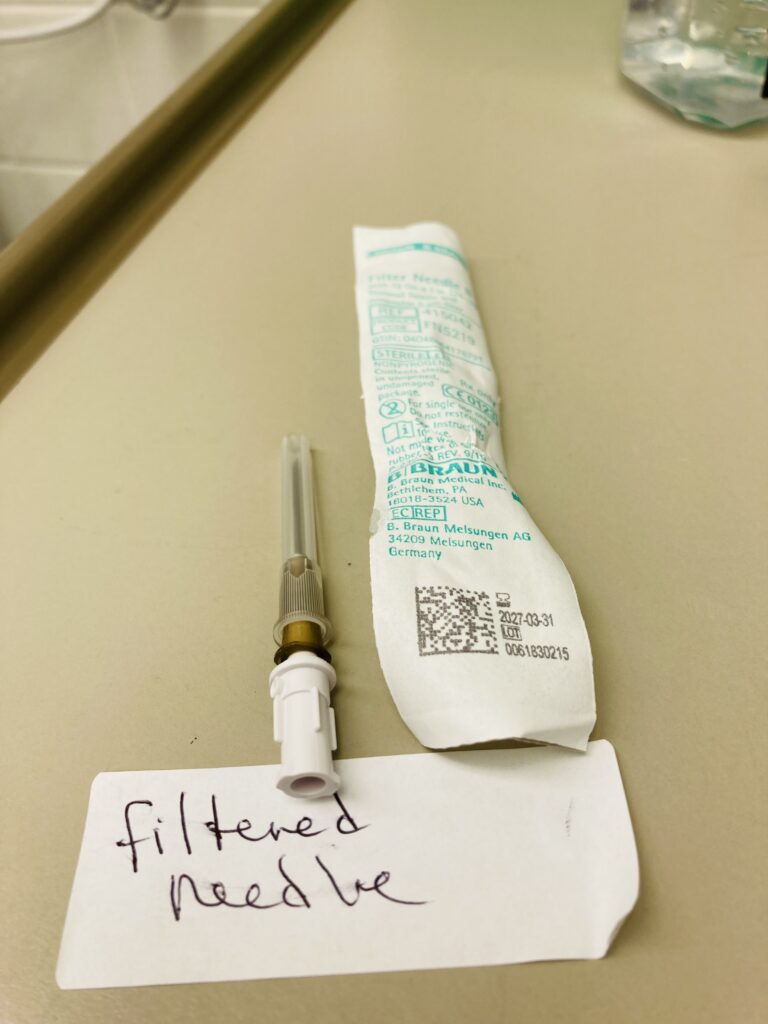
Blunt Needle:
- Sharpness: Blunt needles have a rounded or blunt tip rather than a sharp one.
- Typical Use: They are used when the penetration of the skin is not required, such as with certain types of injections that go directly into an IV line or when accessing ports or catheters.
- Material: They are often made of plastic or stainless steel.
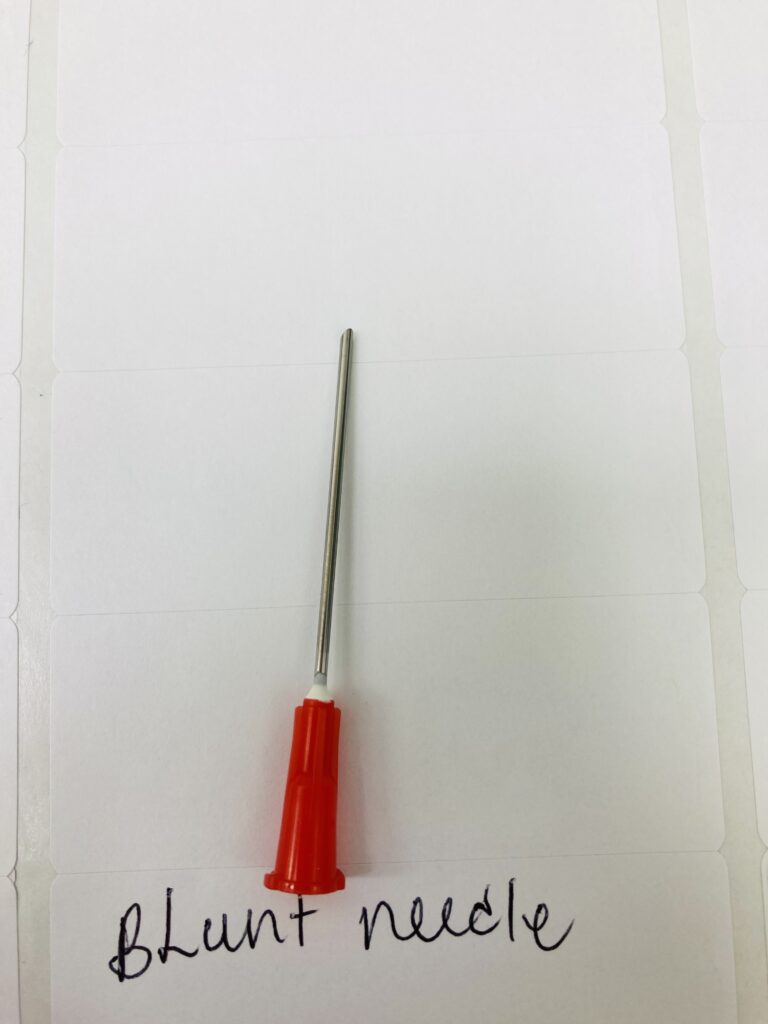


Regular Hypodermic Needle:
- Sharpness: Regular needles have a sharp, pointed tip designed for puncturing the skin and tissues.
- Typical Use: They are commonly used for procedures where precise penetration is crucial, such as vaccinations, blood draws, and injections.
- Material: They are usually made of stainless steel or other metals.


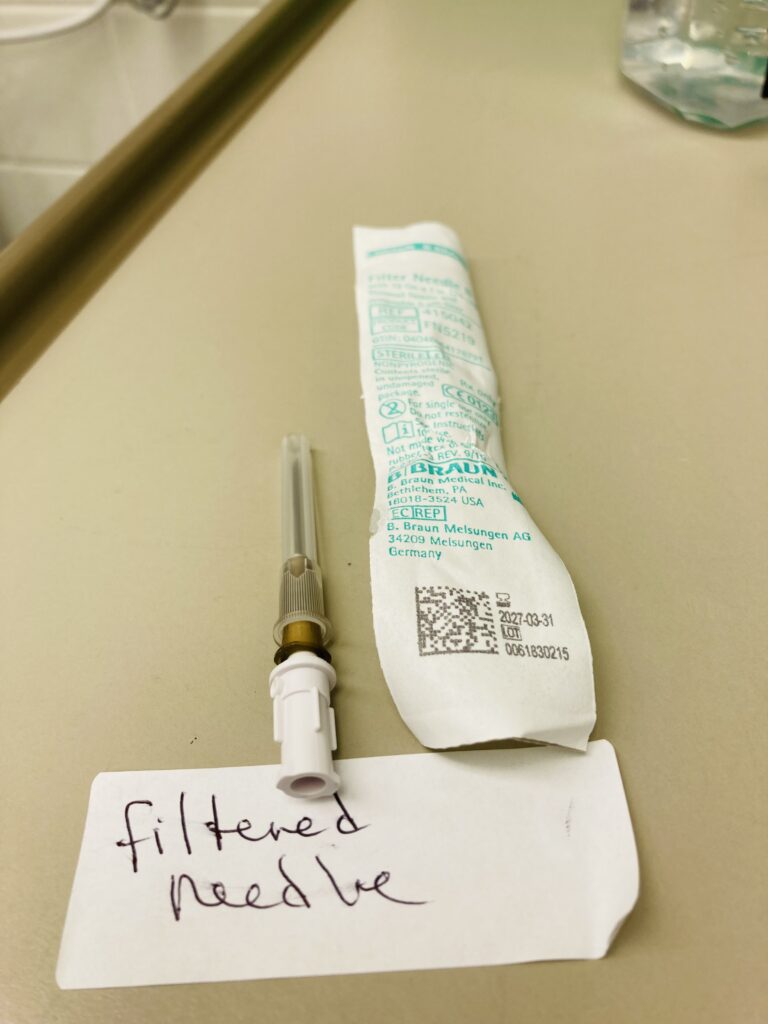
What is a Filtered Hypodermic Needle
A filtered hypodermic needle is a specialized type of needle used in medical procedures. It is designed with an integrated glass filtering device at the base of a syringe needle The filter made of materials like nylon or cellulose acetate. The filter to help prevent the passage of particulate matter, such as small solid particles or microorganisms, from the syringe into the patient’s body during an injection.
Video compliments Paolo Broccardo
Filtered needles are commonly used in situations where it is particularly important to maintain a sterile environment, such as when administering certain medications or performing sensitive medical procedures. The filter in the needle helps to ensure that only the intended liquid medication or solution is delivered to the patient, minimizing the risk of contamination or infection.
Key Description of Filtered needle
It has a thin, hollow metal tube (the needle) attached to a plastic or metal hub, which serves as a handle for the healthcare professional administering the injection. What sets a filtered hypodermic needle apart from a standard needle is the presence of a filter element integrated into the hub.
The filter in a hypodermic needle is typically a small, porous membrane made of materials like polypropylene or other synthetic materials. Its purpose is to trap and remove particulate matter, such as microorganisms, debris, and potentially harmful contaminants, from the medication or fluid being administered. This helps to ensure the purity and sterility of the injected substance.
Filtered hypodermic needles are commonly used in healthcare settings where maintaining a high level of sterility is crucial, such as in hospitals, clinics, and other medical facilities. They are particularly important when administering medications or fluids to individuals with compromised immune systems or in situations where infection control is of utmost importance.
Filtered hypodermic needles come in various sizes and configurations to suit different clinical needs. Healthcare professionals select the appropriate needle based on factors like the type of medication, the patient’s age and condition, and the volume of fluid to be administered.
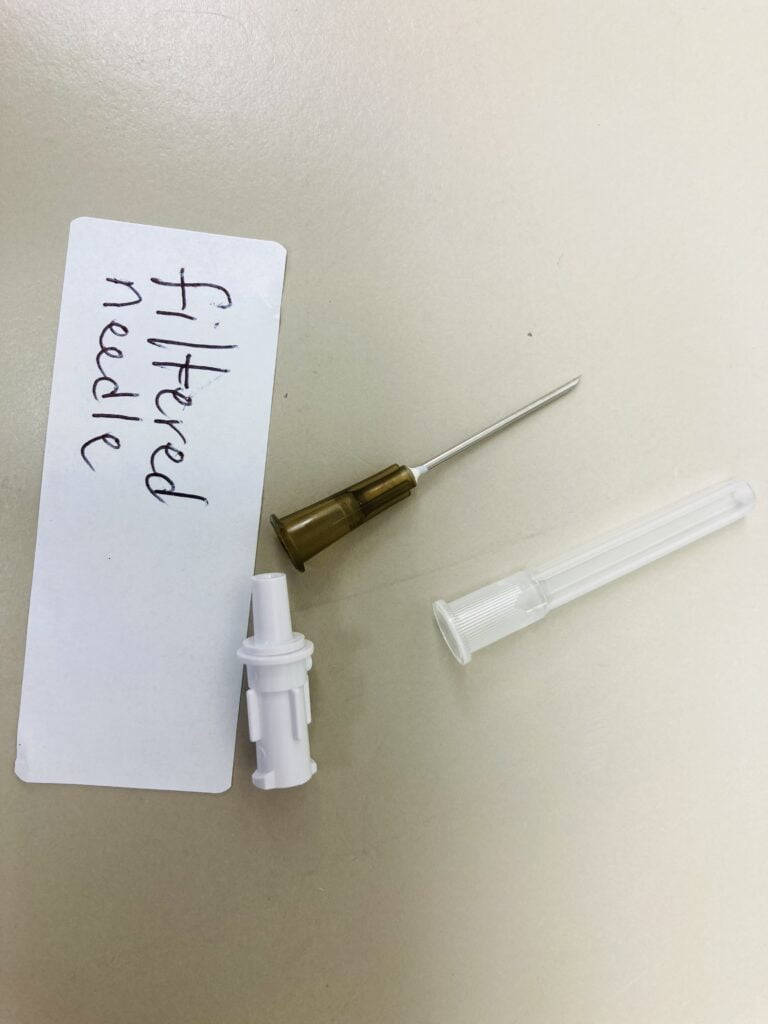

10 Uses of Filtered Hypo-Needle
- Administration of Medications: Filtered Hypo-Needles are used to administer medications, especially when particulate matter or impurities need to be filtered out to ensure patient safety. Lots of medications have glass ampoules, when an ampoule is opened by breaking the neck, it can produce small glass shards that may potentially fall into the vial. If medication containing these glass shards is administered, it can lead to inflammation of the veins and the risk of infection. By using a filter needle, the likelihood of introducing glass into the medication is significantly reduced.
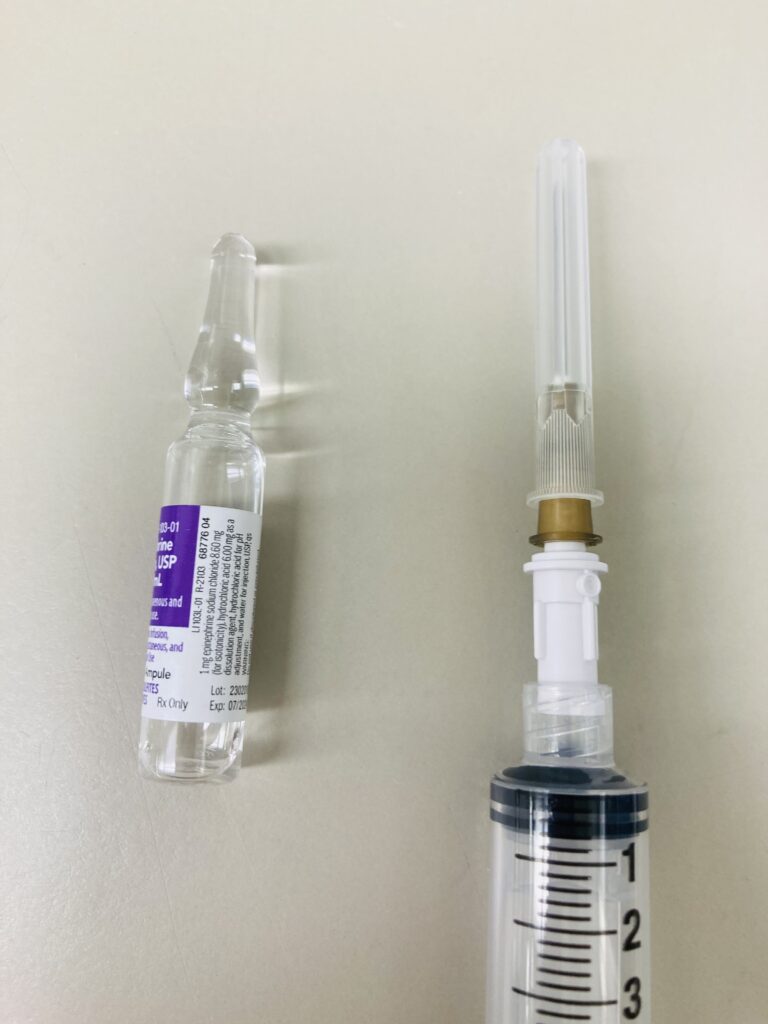
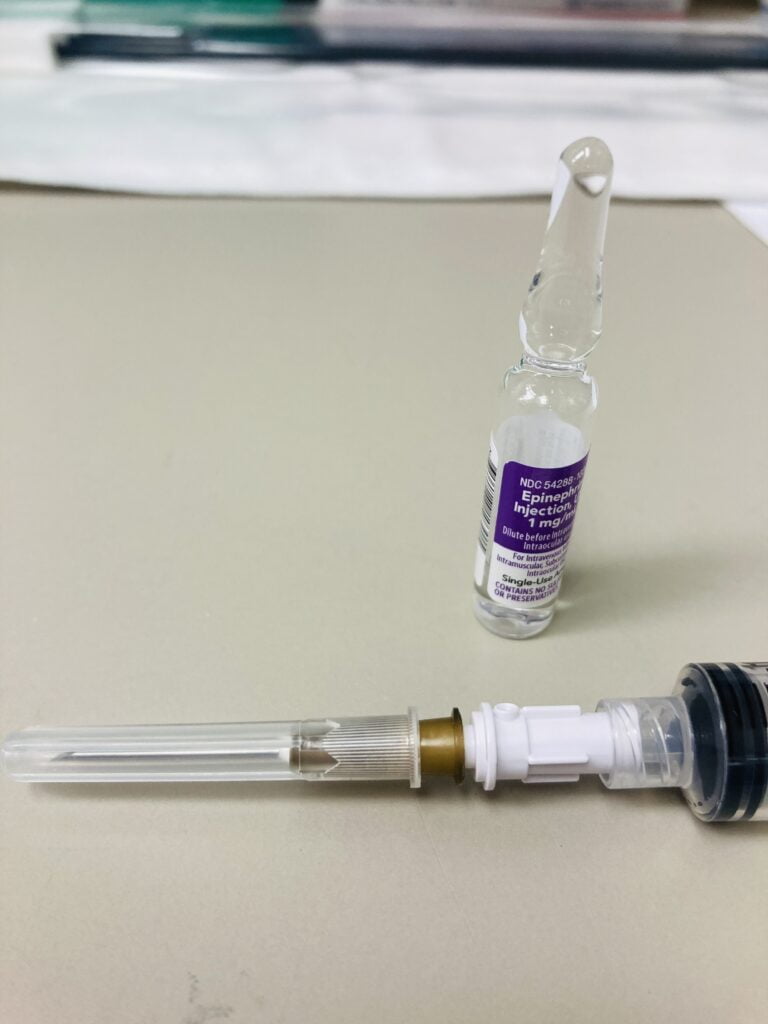
- Intravenous (IV) Injections: They are employed in delivering fluids, medications, and other substances directly into the bloodstream through an IV line, ensuring that any potential contaminants are filtered out.
- Chemotherapy: Filtered Hypo-Needles are utilized in chemotherapy administration to prevent the introduction of any solid particles or contaminants that may be present in the medication.
- Parenteral Nutrition: They are employed in the administration of parenteral nutrition solutions to ensure that the patient receives a clean and sterile mixture without any impurities.
- Blood Transfusions: Filtered Hypo-Needles can be used during blood transfusions to remove any potential clots or particles from the blood before it is introduced into the patient’s circulatory system.
- Intrathecal Injections: These injections are delivered directly into the spinal canal. A filtered needle helps ensure that the medication is free from particulate matter that could potentially cause complications.
- Contrast Media Administration: When injecting contrast media for medical imaging procedures like CT scans or angiograms, a filtered needle helps ensure that the contrast agent is free from impurities.
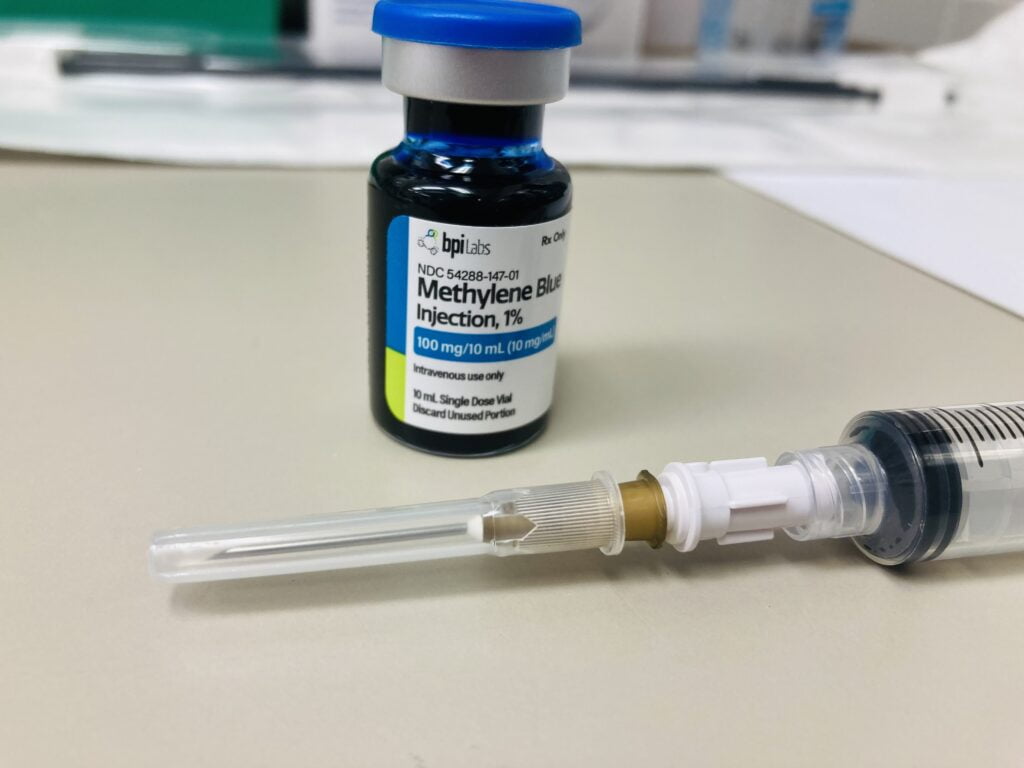
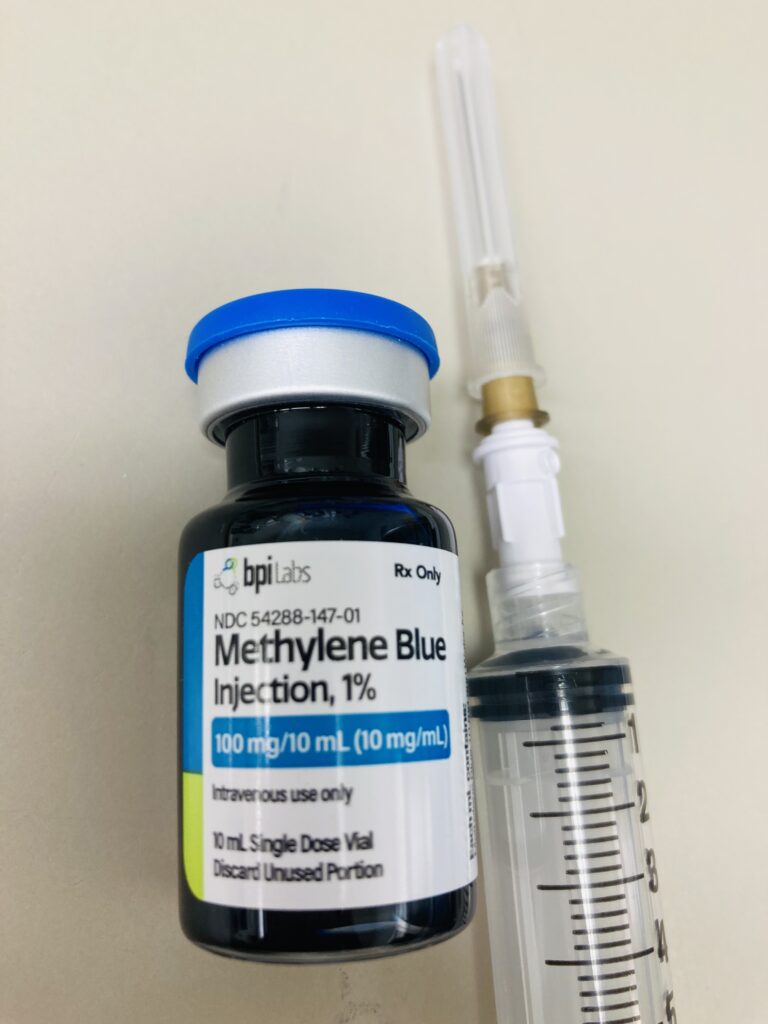
- Cell Culture and Biotechnology: Filtered Hypo-Needles are employed in research and biotechnological processes where sterile and filtered solutions are crucial for cell culture and related applications.
- Veterinary Medicine: They are used in veterinary practice for similar applications as in human medicine, ensuring the safe administration of medications and substances to animals.
- Research and Laboratory Applications: Filtered Hypo-Needles find use in various research settings, ensuring precise and sterile delivery of substances in laboratory experiments.
It is important to note that the specific use of a Filtered Hypo-Needle may vary depending on the manufacturer’s recommendations and the requirements of the medical procedure or application. Always follow proper protocols and guidelines for the safe and effective use of medical instruments.
How dose Filter Hypodermic Needle works
When you insert the filter needle into an ampoule or vial and draw back on the plunger of the syringe, the liquid medication is pulled through the filter and into the syringe barrel. As the medication passes through the filter, any particulate matter or impurities present in the solution get trapped by the filter. This prevents these particles from entering the syringe and, ultimately, the patient’s body
The filter in a hypodermic needle establishes a unidirectional flow, allowing either the withdrawal or injection of fluid into or from the syringe, but not both. It operates in a manner where it can be either pulled or pushed, but only in a single direction.
When an ampoule is opened by breaking the neck, it can produce small glass shards that may potentially fall into the vial. If medication containing these glass shards is administered, it can lead to inflammation of the veins and the risk of infection. By using a filter needle, the likelihood of introducing glass into the medication is significantly reduced.
8 Types of Filtered Hypo-Needles
Filtered hypo-needles, also known as filter needles or safety needles, come in various types designed for specific purposes. Here are some common types:
- Standard Filter Needle: This type of filter needle is equipped with a filter membrane that helps prevent particulate matter, such as glass shards or other contaminants, from entering the syringe. It is commonly used in healthcare settings for drawing up medications from ampoules or vials.
- Air Elimination Filter Needle: These filter needles are designed to remove air bubbles from the medication while drawing it up into the syringe. They have an additional filter to prevent air from entering the syringe barrel.
- Chemotherapy Filter Needle: These specialized filter needles are designed for the safe handling and administration of chemotherapy drugs. They have a reinforced filter membrane to prevent the escape of hazardous substances.
- Particulate Filter Needle: These filter needles are designed to remove even smaller particles from the medication, providing an extra level of filtration compared to standard filter needles.
- Insulin Filter Needle: These are designed specifically for drawing up insulin. They have a finer filter membrane to ensure smooth and precise insulin administration.
- Pediatric Filter Needle: These filter needles are designed with a smaller gauge size and are suitable for use with pediatric patients. They are optimized for drawing up smaller volumes of medication accurately.
- Prefilled Syringe Filter Needle: Some filter needles are integrated into prefilled syringes, ensuring that the medication is already filtered before administration.
- Biopsy Needle with Filter: These filter needles are designed for use in biopsy procedures, where it is crucial to minimize the introduction of tissue fragments or contaminants into the sample.
Filtered Needles also come in Blunt form for the purpose of drawing up medication etc.
8 Safety Features of Filtered Hypodermic Needle
Filtered hypodermic needles are designed with several safety features to enhance the protection of healthcare workers and patients. These features aim to reduce the risk of accidental needlestick injuries and prevent contamination. Here are some common safety features found in filtered hypodermic needles:
- Needlestick Prevention Devices (NPDs): Many filtered hypodermic needles come equipped with NPDs, which are mechanisms that help cover or retract the needle after use. This prevents accidental needlestick injuries by reducing the risk of direct contact with the sharp needle.
- Protective Sheaths or Shields: Some filtered hypodermic needles have protective sheaths or shields that can be activated to cover the needle after use. This creates a physical barrier, preventing accidental contact with the sharp tip.
- Self-Retracting Needles: These needles have a mechanism that automatically retracts the needle into the syringe or hub after use. This eliminates the need for manual activation and reduces the risk of needlestick injuries.
- Activation Buttons or Sliders: Some filtered hypodermic needles have a button or slider that allows the healthcare worker to manually activate the safety feature, covering or retracting the needle.
- Audible or Visual Confirmation: Certain safety needles provide an audible or visual indicator to confirm that the safety feature has been activated. This provides assurance to the healthcare worker that the needle is safely secured.
- Single-Handed Activation: Many filtered hypodermic needles are designed to be activated with one hand, allowing for easy and efficient use in clinical settings.
- Tamper-Evident Packaging: The packaging of filtered hypodermic needles may include features to indicate if it has been tampered with, providing an extra layer of security and ensuring the integrity of the product.
- Color-Coding or Unique Design: Some filtered hypodermic needles have distinctive colors or designs to differentiate them from standard needles, making it easier for healthcare workers to identify and use the correct needle.
These safety features are crucial in reducing the risk of needlestick injuries, which can lead to the transmission of bloodborne pathogens. Healthcare facilities and providers should always follow proper disposal protocols for used needles, ensuring that they are disposed of in puncture-resistant containers designed for sharps disposal.
Blunt Hypodermic Needle
A blunt hypodermic needle is a type of needle that has a rounded or flattened tip, as opposed to a sharp, pointed one. These needles are designed for specific medical purposes, such as injecting fluids into or aspirating fluids from delicate tissues or cavities where a sharp needle could cause damage.
Blunt needles are often used in procedures like epidurals, spinal taps, or when injecting medication into joints or other sensitive areas. They can also be used for certain types of biopsies or for accessing certain body cavities.
The use of blunt needles can help reduce the risk of injury or trauma to tissues, nerves, or blood vessels, which may be more likely with a sharp-pointed needle. Additionally, they can be beneficial in situations where precise control over the depth and angle of needle insertion is important.
Description of a Blunt hypo-Needle
Unlike a traditional hypodermic needle, which has a sharp, pointed tip designed for puncturing skin and tissues, a blunt hypodermic needle has a rounded or flattened tip. This design is intended to reduce the risk of accidental needlesticks and minimize tissue damage during insertion.
Blunt cannulas are typically made from materials like stainless steel or medical-grade plastics. The choice of material may depend on factors like compatibility with the substances being used and specific procedural requirements.

How Blunt Needles Are Use
Blunt needles, also known as non-sharp or dull needles, have a variety of applications across different fields. Here are some common uses:
- Medical Training: Blunt needles are often used in medical training scenarios to simulate the process of giving injections or drawing blood without actually puncturing the skin.
- Animal Handling: Veterinarians and animal handlers may use blunt needles to administer medications to animals or to draw blood for testing.
- Cannula Insertion: Blunt needles can be used to guide the placement of a cannula (a flexible tube) into a vein or artery. Once the cannula is in place, it can be replaced with a sharper needle or catheter.
- Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems: Blunt needles can be used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems for tasks such as filling or topping off fluids, and to reduce the risk of injury when working with high-pressure systems.
- Liquid Dispensing: Blunt needles can be used for precision dispensing of liquids in laboratory settings, such as in chemistry or biology experiments.
- Intramuscular Injections (IM): In some cases, especially for sensitive patients, a blunt needle may be used to administer intramuscular injections.
- Tattooing: Blunt needles can be used in tattooing to push ink into the skin without causing excessive trauma.
- Industrial Applications: Blunt needles are used in various industrial settings for tasks like precision lubrication, adhesive application, and injecting fluids into tight spaces.
- Cosmetic Procedures: Blunt needles can be used in cosmetic procedures, such as dermal fillers, where a more controlled and less invasive approach is needed.
- Laboratory Research: Blunt needles are used in laboratories for tasks like sample collection, liquid handling, and other procedures that require precision and control.
- Art and Craft: Blunt needles can be used in various art and craft projects that involve sewing or working with fabric, leather, or other materials.
- Automotive and Aerospace Industries: Blunt needles are used for tasks like applying lubricants, sealants, and adhesives in tight or delicate areas.
Remember that the use of blunt needles should always be performed by trained professionals to ensure safety and effectiveness. It’s important to note that even though blunt needles are less sharp, they can still cause injury if not used properly or if excessive force is applied.
7 Types of Blunts Hypo-Needle
A blunt hypodermic needle is a type of needle that has a rounded tip, as opposed to a sharp, pointed tip like a regular hypodermic needle. Blunt needles are often used for procedures where a sharp needle might cause tissue damage or where precision isn’t as critical. Here are some common types of blunt hypodermic needles:
- Blunt Fill Needle (BFN): These needles are designed for drawing up medication from vials or ampoules. They have a blunt tip to reduce the risk of needlestick injuries.
- Blunt Cannula Needle: This type of needle is used for atraumatic procedures, such as injecting fluids into fragile or sensitive tissues. They are often used in cosmetic procedures, like dermal fillers.
- Blunt Dispensing Needle: These needles are used for precision dispensing of fluids or adhesive materials. They are commonly used in industries like electronics, automotive, and manufacturing.
- Blunt Filter Needle: These needles are designed for drawing medication through a filter, removing any particles or contaminants before administration.
- Blunt Safety Needle: These needles are equipped with a safety mechanism to protect healthcare workers from accidental needlestick injuries after use.
- Blunt Angled Needle: These needles have a sharp angle at the end and are used for procedures where a precise angle of entry is required, but a sharp, pointed tip is not suitable.
- Blunt Micro Cannula: Similar to the blunt cannula needle, these are used in procedures where precise placement is important but tissue damage needs to be minimized.
Remember that the choice of needle type should always be made by a trained healthcare professional based on the specific requirements of the procedure. Additionally, regulations and available types of needles may vary by region and medical institution. Always follow proper safety procedures and disposal protocols when using any type of needle.
Safety Features of Blunt Hypo-Needle
Here are some safety features of blunt hypodermic needles:
- Reduced Risk of Puncture Injuries: Blunt needles have a rounded tip, which makes them less likely to puncture blood vessels, nerves, or other vital structures beneath the skin. This reduces the risk of accidental injuries during procedures.
- Precise Placement: Blunt needles can be more easily controlled and positioned during procedures, which can lead to more accurate and precise injections or insertions.
- Minimized Tissue Trauma: The rounded tip of a blunt needle is designed to push through tissue rather than cut it. This can result in less tissue trauma and a potentially quicker recovery for the patient.
- Decreased Bruising and Swelling: Because blunt needles are less likely to cause trauma to the surrounding tissue, patients may experience less bruising and swelling after a procedure.
- Improved Comfort for Patients: The use of a blunt needle can lead to a more comfortable experience for the patient, as it is generally less painful than a sharp needle.
- Reduced Risk of Contamination: Blunt needles are typically single-use, which can reduce the risk of contamination or infection associated with reused needles.
- Versatility in Medical Procedures: Blunt needles are used in a variety of medical procedures, including liposuction, dermal fillers, fat transfers, and certain injections. Their versatility makes them a valuable tool for healthcare professionals.
- Compliance with Regulations: The use of blunt needles may be required or recommended by regulatory agencies or professional organizations to enhance patient safety and reduce the risk of accidental injuries.
While blunt needles have several safety benefits, it’s important to note that they are not suitable for all medical procedures. Healthcare professionals must assess each case individually and choose the appropriate needle based on the specific requirements of the procedure.
Additionally, even with blunt needles, proper medical training, technique, and hygiene practices are crucial to ensure patient safety and minimize the risks associated with any medical procedure. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for specific advice and recommendations regarding medical procedures and equipment.
Regular Hypodermic Needle
A regular hypodermic needle is a medical device used for injecting fluids (such as medications or vaccines) or withdrawing fluids (such as blood) from the body. It consists of a hollow, cylindrical tube with a sharp, pointed tip, which is attached to a syringe. The syringe is used to draw in or expel fluids through the needle.
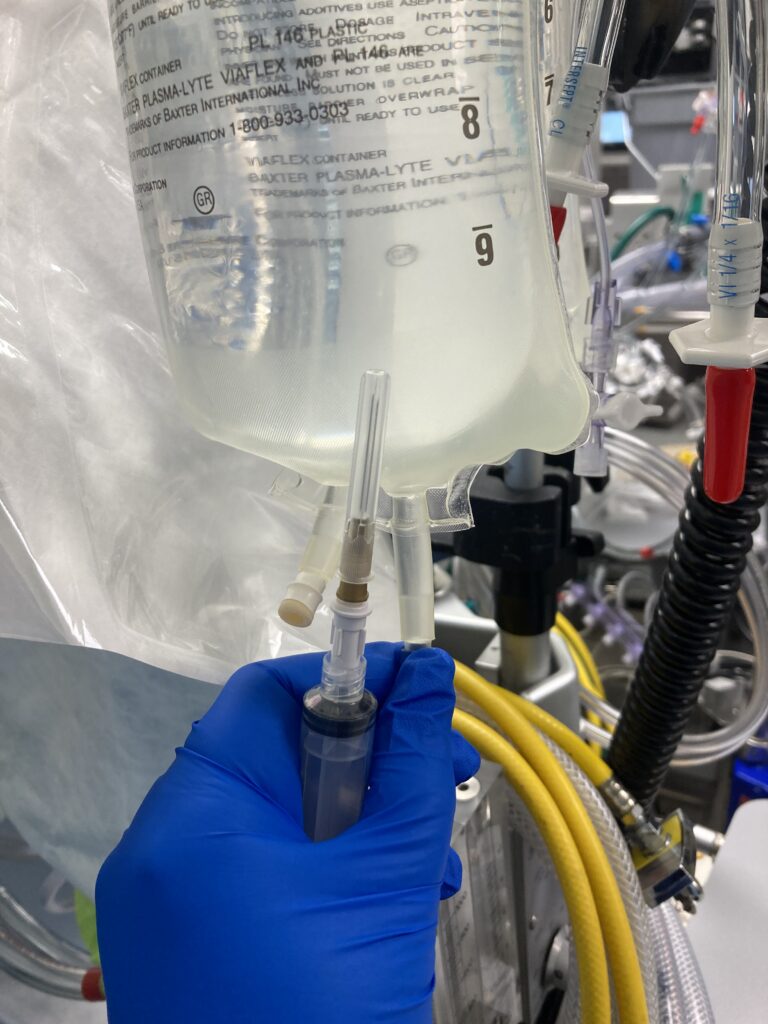
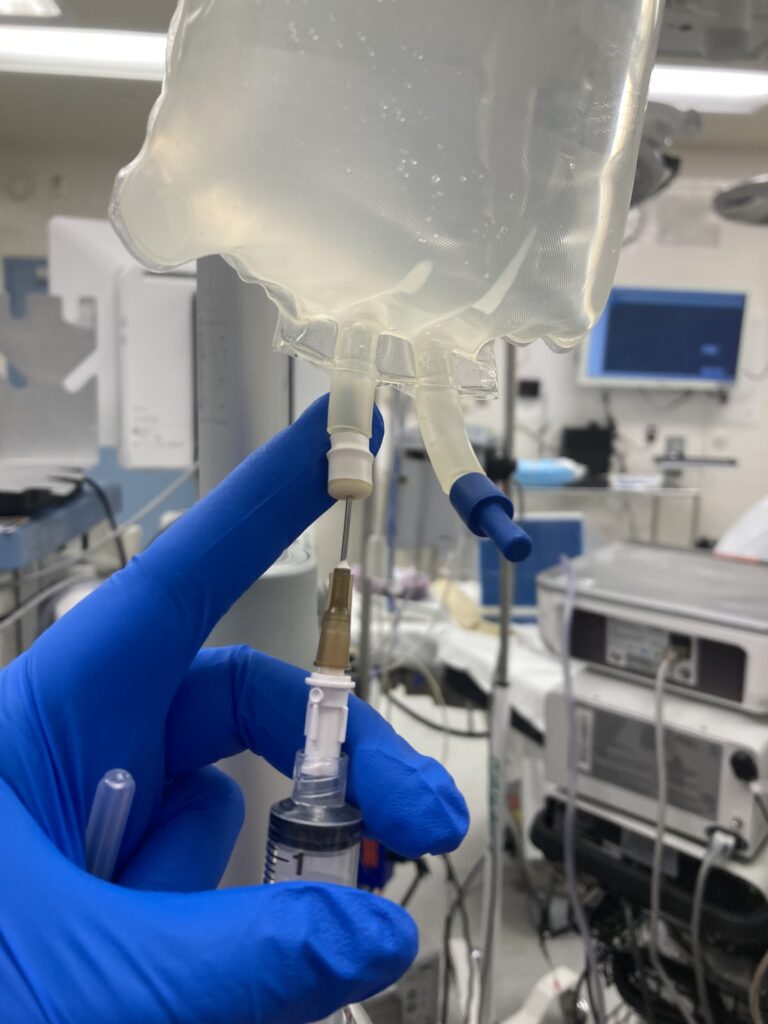
Hypodermic needles come in various sizes, with different gauges (diameters) and lengths. The gauge of a needle refers to its thickness, where a lower gauge number indicates a thicker needle. For example, a 25-gauge needle is thinner than a 21-gauge needle.
The length of a hypodermic needle can also vary, with shorter needles typically used for intradermal or subcutaneous injections, and longer needles used for intramuscular or deep tissue injections.
Description of Regular Hypodermic Needle
It consists of a thin, hollow metal tube with a sharp, beveled tip at one end and a hub at the other end. The hub is designed to securely attach to a syringe, allowing for the controlled administration or withdrawal of fluids.
The beveled tip of the needle is designed to easily penetrate the skin and underlying tissues with minimal discomfort. It is typically made of stainless steel or other metals that are sharp and durable. The outer surface of the needle is smooth to facilitate smooth insertion and reduce tissue damage.
Hypodermic needles come in various sizes, with different gauges (thickness) and lengths, depending on the specific medical application. The gauge refers to the thickness of the needle, and it is typically denoted by a number. A lower gauge number indicates a thicker needle, while a higher gauge number indicates a thinner needle.
For example, a 22-gauge needle is thicker than a 25-gauge needle. Needle lengths can also vary, ranging from very short for specific procedures to longer needles for deeper injections

How Regular Hypodermic Needle are best Use
Regular hypodermic needles have a wide range of medical and non-medical applications. Here are some common uses:
- Administering Medications: This is the most well-known use of hypodermic needles. They are used to inject various types of medications, such as vaccines, antibiotics, pain relievers, insulin, and many others.
- Drawing Blood: Hypodermic needles are used to draw blood for diagnostic tests, blood donations, or medical procedures like transfusions.
- Intravenous (IV) Therapy: Needles are used to establish an intravenous access point for administering fluids, medications, or blood products directly into the bloodstream.
- Subcutaneous Injections: These injections are administered just below the skin’s surface. Common examples include insulin injections for diabetes management.
- Intramuscular Injections: These are injections administered directly into a muscle. They are often used for certain types of medications, such as vaccines or certain antibiotics.
- Aspiration of Fluids or Tissue Samples: Hypodermic needles can be used to withdraw fluid or obtain tissue samples for diagnostic purposes, such as in biopsies or aspiration of joint fluids.
- Dental Procedures: Dentists use needles for local anesthesia before procedures like fillings, extractions, or root canals.
- Cosmetic Procedures: In the field of aesthetics, needles are used for procedures like Botox injections, dermal fillers, and various types of facial injections.
- Veterinary Medicine: Hypodermic needles are used in veterinary practices for similar purposes as in human medicine, including administering medications and drawing blood.
- Research and Laboratory Work: Hypodermic needles are used in laboratories for various applications, including precision fluid handling, cell and tissue culture, and for injecting substances into lab animals.
- Tattooing and Body Piercing: In the tattoo and piercing industry, needles are used to deposit ink or insert jewelry into the skin.
- Industrial Applications: Hypodermic needles can be used in industrial settings for tasks like precision dispensing of fluids or for collecting samples from inaccessible areas.
- Horticulture: In gardening and horticulture, hypodermic needles can be used for grafting and other delicate plant procedures.
- DIY Projects and Crafts: In some crafting hobbies, especially in intricate tasks like model-making or jewelry crafting, needles can be used as precision tools.
It’s important to note that the use of hypodermic needles should be done by trained professionals to ensure safety and minimize the risk of complications. Needle disposal is also crucial to prevent the spread of infections or injuries due to improper handling. Always follow appropriate safety protocols and disposal guidelines when using hypodermic needles.
Types Of Regular Hypo-Needle


- Standard Hypodermic Needle:
- These are the most common type of hypodermic needles used for a wide range of medical procedures, such as injections and blood draws. They come in various sizes, with different gauge (thickness) and length options.
- Safety Needle:
- Safety needles are designed with features to minimize the risk of accidental needlestick injuries. They often have a retractable or protective mechanism that covers the needle after use.
- Insulin Needle:
- Insulin needles are specifically designed for administering insulin to people with diabetes. They are very fine gauge needles, typically around 29 to 31 gauge, to minimize discomfort.
- Intradermal Needle:
- These needles are short and thin and are used for intradermal injections, where a small amount of medication is injected just under the skin.
- Subcutaneous Needle:
- Subcutaneous needles are longer than intradermal needles and are used to administer medications into the fatty tissue just beneath the skin.
- Intramuscular Needle:
- Intramuscular needles are longer and thicker than subcutaneous needles, designed to reach the muscle tissue. They are commonly used for vaccinations and certain medications.
- Spinal Needle:
- Spinal needles are used for procedures like spinal taps or epidurals. They have a very sharp, beveled tip for precise insertion into the spinal canal.
- Butterfly Needle:
- Also known as winged infusion sets, butterfly needles have a set of “wings” on the sides that allow for better control and stabilization during venipuncture (drawing blood from veins).
- Cannula Needle:
- Cannula needles have a flexible, thin tube attached to the needle, allowing for the administration of fluids or medications directly into a vein or artery.
- Huber Needle:
- Huber needles are specifically designed for accessing implanted ports or central venous catheters.
Essential Safety Features of Regular Hypodermic Needle

Here is a list of some essential safety features of a regular hypodermic needle:
- Needle Cap/Sheath: A protective cover that covers the sharp tip of the needle when it is not in use.
- Retractable Needle: A mechanism that allows the needle to retract into the syringe after use, reducing the risk of accidental needlestick injuries.
- Needle Shield: A protective shield that covers the needle after use, preventing contact with the sharp tip.
- Single-Use Design: Some needles are designed for one-time use only, making it more difficult to accidentally reuse them.
- Tamper-Evident Packaging: Packaging that indicates whether the needle has been previously opened or tampered with.
- Anti-Needlestick Features: These may include additional safety mechanisms or engineering controls to minimize the risk of needlestick injuries.
- Color Coding: Some needles may be color-coded to help healthcare professionals quickly identify the gauge and type of the needle.
- Needle Gauge Indicator: Markings on the needle indicating its size (gauge) for proper selection and use.
- Luer Lock or Luer Slip Connection: These are standardized fittings that ensure a secure and leak-proof connection between the needle and the syringe.
- Sterile Packaging: Needles are typically packaged in sterile containers to maintain their sterility until use.
- Clear Graduations: Clear markings on the syringe barrel for accurate measurement of medication doses.
- Needle Point Type: Different needle tips (e.g., beveled, blunt, etc.) may be used for specific purposes.
Remember that proper training and adherence to safe injection practices are essential to ensure the safe use of hypodermic needles. Additionally, appropriate disposal procedures for used needles are crucial to prevent accidental injuries and potential transmission of infections.
The regular hypodermic needle is the standard needle used in medical procedures for administering medications or drawing fluids from the body. It has a sharp, pointed tip designed to puncture the skin and underlying tissues with precision.
The blunt hypodermic needle, on the other hand, features a rounded tip, reducing the risk of accidental needlestick injuries and tissue damage. It is commonly used in situations where precision is less critical.
The filtered hypodermic needle includes a built-in filter to ensure that the injected substance is free from contaminants that could potentially harm the patient. This type is used when it is crucial to maintain a sterile environment during medication administration. Each type of needle serves specific purposes in medical practice, and their selection depends on factors such as the intended procedure and patient condition.
.
Resources
https://professionals.wrha.mb.ca/old/professionals/immunization/files/FilterNeedles.pdf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypodermic_needle
https://www.terumotmp.com/products/hypodermics/terumo-hypodermic-syringes-with-needle.html
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfPCD/classification.cfm?RegulationNumber