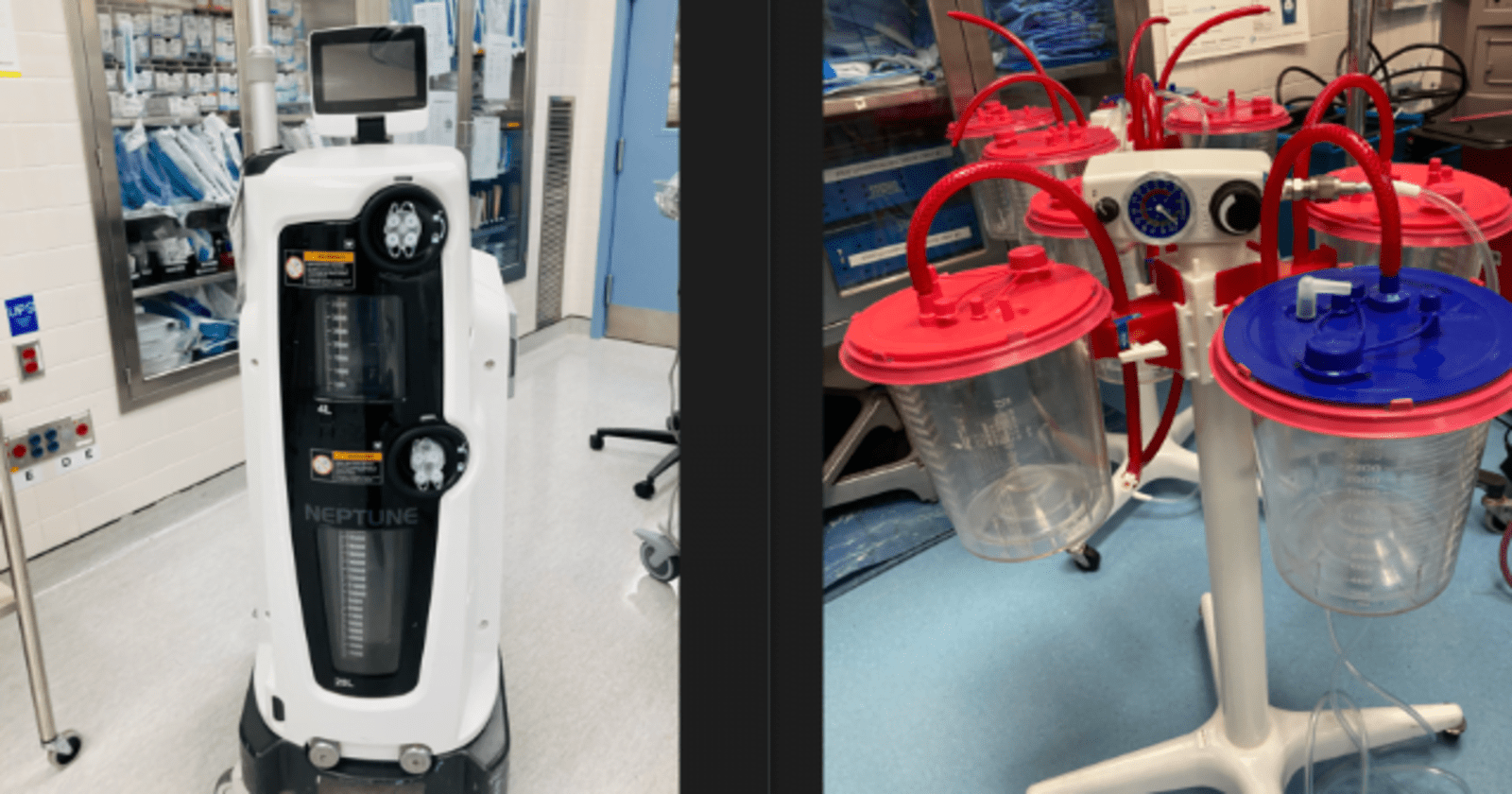
Neptune 3 is a negative pressure suction waste management system use in the operating room and clinical settings, designed to securely handle surgical waste fluids. By collecting, transporting, and disposing of these fluids, it enhances safety for medical staff and optimizes operational efficiency within the operating room.
A medical suction is a negative pressure suction that operate from a vacuum pump or suction generator that creates negative pressure. This system use in all health care setting in emergency situations, surgical procedures, and various clinical interventions. It ensures the prompt removal of bodily fluids, maintaining airways and preventing complications.
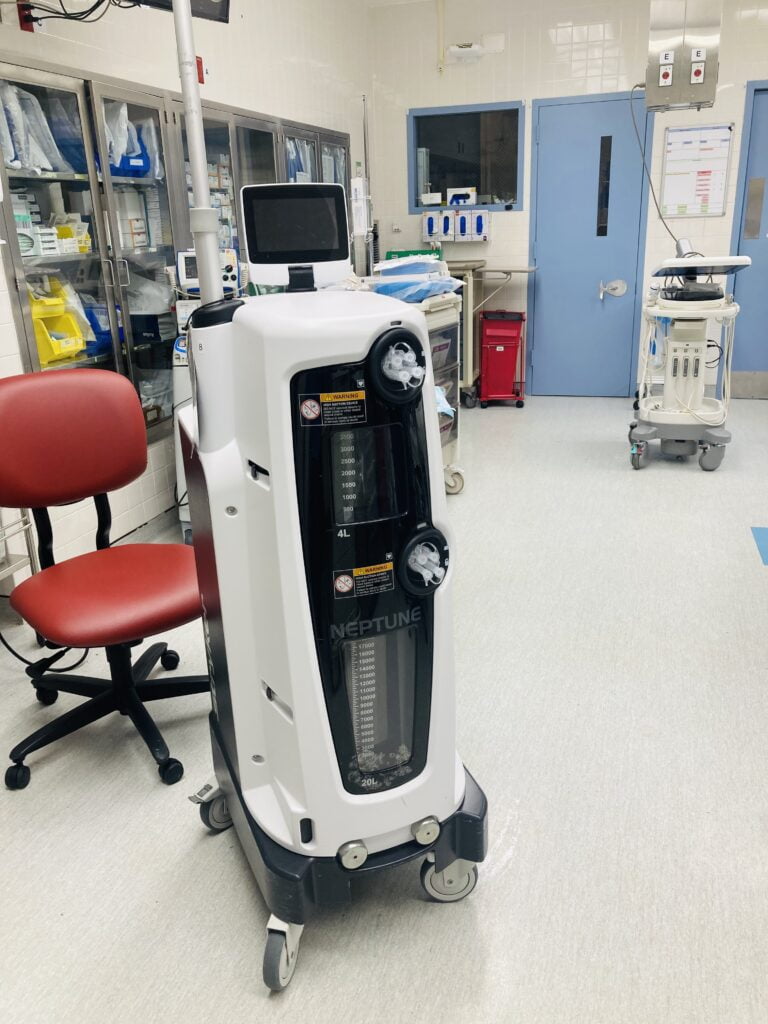

On the other hand, The Neptune 3 Waste Management System, featuring the E-SEP Smoke Evacuation Pencil and Floor Fluid Disposables, serves as a comprehensive defense against potential operating room risks. From maintaining the cleanliness of the operating room floor to ensuring the purity of the air you inhale, it provides a multi-faceted safeguard. Additionally, its ability to securely contain surgical fluid and smoke is equally advantageous for the well-being of your patient.
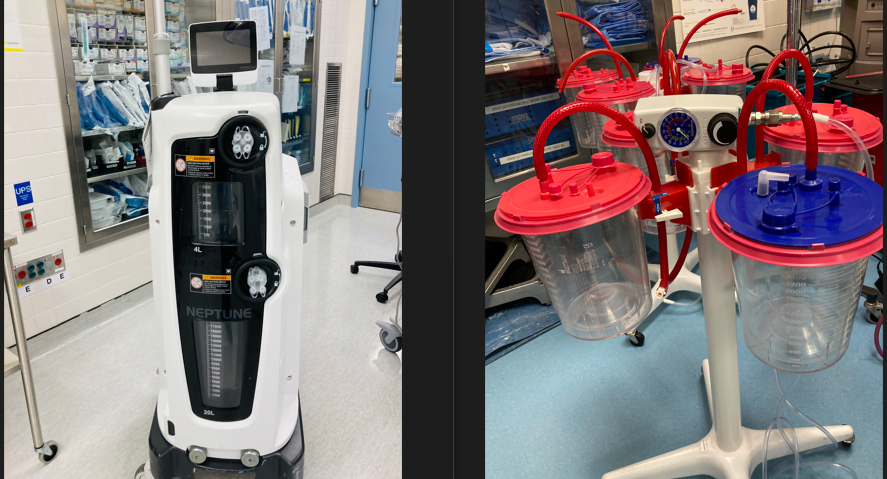

Neptune waste management system vs regular medical vacuum suction.These tools are essential for fluid management during surgeries and other medical procedures, helping healthcare professionals maintain a sterile and efficient workspace.
Types of Neptune waste management Suctions
The Neptune waste management system, used in medical settings, includes several models designed for different levels of use and requirements. Here are some of the primary types of Neptune waste management suction systems:
- Neptune 2 Waste Management System:
- This model is designed for comprehensive fluid waste management in the OR and other critical areas. It features smoke evacuation capabilities, a large fluid collection capacity, and the ability to handle various surgical fluid waste scenarios.
2. Neptune 3 Waste Management System:The Neptune 3 is an advanced version with enhanced features like an integrated suction and smoke evacuation system, touchscreen interface, and improved mobility. It is designed for easier use and better user interface compared to earlier models.
3. Neptune 2 Rover:
- This is a more mobile and compact version of the Neptune 2 system, specifically designed for facilities that require flexibility and ease of movement. It maintains the key features of the Neptune 2 but in a more portable format.
4. Neptune 3 Rover:
- Similar to the Neptune 2 Rover, this model offers mobility and flexibility but with the advanced features of the Neptune 3 system, including improved data management and user-friendly controls.
5. Neptune E-SEP Smoke Evacuator:
- This system focuses on surgical smoke evacuation, designed to remove smoke, aerosols, and odors generated during surgical procedures. It can work in conjunction with other Neptune systems or as a standalone unit.
6. Neptune S: The Neptune S offers an 8-liter fluid capacity while boasting a 30% smaller footprint compared to the Neptune 3, making it an ideal choice for medical environments where space is at a premium.

Despite its more compact size, the Neptune S doesn’t compromise on functionality; it includes an integrated specimen collection system, allowing for efficient and secure handling of surgical specimens. This model is designed to deliver the same high-performance waste management capabilities as larger systems, but with enhanced mobility and ease of use, making it particularly well-suited for smaller operating rooms or facilities with limited space.
What is the Neptune 3
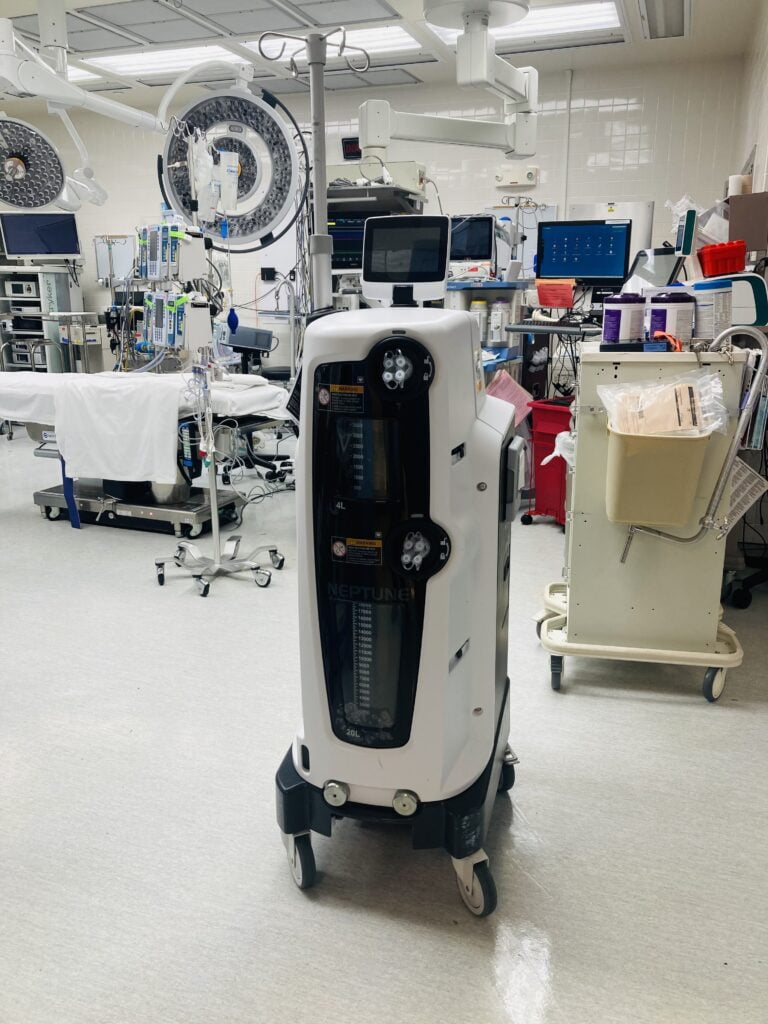
The Neptune 3 Waste Management Suction is an essential medical electrical device utilized in the operating room to efficiently suction and contain surgical fluids, smoke, as well as airborne pathogens.
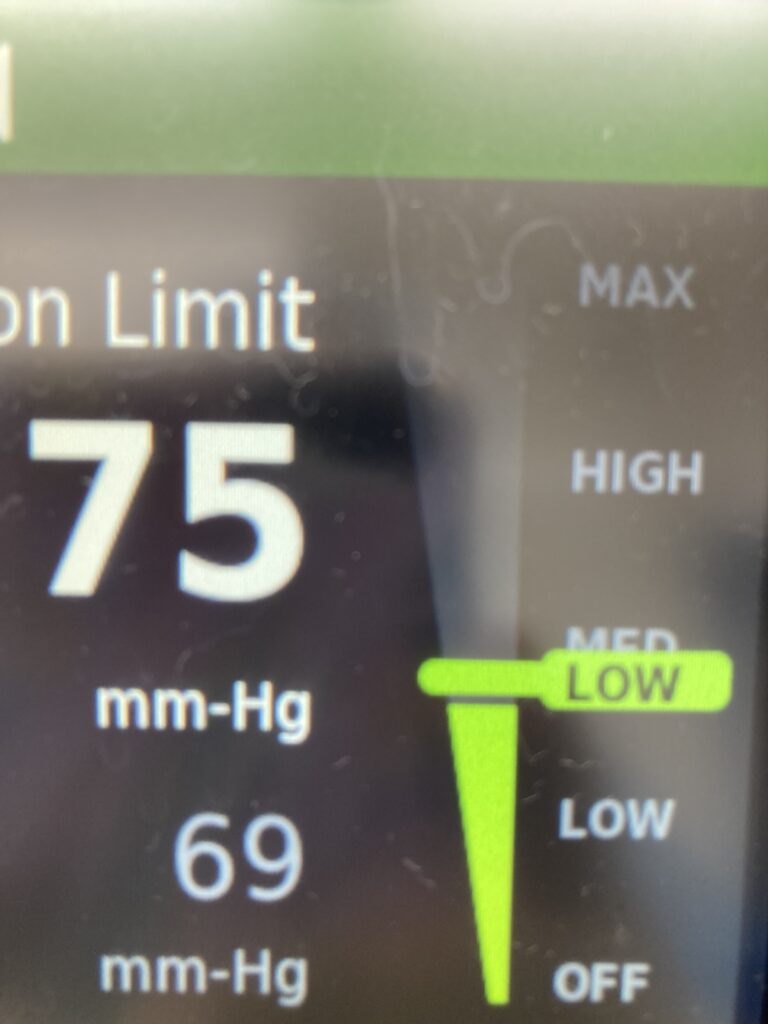
- The Neptune Waste Management Suction features numerous suction range indicators coupled with prominent audio alerts for high suction levels.
- It incorporates an integrated smoke evacuator.
- The Seal Shut Technology ensures the secure containment of suctioned biohazards.
The Neptune 3 stands out as the sole waste management system in the market that maintains a continuous closed-loop operation. This unique feature enables the ongoing containment of surgical fluids, smoke, and airborne pathogens. Additionally, the Neptune 3 comes equipped with an integrated system of HEPA and ULPA filters, setting a new standard for filtration capabilities.
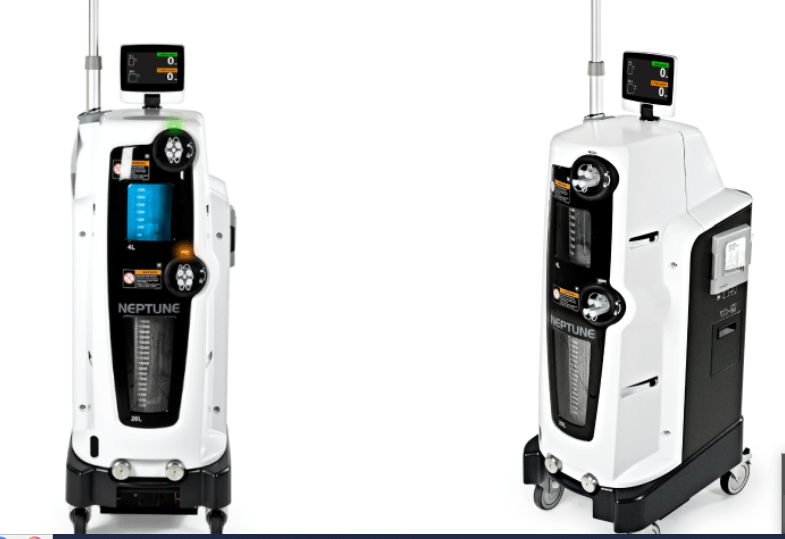

Neptune 3 suction front and side view
For years, healthcare professionals have acknowledged the inherent risk of exposure to dangerous contaminants and pathogens in their line of duty.
Two decades ago, an operating room nurse revolutionized this landscape by creating the inaugural iteration of the Neptune 3. This groundbreaking invention established a higher standard of care, ensuring secure suction and the effective containment of surgical fluids.
Stryker received FDA clearance 12/30/2013.Five years of research and development went into the Neptune 3 System, a multi-tasking device that places focus where it belongs: on safety and efficiency.
How does the Neptune suction waste Management works
- Vacuum Source: Medical suction devices typically have a vacuum pump or suction generator that creates negative pressure.
- Suction Catheter or Tube: A suction catheter or tube is inserted into the area where the suction is needed. This could be the mouth, nose, throat, airway, or a surgical site.
- Application of Negative Pressure: When the vacuum source is activated, negative pressure is applied through the suction catheter or tube.
- Fluid Removal: The negative pressure created by the vacuum source causes fluids, such as blood, saliva, mucus, or other secretions, to be drawn into the catheter or tube.
- Collection Container: The fluids are then collected in a container attached to the suction device, preventing them from re-entering the body.
- Regulation and Monitoring: Medical professionals regulate and monitor the suction process to ensure it is effective without causing harm to the patient.

Functions of the Neptune
- The I.V Pole -this pole can extend up and down for different purposes ,for example when we are doing a cystoscopy or ureteroscopy this pole serve as our hanging device for irrigation fluids and can hold 4 bags of fluids at a time. It helps allow gravity of the fluid to take its course as pole is extended higher. Over the years it has improve the way we do percutaneous nephrolithotomy. The up and down can be control by a touch screen situated on the Neptune 3 itself.
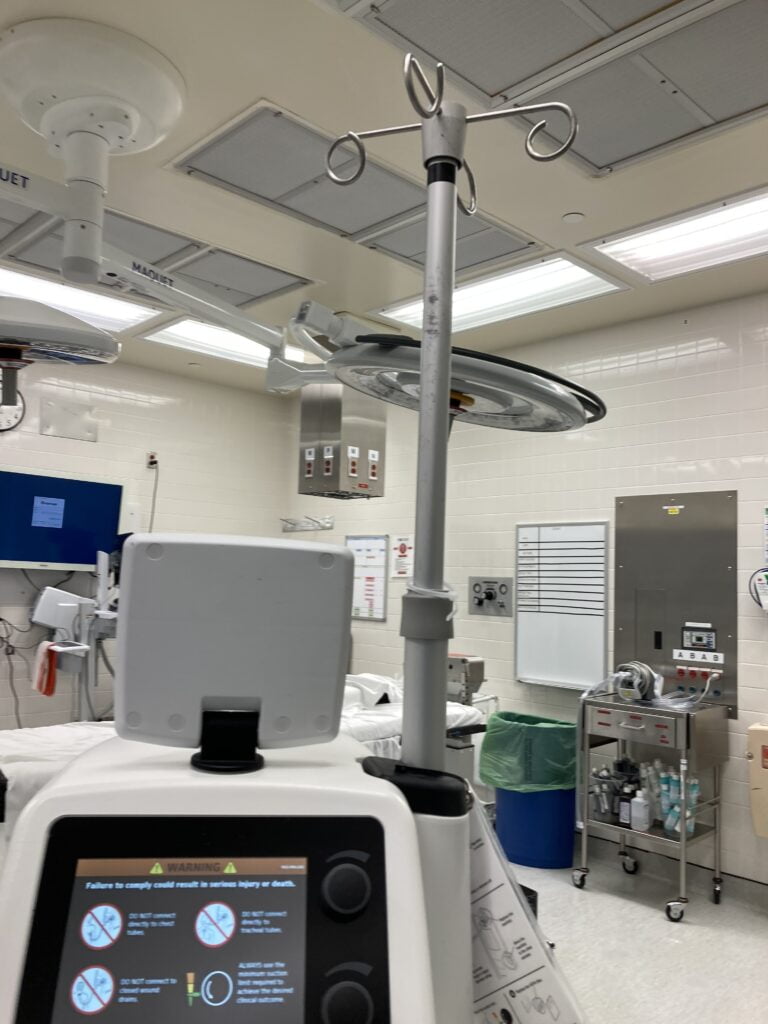

Neptune I.V pole and touch screen display
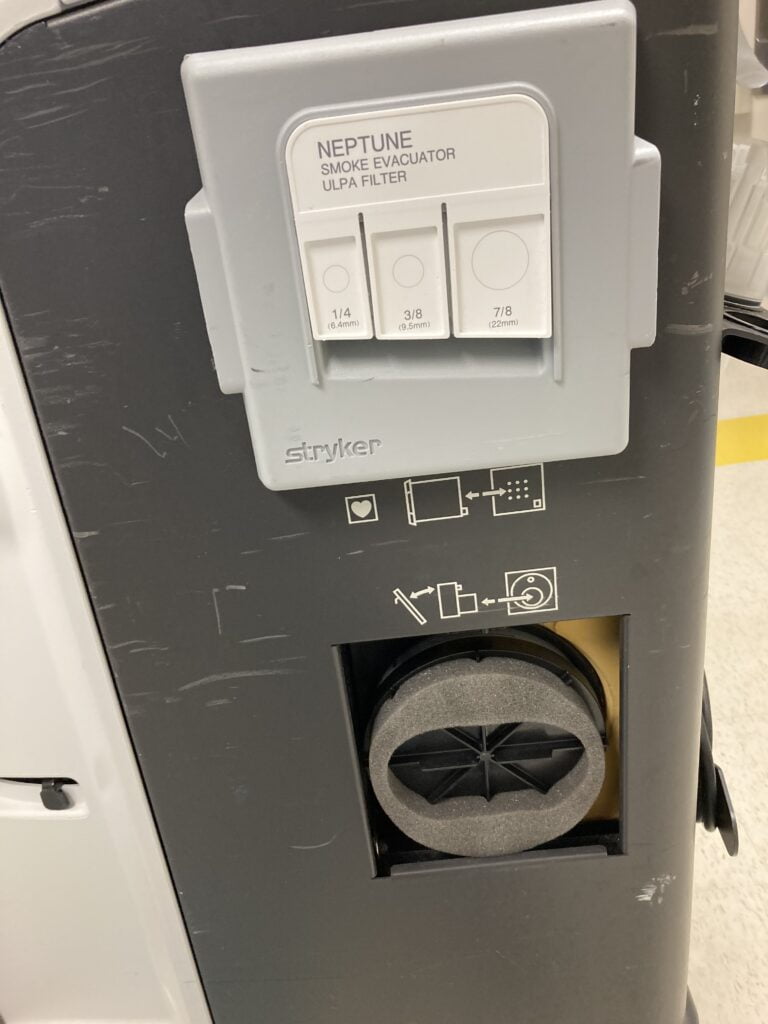
2. Smoke evacuation suction- this helps evacuate smoke during surgery when surgeon is cauterizing .we would hook the cautery pencil smoke evacuation hose to the Neptune this come with 3 sizes.

Neptune smoke evacuator display of the 3 different sizes
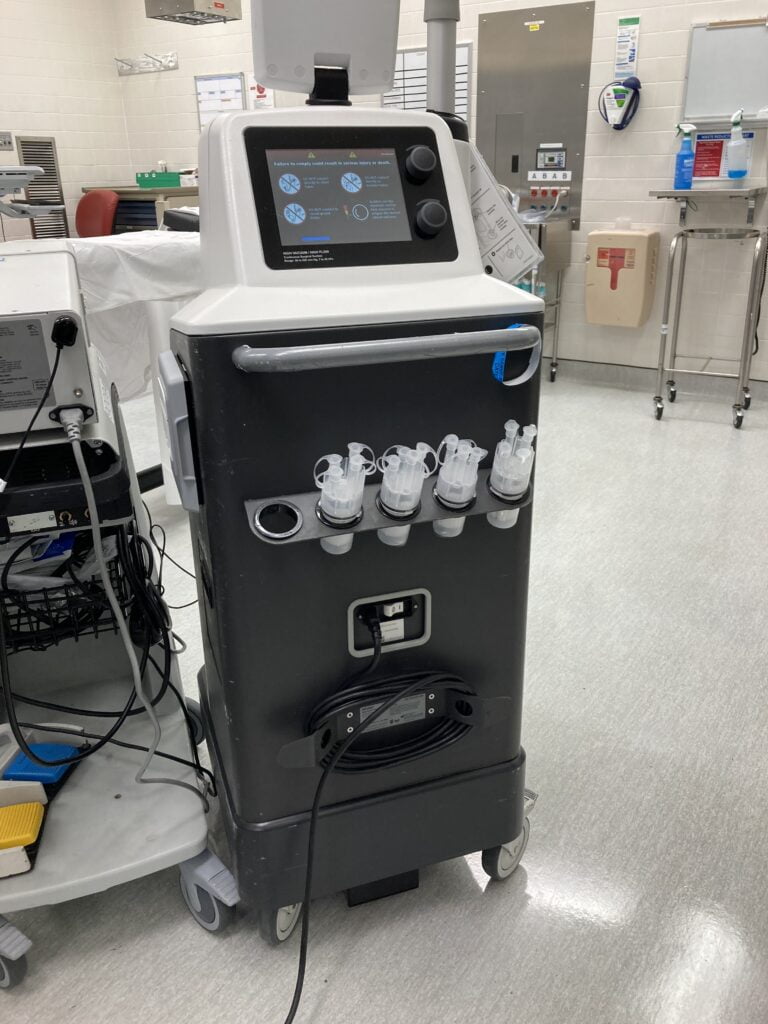
3. TWO COLLECTION CANISTER -The Neptune have 2 fluid Connection Canister
- TOP COLLECTION CANISTER-this is the smaller of both, it is at the top section of the Neptune and holds 4L of fluids 4000mls.It can empty into the second canister.
- BOTTOM COLLECTION CANISTER-This is the bigger collection canister and is at the lower section of the Neptune, it can hold 20L of fluids 20,000mls.

Neptune top collection canister
top of Neptune

top and bottom Neptune canister
4. SUCTION FILTERS– Neptune comes with suction filters that is attached to suction hose during surgery, each filter has 4 hole allowing multiple suctions to be used at the same time ,at least 8 suction can be used at the same time without interruption to function. they trap and filter out particle entering the canisters and can sometimes get clog with bone particles ,tissue and clot

Neptune suction Filters

Neptune filter goes In front

extra filter can be stored at back of Neptune
5. TOUCH SCREEN CONTROL-After plugging in Neptune waste management system to electric the on button at the back is switch on and then then touch screen control panel automatically appears.it has a menu and all the functions you need to apply is there.
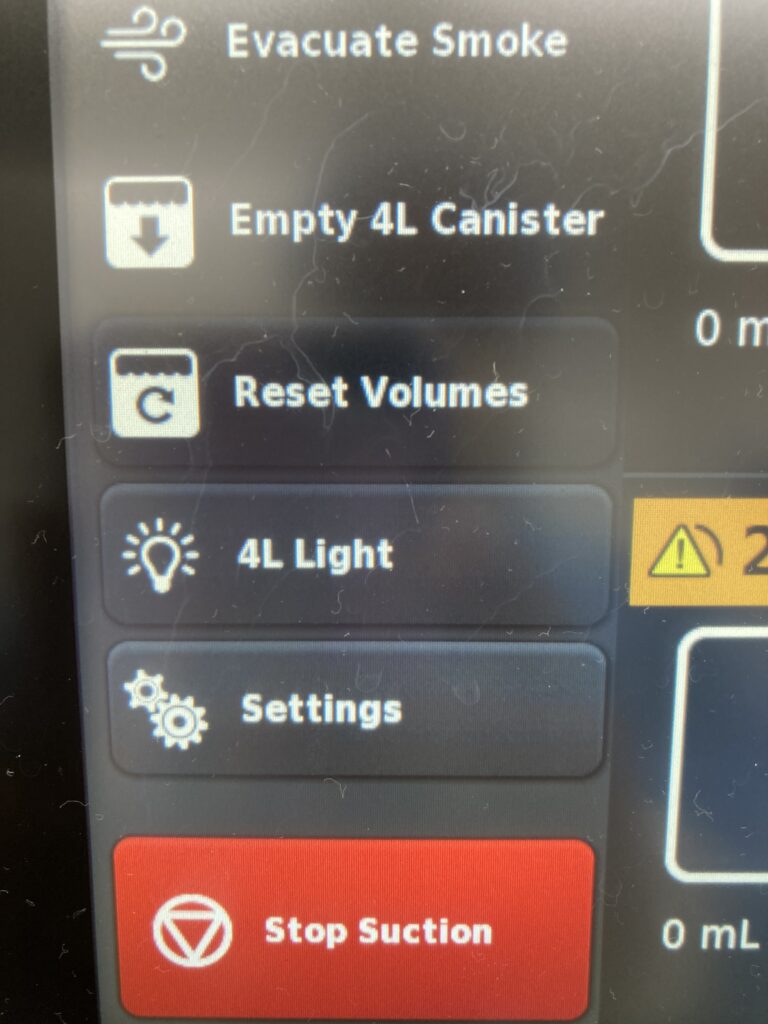

Control Panel of the Neptune
6. WHEELS-Neptune comes on wheels that has a brake system on them. It can move very easily from on place to another .
7. RESET VOLUMES -the Neptune has a reset volume tab on the screen that can reset the volume from last procedure to zero ,so you don’t have to empty the canister to start another procedure this save time between turn over in the operating room.

8. HEPA FILTER and ULPA filters: Waste management systems often deal with hazardous materials or substances that may pose health risks if released into the atmosphere. HEPA and ULPA filters can help contain these materials by capturing particles and preventing their release.

By filtering out particles and contaminants, these filters help protect sensitive equipment and machinery within the waste management system from damage or malfunction. Additionally, they contribute to maintaining a safer working environment for personnel by reducing their exposure to harmful substances.

Care and Cleaning of the Neptune.
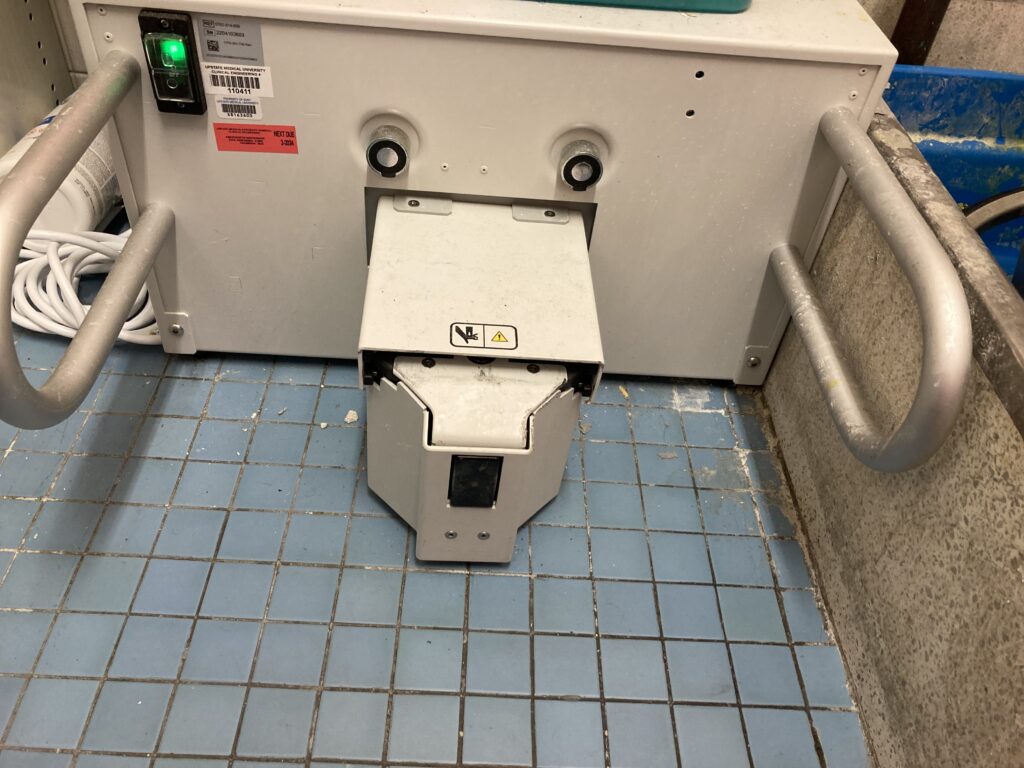
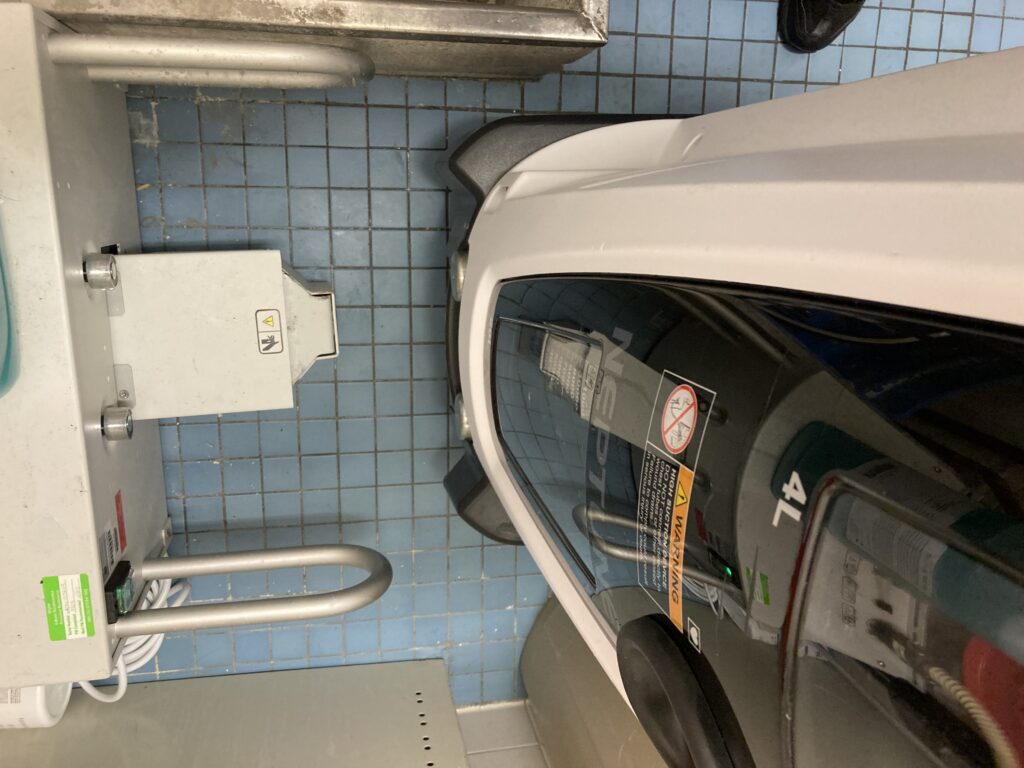


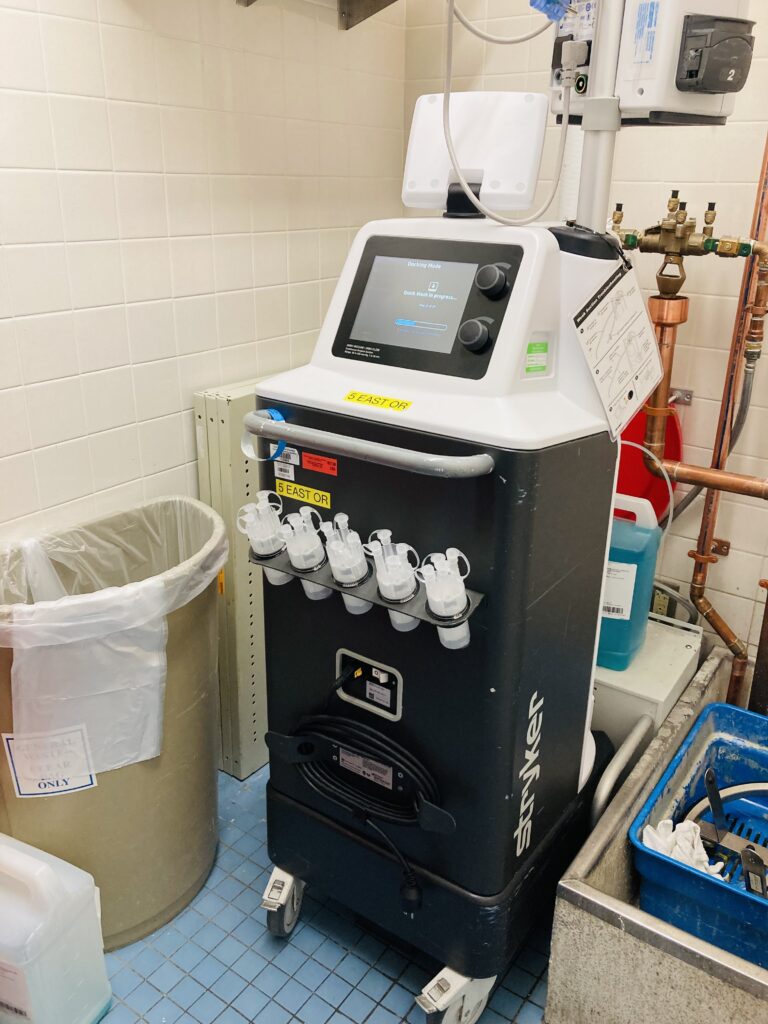
The Neptune waste management System has a very unique way of cleaning and care. In order for hospital to care for and clean the system, multiple docking station were erected in operating room and department. The Neptune waste management system has the ability to quick wash and extended wash.
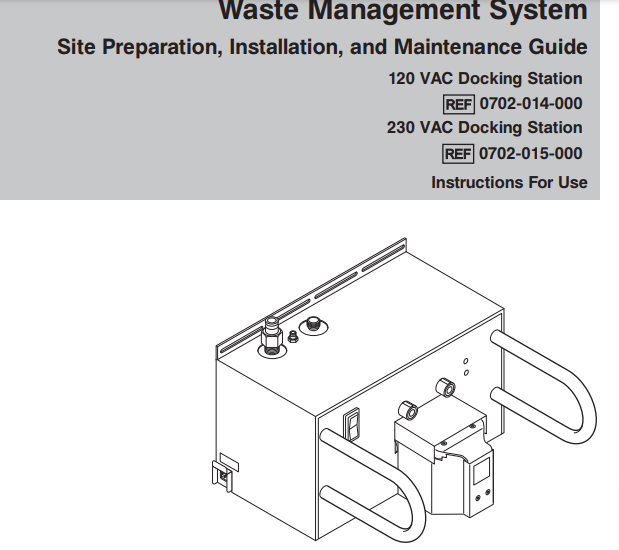
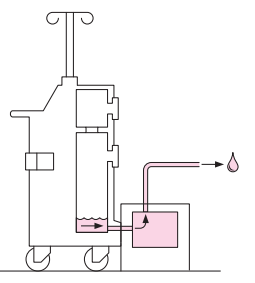
illustration of the Neptune docking station.

Health care worker docking the Neptune after use. This docking station will empty and do wash cycle on the Neptune before it can be release from the dock. Ready to be Release will be display on screen to let you know wash cycle is complete and Neptune is ready to be use again.


Disadvantages of the Neptune
- The use of strong suction for a chest tube can be highly detrimental and is not recommended.
- not recommended for use in suction of airway.
- Not Recommended for neonatal suctioning.
- Suction is very strong and can cause damages to tissue if intensity is to high, use as recommended by Manufacturer.
- Dependence on Electrical Power: Most medical vacuum suction systems rely on electricity. In the event of a power outage or malfunction, it may not be available, potentially compromising patient care.
- Noise and Vibration: The operation of a medical vacuum suction system can produce noticeable levels of noise and vibration, potentially causing discomfort for both patients and healthcare providers.

What is a Medical Vacuum Suction
Medical vacuum suction, often referred to as suction or suctioning, is a crucial medical procedure used to remove unwanted fluids, secretions, or foreign materials from a patient’s body, primarily in surgical and clinical settings. This is achieved by creating a controlled vacuum or negative pressure environment that facilitates the extraction of fluids or other substances through specialized suctioning equipment.
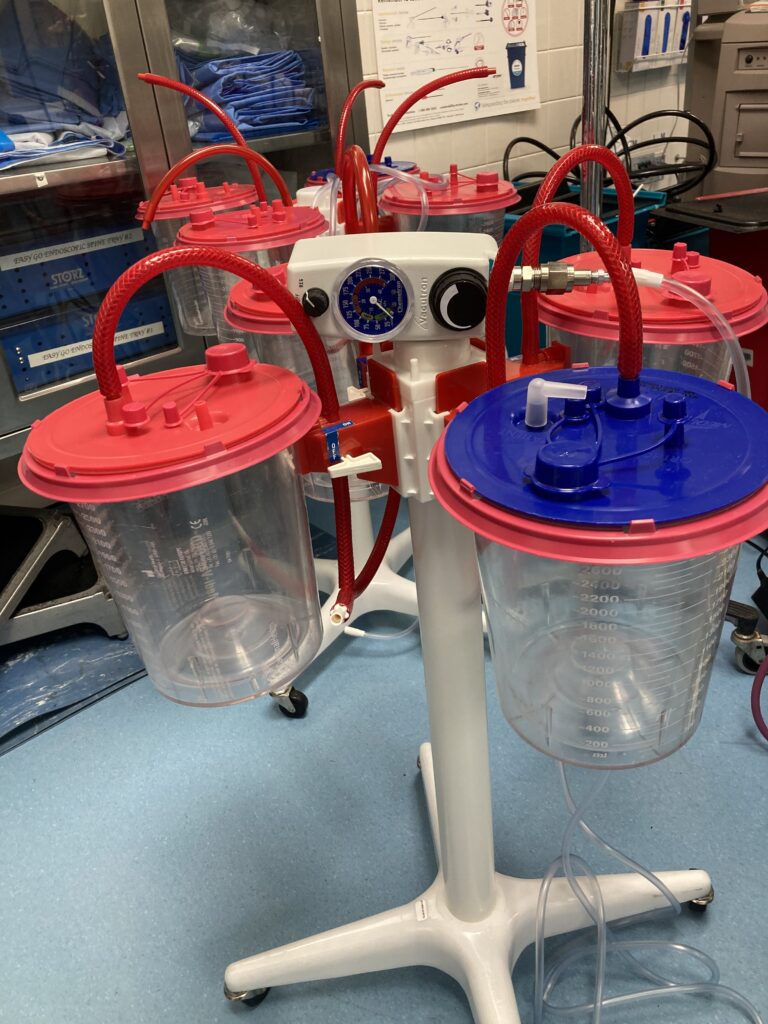

Regular Medical suction.
Medical vacuum suction is commonly employed in various healthcare scenarios:
1. Surgical Procedures: During surgery, suction is used to remove blood, bodily fluids, and other materials from the surgical site, providing a clear field of view for the surgical team.
2. Respiratory Care: It is utilized to clear mucus, saliva, or other secretions from the airways of patients who have difficulty coughing or clearing their own airways, such as those under anesthesia or with certain medical conditions.
3. Emergency Care: Suction devices are essential in emergency situations to clear the airway of an unconscious or choking individual.
4. Wound Care: In wound management, suction can be used to remove excess fluids, debris, or exudate from wounds to facilitate healing.
5. Dental Procedures: In dentistry, suction devices are commonly used to remove saliva, water, and debris from the patient’s mouth during procedures.
6. Neonatal Care: In neonatal intensive care units (NICUs), specialized suction devices are used to clear the airways of premature or ill infants.
7. Gastrointestinal Procedures: Suction is utilized in endoscopy and other gastrointestinal procedures to remove excess fluids, secretions, or debris, providing a clear view of the digestive tract.
8. Labor and Delivery: Suction may be used during childbirth to clear the baby’s airway of mucus and amniotic fluid if necessary.
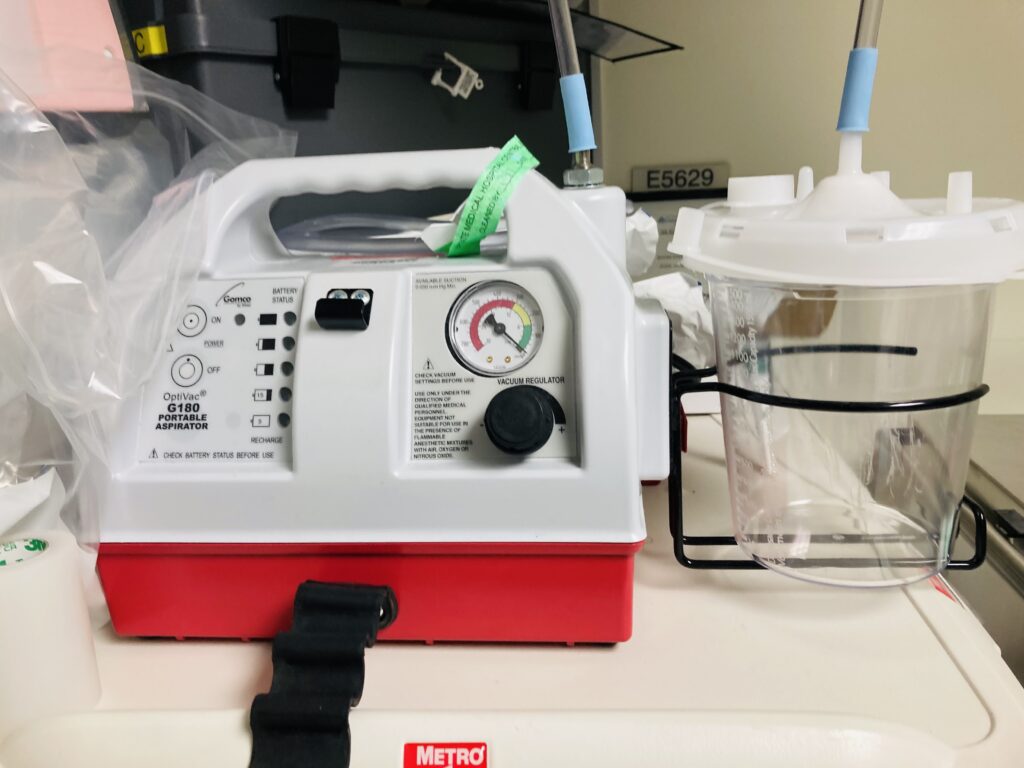

Emergency cart mobile suction an OptiVac G180 Portable Aspirator. This machine is used for medical suction, essential in various healthcare settings to remove bodily fluids like mucus, blood, or other secretions from a patient’s airway or surgical site. The device features a clear plastic collection canister on the right, connected to the main unit with tubing. The control panel on the front of the device includes a vacuum regulator knob, a gauge for monitoring pressure, and status indicators. This portable aspirator is likely used in both emergency and routine medical procedures, where quick and efficient suction is necessary.
Medical vacuum systems are designed to maintain a specific level of negative pressure and are equipped with various attachments and settings to accommodate different types of procedures and patient needs.
These systems are an integral part of healthcare facilities and play a crucial role in maintaining a clean and sterile environment during medical procedures.
Some limitations of medical suction
- Risk of Contamination: If not properly maintained, the system can become a source of infection. Contaminated suction systems can potentially introduce pathogens into patients.
- Noise and Vibration: Operating a medical vacuum suction system can generate noise and vibration, which may be uncomfortable for patients and healthcare providers.
- Limited Mobility: Some suction units are stationary and need to be plugged into a wall outlet. This limits their use in situations where mobility is required, such as during patient transfers.
- Size and Portability: While there are portable suction units available, they may not be as powerful as stationary units and may require more frequent emptying of the collection canister.

5. Collection Canister Capacity: The capacity of the collection canister is finite, and if not monitored and emptied regularly, it can lead to a loss of suction effectiveness.
6. Potential for Tissue Damage: If not used correctly or if excessive suction pressure is applied, it can lead to tissue trauma, particularly in delicate or sensitive areas.
7. Risk of Airway Complications: In certain cases, particularly with aggressive suctioning, there’s a potential risk of inducing airway complications, such as bronchospasm or hypoxia.
8. Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements: Like any medical equipment, vacuum suction systems require regular maintenance, including cleaning and sterilization to prevent contamination and ensure optimal performance.
9. Cost: Depending on the type and brand, medical vacuum suction units can be expensive to purchase and maintain. This cost can be a limiting factor for smaller healthcare facilities.
10. Regulatory Compliance: Healthcare providers need to ensure that their suction systems comply with local and international regulatory standards, which may require additional resources and documentation.
11. Adaptability to Different Fluids: Some suction systems may be designed for specific types of fluids or materials, which can limit their versatility in certain clinical scenarios.
12. Training and Familiarity: Proper training is essential for healthcare providers to use the system effectively and safely. In emergencies, having personnel who are unfamiliar with the equipment can lead to delays or errors.
Healthcare providers need to be aware of these limitations and take appropriate measures to mitigate them. Regular
Comparing Neptune to Medical Suction

| NEPTUNE | MEDICAL SUCTION |
| 1. Very strong suction high-level suction is employed in situations where amore powerful suction force is necessary, such as during surgery. | 1. Low-level suction is typically used for sensitive areas or situations where gentle suction is required. |
| 2. No medical spill all fluids is securely contained | 2. Prone to medical spill and accidents when removing covers to clean |
| 3. Electrically powered | 3. Vacuumed powered |
| 4. Smoke evacuator. | 4. No smoke evacuator. |
| 5. Digital fluid and suction display along with a fluid reset button | 5. None |
| 6.Holds more volume of fluids than regular suction | 6. Hold limited amounts of fluids |
| 7. Powered IV pole | 7. No IV pole |
| 8. Noise | 8. less noisy |
| 9. Save space and time during surgery | 9. Takes time to manually clean and set up |
| 10. Easy to move from one place to another due to its wheels | 10. Carry disposable canister refill |
| 11. Lighted canister | 11. Canister have no light. |
| 12. Higher cost than regular suction. | 12. Lower cost. |
| 13. Dose not need emptying after every procedure, has a volume reset feature. | 13. Need canisters empty after every procedure ,dose not have a volume reset feature. |
How dose medical suction work
- Vacuum Source: Medical suction devices typically have a vacuum pump or suction generator that creates negative pressure.
- Suction Catheter or Tube: A suction catheter or tube is inserted into the area where the suction is needed. This could be the mouth, nose, throat, airway, or a surgical site.
- Application of Negative Pressure: When the vacuum source is activated, negative pressure is applied through the suction catheter or tube.
- Fluid Removal: The negative pressure created by the vacuum source causes fluids, such as blood, saliva, mucus, or other secretions, to be drawn into the catheter or tube.
- Collection Container: The fluids are then collected in a container attached to the suction device, preventing them from re-entering the body.
- Regulation and Monitoring: Medical professionals regulate and monitor the suction process to ensure it is effective without causing harm to the patient.
Benefits and drawbacks of th neptune vs the regular medical suction in an emergency setting.
Neptune System
Benefits:
- Closed-Loop System: The Neptune system is a closed-loop waste management system, reducing the risk of exposure to bodily fluids and contaminants, which is crucial in maintaining sterility and reducing infection risks.
- High Suction Capacity: It typically offers a powerful suction capability, making it effective for quickly removing large volumes of fluid or debris.
- Waste Management: The system includes integrated waste collection and storage, simplifying the disposal process and reducing the need for handling potentially hazardous materials.
- Portability: Some Neptune models are mobile, allowing for easy transportation and use in various locations within a healthcare facility.
Drawbacks:
- Complexity: The system is more complex to set up and operate compared to regular suction devices, which could be a disadvantage in urgent situations where time is critical.
- Cost: Neptune systems are generally more expensive, both in terms of initial investment and ongoing maintenance, making them less accessible in some settings.
- Size: While some models are mobile, they are still bulkier compared to traditional suction devices, potentially limiting maneuverability in crowded or constrained spaces.
Regular Medical Suction
Benefits:
- Simplicity: Regular suction devices are straightforward to use, with minimal setup required, which is advantageous in emergency situations where quick action is needed.
- Portability: These devices are typically more compact and lightweight, making them easy to move around and position as needed.
- Cost-Effective: Regular suction units are less expensive than systems like Neptune, making them more widely available and easier to maintain.
- Versatility: These devices can be used in a wide range of settings, from pre-hospital environments to various areas within a healthcare facility.
Drawbacks:
- Open System: Regular suction systems are open, meaning there is a higher risk of exposure to bodily fluids and potential contamination, which can increase the risk of infection.
- Limited Waste Management: These devices generally require manual handling and disposal of collected fluids, which can be cumbersome and expose healthcare workers to risks.
- Lower Suction Capacity: Regular suction units may not be as powerful as the Neptune system, which could be a limitation when dealing with large volumes of fluid or thick debris.
The Neptune system offers advantages in terms of safety, suction power, and waste management, but it comes with higher costs, complexity, and reduced portability. Regular medical suction devices are simpler, more affordable, and easier to use in varied settings, but they carry higher risks of contamination and may have lower suction capacity. The choice between the two depends on the specific needs and constraints of the emergency situation.
How much dose a Neptune suction hold vs a regular suction
The capacity of the Neptune system versus a regular suction device varies significantly, reflecting their different designs and intended uses.
Neptune System:
- Capacity: The Neptune system typically has a much larger capacity for fluid collection, often holding up to 20 liters (approximately 5 gallons) of waste in its canister. Some models might have even higher capacities depending on the specific version and configuration.
- Multiple Canisters: The Neptune system can often be configured with multiple canisters, further increasing its total capacity. The top canister holds an additional 4 liters of fluids.
Regular Medical Suction:
- Capacity: Regular suction devices usually have a much smaller capacity, typically ranging from 500 milliliters (0.5 liters) to 2 liters (0.5 to 0.53 gallons) per canister. These canisters are often disposable and need to be replaced or emptied more frequently.
- Portability Considerations: The smaller size and capacity of regular suction canisters make them more portable but less suited for managing large volumes of fluid over extended procedures or multiple patients without frequent interruptions to empty the canister.
In summary, the Neptune system can hold significantly more fluid than a regular suction device, making it more suitable for extended or high-volume situations where large amounts of waste are generated.
Here are some things you should never hook the Neptune system to:
1. Nasogastric (NG) tube:
You should not hook a Neptune suction system directly to a nasogastric (NG) tube. The Neptune system is primarily designed for high-volume, continuous suction in surgical and procedural settings, where it collects and measures fluid waste. NG tubes, on the other hand, are used for lower-volume gastric decompression, feeding, or medication administration.
Using a Neptune system with an NG tube could create excessive suction pressure, potentially causing damage to the stomach lining, mucosa, or even the NG tube itself. NG tubes typically require low, intermittent suction, which is different from the high, continuous suction provided by the Neptune system.
For NG tubes, it’s safer and more appropriate to use a suction regulator designed specifically for gastric decompression, which allows for adjustable and controlled suction levels that are safe for the stomach and esophagus.
2. Intravenous (IV) Lines:
The Neptune system is designed for suction and fluid management, not for delivering fluids. Connecting it to an IV line would be highly inappropriate and dangerous.
3. Patient Airways Directly:
The Neptune system is not designed to be directly connected to a patient’s airway (e.g., tracheostomy tube or endotracheal tube). Suctioning airways should be done using equipment specifically designed for that purpose.
4. Chest tube
Chest tubes typically require controlled, low-pressure suction (usually around -20 cm H₂O). The Neptune system’s suction is very powerful and should not be use on chest tubes.
5. Pressurized Gas Lines:
Never connect the Neptune system to pressurized gas lines like oxygen or medical air. This could cause the system to malfunction or create dangerous pressure buildups.
6. Drainage Systems or Plumbing:
It should not be connected to any plumbing or drainage systems not intended for medical waste. Doing so could cause contamination or blockages.
7. Non-Medical Equipment:
Never connect the Neptune system to any non-medical equipment, as it could cause contamination, equipment damage, or safety risks.
8. Reusable Suction Canisters (Non-Disposable):
The Neptune system uses proprietary, sealed canisters for waste collection. Attaching non-approved, reusable canisters could compromise the system’s functionality and safety.
9. Electrical Outlets:
The Neptune system is an electrical device itself, but it should never be connected or hooked into electrical outlets in any way other than its designed power source. Never use unauthorized power adapters or attempt to modify its electrical connections.
Resources
https://www.safeor.com/products/neptune
https://fda.report/PMN/K153407
https://www.stryker.com/us/en/surgical-technologies/products/neptune-waste-management-system.html
Work experience and training in using this equipment correctly.