A clean air filter is a device designed to remove contaminants and impurities from the air in your home, ensuring the air you breathe is clean and healthy. It can be made of various materials such as fiberglass, pleated paper, or synthetic fibers.
It is comprised of a frame that holds the filter media in place. Typically made of cardboard or metal. A gasket that ensures a tight seal within the air filtration system to prevent air bypass and a filter Media The material that traps particles.
| Health Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Respiratory Health | Reduces allergens like dust and pollen, improving air quality and breathing. |
| Better Sleep Quality | Minimizes irritants, promoting more restful sleep. |
| Strengthened Immune System | Reduces contaminants, supporting overall immune health. |
| Lower Risk of Illness | More efficient at capturing bacteria, viruses, and mold spores. |
| Improved Cardiovascular Health | Reduces particulate matter, benefiting heart health. |
| Increased Energy Levels | Cleaner air leads to less fatigue and better oxygen intake. |
| Elimination of Indoor Odors | Removes unpleasant odors, enhancing comfort. |
| Long-Term Health Benefits | Reduces the risk of chronic diseases related to poor air quality. |
| Protection from External Pollutants | Acts as a barrier against outdoor pollution. |
| Mental Health Benefits | Improves cognitive function, reduces stress and anxiety. |
Using an air filter cleaner in your home can greatly enhance the effectiveness of your air filtration system, leading to several health benefits. Here are the top health benefits:

1. Enhanced Respiratory Health
- Reduction of Allergens: An air filter cleaner helps maintain the efficiency of air filters in trapping dust, pollen, pet dander, and other allergens, reducing respiratory issues such as asthma and allergies.
- Improved Air Quality: Regular cleaning of air filters ensures they function optimally, providing cleaner air for easier breathing.
2. Better Sleep Quality
- Minimized Irritants: Clean air filters reduce the presence of irritants like dust and pet dander, contributing to a more restful sleep environment.
- Fresher Environment: Clean filters help maintain a fresh air environment, promoting better sleep.
3. Strengthened Immune System
- Reduced Contaminants: Keeping air filters clean ensures they effectively remove pollutants and harmful particles, reducing the burden on your immune system.
- Healthier Indoor Air: Cleaner air supports overall immune health, helping the body resist illnesses more effectively.
4. Lower Risk of Illness
- Bacteria and Virus Capture: Clean air filters are more efficient at capturing bacteria and viruses, reducing the spread of airborne diseases.
- Mold Spore Reduction: Regularly cleaned filters prevent the spread of mold spores, which can cause health issues.
5. Improved Cardiovascular Health
- Reduced Particulate Matter: Clean air filters reduce fine particulate matter in the air, which can enter the bloodstream and affect cardiovascular health.
- Stress Reduction: Better air quality can lower stress levels, benefiting heart health.
6. Increased Energy Levels
- Reduced Exposure to Pollutants: Cleaner air means less exposure to pollutants, leading to increased energy levels and reduced fatigue.
- Better Oxygen Intake: Cleaner air improves oxygen intake, boosting overall energy and vitality.
7. Elimination of Indoor Odors
- Odor Removal: Clean air filters help remove unpleasant indoor odors, creating a more pleasant living environment.
- Fresher Air: Maintaining a fresh-smelling home enhances mental well-being and comfort.
8. Long-Term Health Benefits
- Prevention of Chronic Diseases: Prolonged exposure to clean air can reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases related to poor air quality, such as respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Improved Quality of Life: Overall, better air quality leads to a higher quality of life, with fewer health problems and increased well-being.
9. Protection from External Pollutants
- Barrier Against Outdoor Pollution: Clean air filters act as a barrier against outdoor pollutants, especially important in areas with high pollution levels.
- Seasonal Protection: During allergy seasons or high pollution periods, clean filters provide added protection for sensitive individuals.
10. Mental Health Benefits
- Enhanced Cognitive Function: Cleaner air can improve cognitive function and concentration, leading to a more productive living space.
- Reduced Stress and Anxiety: Better air quality contributes to lower stress and anxiety levels, promoting improved mental health.
7 ways in which air filters clean and improve indoor air quality
Clean air filters improve indoor air quality in several ways
- Removal of Particulate Matter: Clean air filters capture and remove dust, pollen, pet dander, and other airborne particles, preventing them from circulating in the air and being inhaled.
- Reduction of Allergens: By filtering out common allergens like mold spores and pollen, clean air filters help reduce allergy symptoms and improve respiratory health.
- Capture of Harmful Contaminants: Clean filters are effective at trapping bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms, which can reduce the spread of illnesses and improve overall health.
- Elimination of Odors: Air filters can also remove unpleasant odors caused by cooking, pets, or smoking, leading to a fresher indoor environment.
- Reduction of Chemical Pollutants: Some air filters, especially those with activated carbon, can absorb volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other harmful chemicals, improving air quality and reducing health risks.
- Prevention of Airflow Obstruction: Clean filters maintain proper airflow in HVAC systems, ensuring efficient operation and consistent air exchange, which contributes to better ventilation and air quality.
- Enhanced Performance of HVAC Systems: Regularly cleaned or replaced filters help HVAC systems operate efficiently, reducing energy consumption and maintaining effective air filtration throughout the home.
How Clean Air Filters Can Improve Respiratory Health
Clean air filters can significantly improve respiratory health by reducing airborne contaminants and providing cleaner air to breathe. Here’s how they help with asthma, allergies, and respiratory infections:
1. Asthma and Allergies
Asthma:
- Reduction of Triggers: Air filters, especially HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters, can trap fine particles like dust, pollen, pet dander, and mold spores that can trigger asthma attacks. By removing these particles from the air, air filters help to reduce the frequency and severity of asthma symptoms.

- Improved Air Quality: Cleaner air can reduce irritation and inflammation in the airways, making it easier for asthma sufferers to breathe.
Allergies:
- Allergen Removal: Air filters can capture common allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander. This helps to reduce the overall allergen load in the environment, which can alleviate allergic reactions.
- Symptom Relief: By decreasing the number of allergens in the air, air filters can help to minimize symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and throat irritation.
2. Reduction of Respiratory Infections
- Removal of Bacteria and Viruses: Some air filters, particularly those with UV light or ionizing features, can help to inactivate or remove bacteria and viruses from the air. This can lower the risk of respiratory infections, especially in environments where people are in close proximity, such as homes, offices, or schools.
- Reduction of Airborne Pathogens: By continuously filtering the air, these devices can reduce the concentration of airborne pathogens, decreasing the likelihood of inhaling infectious particles.
- Support for Immune System: Cleaner air reduces the burden on the respiratory system and immune system, allowing the body to better fight off infections and maintain overall respiratory health.
Using clean air filters can provide significant benefits for those suffering from asthma and allergies by reducing exposure to triggers and allergens.
They also help in reducing the risk of respiratory infections by removing harmful pathogens from the air.
For optimal results, it’s important to choose the right type of air filter for your needs and ensure it is regularly maintained and replaced according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
The Role of Air Filters in Reducing Indoor Air Pollutants
Indoor air quality is a crucial aspect of health and wellness, as people spend a significant amount of time indoors. Air filters play a key role in reducing indoor air pollutants, which can include a wide range of substances.

Types of Pollutants Air Filters Remove
- Particulate Matter (PM):
- Dust and Dust Mites: Common in homes, particularly in bedding, upholstery, and carpets.
- Pollen: Seasonal outdoor allergens that can enter homes through windows and doors.
- Pet Dander: Tiny flecks of skin shed by cats, dogs, and other pets.
- Mold Spores: Airborne spores from mold that can grow in damp or humid areas of the home.
2. Chemical Pollutants:
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Emitted by household products like paints, cleaners, and building materials.
- Tobacco Smoke: Contains a mixture of harmful chemicals and particulate matter.
- Household Chemicals: Cleaning agents, pesticides, and other household products can release harmful chemicals into the air.
3. Biological Pollutants:
- Bacteria and Viruses: Can be present in indoor air and pose health risks, particularly in poorly ventilated spaces.
- Fungi: Besides mold spores, other fungal particles can be airborne.
4. Other Particles:
- Cooking Emissions: Particles released from cooking, especially from frying and grilling.
- Fibers: From clothing, carpets, and other textiles.
Effectiveness of Air Filters Against Common Indoor Allergens
- High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) Filters:
- Efficiency: HEPA filters are highly effective, capturing at least 99.97% of airborne particles that are 0.3 microns in diameter.
- Common Allergens: HEPA filters are particularly effective against dust, pollen, pet dander, and mold spores. They can also capture some bacteria and viruses, although their effectiveness against very small viruses may be limited.
- Activated Carbon Filters:
- Efficiency: These filters are excellent at removing gases and odors, including VOCs and smoke.
- Common Allergens: While not as effective as HEPA filters for particulate matter, they complement HEPA filters by removing gaseous pollutants and odors that HEPA filters cannot capture.
- UV-C Light Filters:
- Efficiency: These use ultraviolet light to kill bacteria and viruses, adding an extra layer of protection.
- Common Allergens: They are effective in reducing biological pollutants but do not remove particulate matter.
- Electrostatic Filters:
- Efficiency: These use static electricity to attract and trap particles.
- Common Allergens: They are moderately effective against dust and pet dander but less effective than HEPA filters.
Key Points what you need to know when choosing the right Air filter
- HEPA Filters: The gold standard for particulate removal, HEPA filters excel in capturing a wide range of indoor allergens, including dust, pollen, pet dander, and mold spores. Their fine mesh traps particles as small as 0.3 microns, making them indispensable for allergy sufferers.

- Combination Filters: Many air purifiers use a combination of HEPA and activated carbon filters to address both particulate and chemical pollutants. This dual approach ensures comprehensive indoor air purification, removing allergens and harmful gases.
- Maintenance and Replacement: The effectiveness of air filters depends on regular maintenance and timely replacement. Clogged or dirty filters can reduce air flow and filtration efficiency, negating the benefits of having an air filter.
- Room Size and Air Change Rate: The effectiveness of an air filter also depends on the size of the room and the air change rate. It’s essential to choose an air purifier appropriate for the size of the space to ensure optimal air quality improvement.
Air filters are highly effective in reducing indoor air pollutants, particularly common allergens like dust, pollen, pet dander, and mold spores. By choosing the right type of filter and maintaining it properly, you can significantly improve indoor air quality and reduce allergen exposure.
Comparing Different Types of Air Filters: Which is Best for Your Home
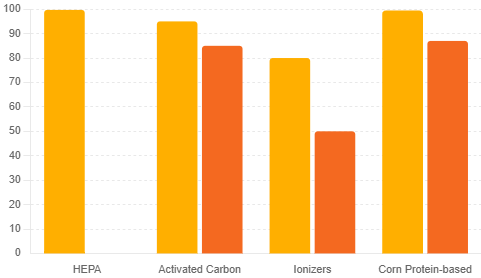
against particulate matter and formaldehyde pollution.
HEPA Filters
High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) Filters:
- Mechanism: Uses a dense mat of fibers to trap particles.
- Effectiveness: Capable of capturing 99.97% of particles that are 0.3 microns or larger, including dust, pollen, mold spores, and pet dander.
- Best For: Removing allergens and fine particles from the air.
- Pros: Highly effective at trapping airborne particles, including those that cause allergies and asthma.
- Cons: Doesn’t remove gases, odors, or volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Activated Carbon Filters

- Mechanism: Uses a bed of activated carbon to adsorb gases and odors.
- Effectiveness: Excellent at removing smoke, fumes, odors, and VOCs.
- Best For: Addressing chemical pollutants, smoke, and odors.
- Pros: Effective at trapping gases and odors that HEPA filters cannot.
- Cons: Needs to be replaced frequently, doesn’t capture particulates as efficiently as HEPA filters.
UV Filters
Ultraviolet (UV) Filters:
- Mechanism: Uses ultraviolet light to kill bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms.
- Effectiveness: Effective at sterilizing air by killing pathogens.
- Best For: Disinfecting air and killing microorganisms.
- Pros: Adds an additional layer of protection against biological contaminants.
- Cons: Ineffective against dust, allergens, and chemical pollutants; often used in combination with other types of filters.
Corn protein-base
Work by utilizing amino acid functional groups in the protein to trap particulate matter and toxic chemicals like formaldehyde.
As of now, these filters are not FDA approved. Research on corn protein-based air filters started in 2023 and is still on goin.
Comparing Effectiveness for Allergens
| Air Quality Concern | Best Filter Type |
|---|---|
| Allergen Removal | HEPA Filters: Captures 99.97% of particles ≥ 0.3 microns (dust, pollen, mold spores, pet dander) |
| Odor and Chemical Pollutant Removal | Activated Carbon Filters: Adsorbs gases, odors, smoke, and VOCs |
| Killing Microorganisms | UV Filters (in conjunction with HEPA or Activated Carbon): Sterilizes air by killing bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms |
For removing allergens, HEPA filters are the most effective. They are specifically designed to trap airborne particles that are common allergens, such as dust mites, pollen, pet dander, and mold spores.
While activated carbon filters are excellent for removing odors and chemical pollutants, they do not capture allergens effectively. UV filters can help reduce the number of airborne pathogens but do not remove allergens from the air.
How Often Should You Change Your Air Filters
Changing air filters regularly is crucial for maintaining good indoor air quality and ensuring the optimal performance of your air filtration system.
| Filter Type | Replacement Frequency |
|---|---|
| HEPA Filters | Residential: 6-12 months, High-Usage: 3-6 months |
| Activated Carbon Filters | Residential: 3-6 months, High-Usage: 2-3 months |
| UV Filters | Lamp: 12 months |
| Standard HVAC Filters | Low Usage: 90 days, Moderate: 60 days, High Usage: 20-45 days |
| Homes with Pets | 30-60 days |
| Allergy/Asthma Sufferers | 30-60 days |
| Homes with Smokers | 30-45 days |
Signs You Need to Change Your Air Filter
- Visible Dirt and Dust: If you can see a significant buildup of dust and debris on the filter, it’s time to change it.

2. Reduced Airflow: Noticeably reduced airflow from your HVAC system can indicate a clogged filter.
3. Increased Allergy Symptoms: If allergy symptoms or respiratory issues are worsening, it might be due to a dirty air filter.
4. Higher Energy Bills: A clogged filter makes your HVAC system work harder, leading to higher energy consumption.
5. Unpleasant Odors: Persistent musty or unpleasant odors in your home can be a sign of a dirty air filter.
6. Dust Accumulation: Excessive dust on surfaces in your home could indicate your air filter isn’t effectively trapping dust.
The Impact of Clean Air Filters on Sleep Quality
Can Clean Air Filters Improve Sleep Quality?
Yes, clean air filters can significantly improve sleep quality by reducing airborne pollutants and allergens, which can interfere with restful sleep.
How Do Air Filters Help Create a Healthier Sleep Environment?
- Reduction of Allergens:
- HEPA Filters: Capture allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold spores, reducing allergy symptoms that can disrupt sleep.
- Removal of Airborne Particles:
- Activated Carbon Filters: Eliminate odors, smoke, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can cause respiratory irritation and discomfort during sleep.
- Improvement of Respiratory Health:
- Clean air filters help reduce the presence of irritants that can cause coughing, sneezing, and other respiratory issues, leading to uninterrupted sleep.
- Reduction of Asthma Triggers:
- By removing common asthma triggers such as dust, smoke, and chemical pollutants, clean air filters can help prevent nighttime asthma attacks.
- Enhanced Overall Air Quality:
- Clean air contributes to a fresher, more pleasant sleeping environment, promoting relaxation and better sleep hygiene.
- Decrease in Indoor Pollutants:
- Reduces indoor pollutants that can lead to headaches, fatigue, and general discomfort, all of which can negatively impact sleep quality.
Clean air filters play a crucial role in creating a healthier sleep environment by reducing allergens, airborne particles, and other pollutants. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of air filters ensure optimal air quality, which is essential for achieving restful and uninterrupted sleep.
The Importance of Clean Air Filters for Children and the Elderly
Clean air filters are crucial for homes with children and elderly residents because they improve indoor air quality by removing allergens and harmful pollutants. This leads to better respiratory and cardiovascular health, supports immune function, and enhances overall well-being.
Cleaner air helps prevent respiratory infections, improves sleep quality, and supports cognitive development in children while maintaining cognitive function in the elderly. Overall, clean air filters create a healthier living environment for these vulnerable populations.
Children: Young lungs are still developing, and clean air is crucial to prevent respiratory issues and support healthy growth.
Elderly: Older adults often have weaker immune systems and pre-existing health conditions that can be exacerbated by poor air quality.
Children: Clean air filters help remove allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander, reducing the risk of asthma and allergies.
Elderly: Reduced allergens can prevent flare-ups of chronic respiratory conditions such as asthma and COPD.
Children: Exposure to pollutants like smoke, mold, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can affect cognitive development and overall health.

Elderly: Pollutants can aggravate heart and lung conditions, leading to severe health complications.
Common Myths and Misconceptions About Air Filters
- All Air Filters Are the Same
- Many believe that all air filters perform equally well, but there are significant differences in their efficiency and the size of particles they can trap. High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters, for example, are more effective than standard filters.
- More Expensive Filters Are Always Better
- Price doesn’t always correlate with performance. While some expensive filters offer superior filtration, others may not provide much benefit over cheaper alternatives. It’s essential to check the filter’s specifications rather than relying solely on price.
- You Only Need to Change Filters Once a Year
- The frequency of filter changes depends on various factors, including the type of filter, the air quality, and the environment. Some filters may need to be changed every three months, especially in homes with pets or allergy sufferers.
- Filters Only Need to Be Changed When They Look Dirty
- By the time a filter looks visibly dirty, it’s likely already clogged and not functioning optimally. Regular replacement based on the manufacturer’s recommendation ensures efficient operation.
- Higher MERV Ratings Are Always Better
- While filters with higher Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value (MERV) ratings capture more particles, they can also restrict airflow in some HVAC systems. It’s crucial to use a filter with a MERV rating suitable for your system to avoid reducing its efficiency.
- Air Filters Eliminate All Airborne Pollutants
- Air filters can significantly reduce airborne particles but are not 100% effective in eliminating all pollutants. Gaseous pollutants and some smaller particles might still pass through.
- Using an Air Filter Means You Don’t Need to Clean as Often
- Air filters can help reduce dust and allergens but won’t eliminate the need for regular cleaning. They are a complementary tool to maintain a cleaner home environment.
Ensuring Proper Use of Air Filters
- Choose the Right Filter
- Select a filter with a suitable MERV rating for your HVAC system. Consult the system’s manual or a professional to determine the appropriate filter.
- Regular Replacement
- Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for filter replacement. Set reminders to check and replace filters every three months or as recommended.
- Proper Installation
- Ensure the filter is installed correctly, with the airflow direction arrow pointing in the correct direction. An improperly installed filter can reduce its efficiency.
- Regular Maintenance
- Maintain your HVAC system regularly to ensure it’s working efficiently. Clean the ducts, coils, and other components as recommended.
- Monitor Air Quality
- If you notice an increase in dust or allergens, check the filter more frequently. High levels of pollutants may require more frequent filter changes.
- Use Additional Air Purification
- In areas with high levels of pollutants or allergens, consider using additional air purifiers or dehumidifiers to enhance air quality.
- Check for Air Leaks
- Ensure there are no leaks in the ducts or around the filter housing. Leaks can allow unfiltered air to bypass the filter.
By understanding these myths and following best practices, you can ensure your air filters are used effectively, contributing to better indoor air quality and a more efficient HVAC system.
Innovative Research on Biodegradable Air Filters Using Corn Protein
Recent research on corn protein-based air filters has shown promising results in improving air quality by capturing a wide range of pollutants. A team of researchers from Washington State University (WSU) has developed an innovative air filter using corn protein, which can capture 99.5% of small particulate matter and 87% of formaldehyde, outperforming traditional HEPA filters in chemical gas filtration (ScienceDaily) (WSU Insider).
The study, published in February 2023 in the journal Separation and Purification Technology, highlights the unique properties of corn protein, which contains functional groups of amino acids capable of trapping various toxic chemicals. This biodegradable and environmentally friendly filter material is seen as a significant advancement, potentially reducing reliance on petroleum-based products and minimizing secondary pollution from filter disposal (ScienceDaily) (WSU Insider).
Researchers, including Katie Zhong from WSU, emphasize the filter’s capability to handle both particulate and gaseous pollutants, which current commercial air purifiers struggle to address simultaneously.
This new technology could be particularly beneficial in areas with severe air pollution, contributing to better public health and environmental sustainability (WSU Insider).
Additionally, similar research at McMaster University has focused on developing compostable and breathable filtration materials for personal protective equipment (PPE) using corn protein. These efforts underline the potential for corn protein in creating effective and sustainable air filtration solutions (Faculty of Engineering).
As of now, these corn protein-based air filters are still in the research and development phase. They are not yet commercially available, and there is no specific mention of FDA approval. Further testing and development are necessary before these innovative filters can be widely adopted and commercialized. The ongoing research aims to refine the materials and explore their broader applications in air purification and PPE (ScienceDaily) (The Daily Chronicle) (Faculty of Engineering).
Common Questions About Air Filters People Ask with Simple Answers
- How do air filters work to improve indoor air quality?
- Air filters trap particles like dust, pollen, pet dander, and other airborne pollutants, preventing them from circulating through the indoor air.
- Are air filters necessary if I already have good ventilation?
- Yes, air filters complement good ventilation by removing particles that ventilation alone cannot capture.
- Can air filters help reduce pet dander and odors?
- Yes, certain air filters, especially those with activated carbon, can help reduce pet dander and odors.
- What are the best air filters for people with allergies?
- HEPA filters are highly recommended for people with allergies as they capture 99.97% of particles as small as 0.3 microns.
- How can I tell if my air filter needs to be replaced?
- Check the filter monthly and replace it when it appears dirty or according to the manufacturer’s recommendation, usually every 3 months.
- Do air filters remove viruses and bacteria from the air?
- HEPA filters can capture some viruses and bacteria, but not all. Additional purification methods may be needed for comprehensive protection.
- Are there any health risks associated with using air filters?
- Generally, air filters are safe. However, if not maintained properly, they can harbor mold or bacteria, potentially causing health issues.
- What is the difference between air purifiers and air filters?
- Air filters are components of HVAC systems that trap particles, while air purifiers are standalone devices that use filters and other technologies to clean the air.
- Can clean air filters help with mold problems in the home?
- Clean air filters can reduce mold spores in the air but won’t solve mold problems caused by moisture or leaks.
- How do I choose the right air filter for my specific needs?
- Consider the filter’s MERV rating, the specific pollutants you want to remove, and the compatibility with your HVAC system. For allergies, choose HEPA filters; for odors, choose filters with activated carbon.
Resources
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2023/02/230223132859.htm
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2023/02/230223132859.htm
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8449022









