Bariatric surgery tends to lead to more substantial weight loss compared to medications like Ozempic, especially in the long term. However, bariatric surgery also carries higher risks and may not be suitable for everyone, where as medications like Ozempic may be a more accessible option for some individuals.
Ozempic (Semaglutide) is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity. It works by mimicking the action of a hormone called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which helps regulate blood sugar levels and appetite. Clinical studies have shown that Ozempic can lead to significant weight loss in people with obesity.
Basic Differences between Ozempic vs Bariatric Surgery
| Ozempic (Semaglutide) | Bariatric Surgery |
|---|---|
| Medication-Injectable | Surgical Procedure |
| GLP-1 receptor agonist Regulates blood sugar and appetite by mimicking a hormone. | Physically alters digestive system |
| Moderate weight loss | Significant, often dramatic weight loss |
| Gradual, over weeks to months | Rapid weight loss post-surgery |
| Reversible | Irreversible, some procedures can be reversed or revised |
| Minimal | Invasive surgery requiring anesthesia and hospitalization |
| Gastrointestinal risk, gall bladder problems, Acute kidney injury | Higher risk due to surgical nature and potential for post-operative complications |
| Ongoing medication costs | Higher initial cost with potential long-term savings on healthcare expenses |
| Supports dietary and exercise modifications | Often necessitates significant dietary and lifestyle changes post-surgery |
| Requires ongoing adherence to medication regimen | Require lifelong monitoring and adjustments |
| Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, injection site reactions | Complications such as malabsorption, vitamin deficiencies, dumping syndrome, gallstones, and potential for surgical complications |
| Improve insulin sensitivity, decrease appetite | Alters metabolism by reducing stomach capacity and affecting nutrient absorption |
| Improve mental Health | Improve mental health, due to rapid weight loss and body changes |
| Covered by insurance for individuals with a BMI over 30 | For those with a BMI over 40 |
| Not approved by FDA for weight management. | Approved by FDA |
Ozempic is a non-invasive injectable medication for weight management, while Bariatric surgery involves invasive surgical procedures. Ozempic offers moderate weight loss over time, whereas Bariatric surgery leads to significant weight loss rapidly. Ozempic effects are reversible, whereas Bariatric surgery is generally irreversible.
Main benefits of Ozempic
1. Weight Loss: Clinical trials have demonstrated that Ozempic treatment leads to significant reductions in body weight compared to placebo, making it an effective option for individuals looking to manage their weight.
2. Improved Glycemic Control: Helps to improve glycemic control by reducing blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
3. Cardiovascular Benefits: Treatment provide cardiovascular benefits, including a reduced risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) such as heart attack, stroke, and cardiovascular death, in individuals with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease.
4. Lower Risk of Hypoglycemia: Unlike some other diabetes medications such as insulin and sulfonylureas, Ozempic is associated with a lower risk of hypoglycemia (dangerously low blood sugar levels). This makes it a safer option for many patients, particularly those at risk of hypoglycemic episodes.
5. Convenient Once-Weekly Dosing: Ozempic is administered via a once-weekly subcutaneous injection, which offers convenience and improved adherence compared to medications that require more frequent dosing.
6. Non-Systemic Action: Unlike some other medications for type 2 diabetes, Ozempic primarily acts locally within the gastrointestinal tract to stimulate insulin secretion and reduce blood sugar levels. This non-systemic action may reduce the risk of adverse effects on other organs or systems in the body.
7. Potential for Long-Term Weight Management: Ozempic has shown promise for long-term weight management in individuals with obesity or overweight, with sustained weight loss observed over extended treatment durations.
8. Improved Beta-Cell Function: Ozempic treatment has been associated with improvements in beta-cell function, which is beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes as it helps to preserve the body’s ability to produce insulin over time.
9. Comprehensive Approach to Type 2 Diabetes Management: By addressing multiple aspects of type 2 diabetes, including glycemic control, weight management, and cardiovascular risk reduction, Ozempic offers a comprehensive treatment approach that can help improve overall health outcomes for individuals with the condition.
How does Bariatric Surgery Benefits Patients?
1.Weight Loss: Bariatric surgery typically leads to significant and sustained weight loss, which can improve overall health and reduce the risk of obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and sleep apnea.
2. Improvement in Obesity-related Health Conditions: Many patients experience improvements or remission of obesity-related health conditions like type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and sleep apnea following bariatric surgery.
3. Enhanced Quality of Life: Weight loss and improvements in health conditions can lead to a better quality of life, including increased mobility, improved self-esteem, and a greater ability to participate in physical activities and social interactions.
4. Long-Term Weight Maintenance: Help patients achieve long-term weight maintenance when combined with lifestyle changes such as healthy eating habits and regular exercise.
5. Reduction in Medication Use: Many patients are able to reduce or eliminate medications they were taking for obesity-related conditions, leading to cost savings and a decreased risk of medication-related side effects.
6. Decreased Mortality Risk: Studies have shown that bariatric surgery is associated with a reduced risk of premature death compared to non-surgical treatments for obesity.
7. Psychological Benefits: Bariatric surgery can have positive effects on mental health, including reduced depression and anxiety symptoms, improved body image, and increased confidence
8. Improvement in Fertility: For obese individuals struggling with fertility issues, weight loss from bariatric surgery can improve reproductive health and increase the chances of conception.
9. Reduction in Joint Pain: Weight loss can alleviate pressure on the joints, leading to a reduction in joint pain and improved mobility for individuals with conditions such as osteoarthritis.
5 Types of bariatric surgery
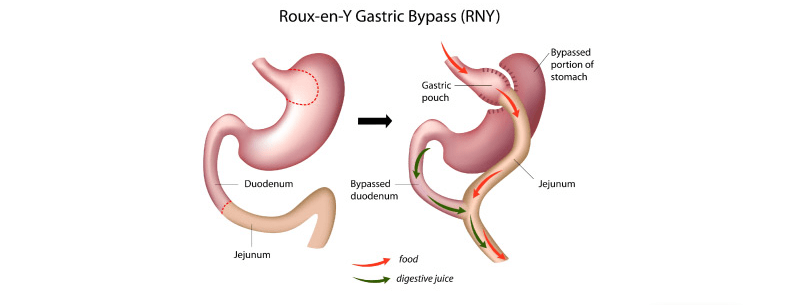
1. Gastric Bypass Surgery (Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass:
This procedure involves creating a small pouch at the top of the stomach and connecting it directly to the small intestine. It restricts food intake and reduces the absorption of nutrients.
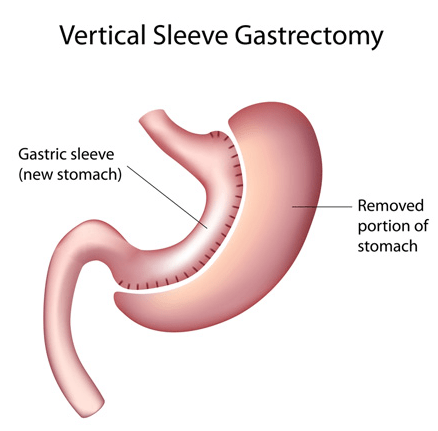
2. Sleeve Gastrectomy:
- In this surgery, a large portion of the stomach is removed, leaving a smaller banana-shaped sleeve. It reduces the stomach’s capacity, leading to reduced food intake and earlier feelings of fullness.
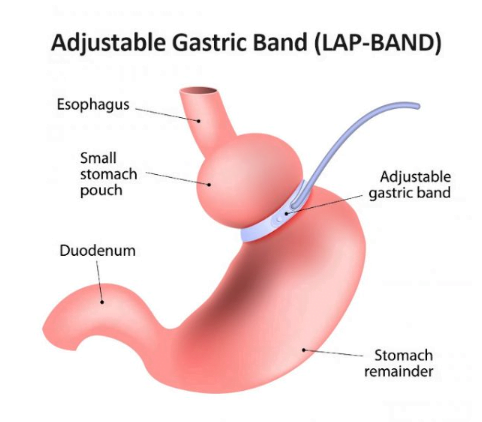
3. Adjustable Gastric Banding (Lap-Band):
- This procedure involves placing an inflatable band around the upper part of the stomach, creating a small pouch above the band and a narrow passage to the rest of the stomach. The band can be adjusted to control food intake.
4. Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS):
- This surgery involves two steps. First, a sleeve gastrectomy is performed to reduce the size of the stomach. Then, a portion of the small intestine is bypassed, limiting the absorption of calories and nutrients.
- Stomach Reduction (Sleeve Gastrectomy): The first step involves removing a large portion of the stomach to create a smaller, sleeve-shaped stomach. This reduces the stomach’s capacity to hold food, leading to feelings of fullness with smaller meals. The removed portion of the stomach is usually discarded.
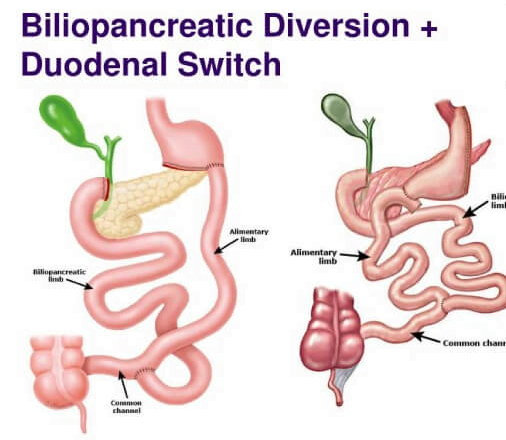
Duodenal Switch: After the sleeve gastrectomy, the surgeon then reroutes a portion of the small intestine to create the “switch” aspect of the procedure. This involves dividing the small intestine and reconnecting it in a way that bypasses a significant portion of the small intestine where nutrient absorption occurs.
Biliopancreatic Diversion: In addition to the duodenal switch, the surgeon may also perform a biliopancreatic diversion. This involves rerouting bile and pancreatic juices to mix with food farther down the small intestine, which aids in digestion. This diversion helps reduce the risk of nutritional deficiencies by ensuring that essential nutrients are still absorbed by the body.
Anastomosis: During the procedure, the surgeon creates connections (anastomoses) between the remaining portion of the stomach (the sleeve) and the rerouted small intestine. This allows food to pass from the stomach into the lower portion of the small intestine, where it mixes with bile and pancreatic juices for digestion.
Closure and Recovery: Once the surgical rearrangements are complete, the surgeon carefully checks for any leaks or bleeding and closes the incisions. The patient is then monitored closely in the hospital for a few days to ensure proper recovery.
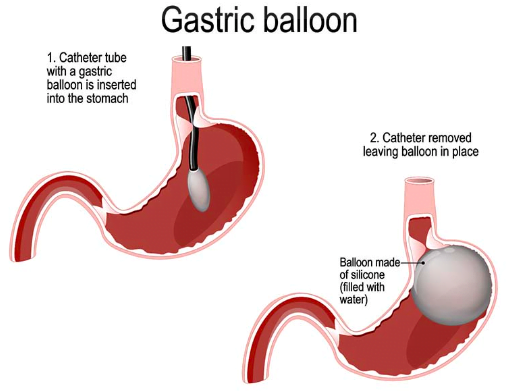
5. Gastric Balloon:
- This is a temporary procedure where a deflated balloon is inserted into the stomach and then inflated to reduce its capacity. It is typically removed after six months.
Each type of bariatric surgery has its own benefits, risks, and considerations, and the choice of procedure depends on factors such as the patient’s health, BMI, and preferences, as well as the surgeon’s recommendation.
Bariatric Surgery vs Ozempic which is better?
Bariatric surgery is typically recommended for individuals with severe obesity who have not been successful with other weight loss methods, and it can lead to significant and sustained weight loss as well as improvements in obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea.
-Bariatric surgery is mostly recommended for patient with BMI over 40.
-Bariatric surgery is better for Individual with medullary thyroid carcinoma or in patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 since patients with these conditions cannot take Ozempic.
-Ozempic is not FDA approved for weight management, so when prescribe for such, patient pay out of pocket which can be very expensive.
Ozempic is recommended for patients with high A1C and type 2 diabetes. It is not for long term Use and Can lead to stool Impaction and pancreatitis.
Individuals with Hepatitis C should avoid taking Ozempic due to the risk of exacerbating pancreatitis, as the medication can potentially worsen the impact of hepatitis on the pancreas.
Safety and side effects of Ozempic and Bariatric surgery
| Ozempic (Semaglutide) | Bariatric Surgery |
|---|---|
| Safety Generally considered safe for most patients | Safety Invasive procedure with associated risks |
| Moderate weight loss efficacy | Significant weight loss effectiveness |
| Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, nutritional deficiencies |
| Potential cardiovascular benefits | Long-term weight loss maintenance, possible complications |
| Reversible (weight may return upon discontinuation) | Irreversible (though some procedures are reversible) |
Side effects of Ozempic
1.Nausea: Feeling sick to the stomach, which may lead to vomiting in some cases.
2. Stool Impaction: Ozempic works by slowing down the rate at which food moves through the stomach and into the intestines. While this can be beneficial for controlling blood sugar levels and promoting weight loss, it can also lead to changes in bowel habits, such as constipation, in some individuals.
3. Headache: Aching or pressure sensation in the head.
4. Hypoglycemia: Low blood sugar levels, especially when used in combination with other diabetes medications like insulin or sulfonylureas.
5. Injection Site Reactions: Redness, itching, or swelling at the site of injection.
6. Decreased Appetite: Loss of appetite or reduced hunger sensation.
7. Indigestion: Difficulty digesting food, leading to discomfort or bloating.
8. Fatigue: Feeling tired or lacking energy.
9. Pancreatitis: During clinical trials and post-marketing surveillance, cases of pancreatitis have been reported in patients using Ozempic.
Side Effects and safety concerns for bariatric surgery
1.Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms are common immediately after surgery and may persist for some time as the body adjusts to changes in digestion.
2. Dumping Syndrome: This occurs when food moves too quickly through the stomach and into the small intestine, leading to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, and sweating.
3. Nutritional Deficiencies: Bariatric surgery can impact the body’s ability to absorb nutrients, leading to deficiencies in vitamins and minerals such as iron, calcium, vitamin D, vitamin B12, and folate. Regular monitoring and supplementation may be necessary.
4. Gallstones: Rapid weight loss after bariatric surgery increases the risk of developing gallstones, which may require additional treatment.
5. Infection: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection at the incision sites or within the abdominal cavity.
6. Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or after surgery is a potential complication that may require further medical intervention.
7. Ulcers: Peptic ulcers may develop in the stomach or small intestine, potentially causing pain and bleeding.
8. Bowel Obstruction: Scar tissue or adhesions from surgery may cause blockages in the intestines, leading to symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and vomiting.
9. Dumping Syndrome: This condition occurs when food moves too quickly through the stomach and into the small intestine, leading to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, and sweating.
10. Changes in Bowel Habits: Some individuals may experience changes in bowel habits, including constipation or diarrhea, following bariatric surgery.
Safety Concerns for Ozempic
1. Pancreatitis: As mentioned earlier, pancreatitis, or inflammation of the pancreas, is a potential side effect of Ozempic. While rare, it can be serious and requires medical attention if symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting occur.
2. Thyroid C-Cell Tumors: In animal studies, Semaglutide, the active ingredient in Ozempic, has been associated with an increased risk of thyroid C-cell tumors. While this risk has not been definitively established in humans, Ozempic is not recommended for individuals with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN
3. Hypoglycemia: Like other medications used to treat diabetes, Ozempic can cause low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia), especially when used in combination with other diabetes medications such as insulin or sulfonylureas. Individuals should be educated about the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia and how to manage it appropriately.
4. Gastrointestinal Side Effects: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation are common side effects of Ozempic. These symptoms usually improve over time as the body adjusts to the medication, but they can be bothersome for some individuals.
5. Acute Kidney Injury: Cases of acute kidney injury, sometimes requiring dialysis, have been reported in individuals taking GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic. It’s essential to monitor kidney function regularly, especially in individuals with pre-existing kidney disease or risk factors for kidney problems.
6. Allergic Reactions: Allergic reactions, including severe hypersensitivity reactions such as anaphylaxis, have been reported with Ozempic. Individuals should seek medical attention immediately if they experience symptoms such as swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, difficulty breathing, or severe itching or rash.
7. Heart Rate Increase: Ozempic may increase heart rate, particularly at higher doses. Individuals with a history of cardiovascular disease should use caution when taking Ozempic, and their cardiovascular status should be monitored regularly.
Long-term outcomes, effectiveness and strategies for weight loss maintenance with Ozempic and Bariatric Surgery
Ozempic:
Long-Term Effectiveness:
- Studies have shown that Ozempic (Semaglutide) can lead to significant and sustained weight loss over the long term.
- Clinical trials demonstrate that individuals using Ozempic along with lifestyle modifications experience greater weight loss compared to those using a placebo.
- Long-term effectiveness appears to be linked to the continued use of the medication and adherence to lifestyle changes.
Sustainability:
- Ozempic sustainability in weight loss relies on consistent adherence to treatment and lifestyle modifications.
- Some individuals may experience plateauing of weight loss over time, necessitating adjustments in dosage or lifestyle factors.
- Continued monitoring by healthcare providers is essential to ensure sustained weight loss and prevent relapse.
Potential for Weight Regain and Maintenance Strategies:
- There is potential for weight regain if medication adherence or lifestyle changes are not maintained.
- Strategies for maintaining weight loss with Ozempic include ongoing support from healthcare providers, regular monitoring of progress, and reinforcement of lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise.
- Behavioral therapy and support groups may also be beneficial for long-term weight maintenance.
Bariatric Surgery:
Long-Term Effectiveness:
- Bariatric surgery, such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy, has been shown to result in significant and sustained weight loss over the long term.
- Studies indicate that many individuals maintain a substantial portion of their weight loss several years after surgery.
Sustainability:
- The sustainability of weight loss with bariatric surgery depends on various factors, including the type of surgery performed, adherence to dietary guidelines, and lifestyle changes.
- Follow-up care, including regular medical monitoring and support from healthcare providers, is crucial for long-term success.
Potential for Weight Regain and Maintenance Strategies:
- While bariatric surgery can lead to significant initial weight loss, some individuals may experience weight regain over time.
- Strategies for maintaining weight loss post-bariatric surgery include adherence to dietary recommendations, regular physical activity, and ongoing support from healthcare providers and support groups.
- Behavior modification techniques, such as mindful eating and stress management, may also play a role in long-term weight maintenance.
Step by step administration of Ozempic
Administering Ozempic (Semaglutide) involves several steps. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Wash your hands: Start by washing your hands thoroughly with soap and water to ensure cleanliness.
- Prepare the injection: Take the Ozempic pen out of the refrigerator. Let it sit at room temperature for about 30 minutes to allow it to warm up slightly. Do not shake the pen.
- Check the medication: Inspect the Ozempic pen. Make sure the liquid is clear and colorless. Do not use the medication if it is discolored or contains particles.
- Choose the injection site: Common injection sites for Ozempic include the abdomen (around the belly button), thigh, or upper arm. Rotate injection sites to prevent lipodystrophy (changes in fat under the skin).
- Clean the injection site: Use an alcohol swab to clean the injection site. Allow the skin to dry completely before injecting.
- Prepare the pen: Remove the cap from the Ozempic pen. Do not remove the needle cap yet.
- Attach the needle: Screw on a new, sterile needle tightly onto the pen. Remove the outer needle cap, but keep the inner needle cap on until just before the injection.
- Prime the pen: Turn the dose selector to select the dose prescribed by your healthcare provider. Hold the pen with the needle pointing up and tap the cartridge gently to remove any air bubbles. Press and hold the dose button until the dose counter returns to 0 and you see a drop of medication at the needle tip. You should only do this the first time you use the pen, or if you haven’t used it for a while.
- Inject the medication: Hold the pen like a dart at a 90-degree angle to the skin. With your other hand, pinch a fold of skin at the injection site. Insert the needle into the skin and press the dose button. Keep the dose button pressed down and count to 10 to make sure you receive the full dose.
- Remove the needle: After the count of 10, release the dose button and then remove the needle from the skin. Do not recap the needle.
- Dispose of the needle: Safely dispose of the needle and pen in a puncture-resistant container according to local regulations.
- Record the injection: Keep track of the date, time, and injection site in your medication log.
Always follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider and the Ozempic package insert for the most accurate administration technique. If you have any questions or concerns about administering Ozempic, don’t hesitate to consult your healthcare provider or pharmacist
How to Safely store Ozempic
1. Ozempic pens, when unopened, should be kept in the refrigerator, away from direct contact with the cooling element. When stored in this manner, they should maintain their efficacy until their expiration date
2. Once used for the first time, an Ozempic pen can be stored either in the refrigerator or at room temperature. It’s important to keep the pen cap on and to store it away from excessive heat and direct sunlight to maintain its effectiveness.
3. After it’s opened, an Ozempic pen can last for up to 56 days.
4. When traveling by plane, it’s recommended to carry your Ozempic pens with you through security rather than packing them in your checked luggage.
5. When traveling by car:
- Ensure your Ozempic pens are kept in a temperature-controlled environment.
- Avoid exposing them to extreme temperatures.
- Store them in a cool, shaded area within the car.
- Do not leave them in direct sunlight or near heating elements.
Do not store Ozempic pen in the Freezer.
Advantages of Ozempic vs Bariatric surgery
Sure, here’s a comparison table outlining some advantages of Ozempic (semaglutide) versus bariatric surgery:
| Ozempic (Semaglutide) | Bariatric Surgery |
|---|---|
| Effective in weight loss for some | Highly effective in significant weight loss |
| weight loss of around 10-15% of body weight | weight loss often exceeding 50% of excess body weight |
| Non-invasive | Invasive surgery requiring |
| No hospitalization | hospitalization and recovery |
| Reversible | Generally irreversible |
| Generally well-tolerated, side effects such as nausea and diarrhea | Complications such as infection, nutrient deficiencies, gastrointestinal issues |
| medication regimen and lifestyle modifications | Requires significant lifestyle changes in diet and exercise |
| Weight loss occurs gradually | Rapid initial weight loss followed |
| over several months | by slower, more gradual weight loss |
| Long-term effects on weight | Potential for long-term weight loss |
| maintenance require ongoing , May lose muscle mass and regain weight | maintenance, but potential for complications or weight regain |
Cost of Ozempic Compare to Bariatric Surgery
Many insurance plans cover Ozempic, for diabetes but not weight management, co-pays and deductibles may apply. Range $700 to $15000 per month without insurance coverage. Prices may vary based on dosage and pharmacy.
| Price with Pharmacy | Price with GoodRx |
|---|---|
| Walmart $1,130 | $1,014 |
| Target (CVS) $1,117 | $998.62 |
| Kinney Drug $1,047 | $937.98 |
| Walgreens $1,130 | $998.87 |
| Wegmans $1,246 | $937.98 |
| Price Chopper $1,490 | $943.89 |
| CVS Pharmacy $1,115 | $998.62 |
| Rite Aid $1,234 | $947.55 |
| Tops Pharmacy $1,256 | $937.98 |
| Costco $1,159 no membership needed | $959.99 |
Bariatric surgery is often covered by insurance if deemed medically necessary due to obesity-related health issues. Coverage may vary based on the insurance plan and individual circumstances.
The average cost of bariatric surgery can range from $15,000 to $25,000 without insurance coverage. Prices may vary based on the type of procedure, location, and surgeon fees.
| Bariatric Surgery Type | Average Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| Gastric Sleeve Surgery | $10,000 – $20,000 |
| Gastric Bypass Surgery | $15,000 – $35,000 |
| Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding (Lap-Band) | $14,000 – $30,000 |
| Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS) | $20,000 – $40,000 |
| Vertical Banded Gastroplasty (VBG) | $15,000 – $30,000 |
These costs can vary significantly depending on factors such as the location of the surgery, the surgeon’s experience, hospital fees, additional medical services, and any complications that may arise during or after the surgery.
Medications that can interact with Ozempic
- Insulin or Insulin Secretagogues: Combining Ozempic with insulin or insulin secretagogues (such as sulfonylureas) may increase the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Dosage adjustments may be necessary when using these medications together.
- Oral Antidiabetic Drugs: Certain oral antidiabetic drugs, such as sulfonylureas or meglitinides, may increase the risk of hypoglycemia when combined with Ozempic. Dose adjustments may be needed.
- Oral Medications Absorbed in the Gastrointestinal Tract: Since Ozempic slows gastric emptying, it may affect the absorption of orally administered medications that rely on rapid gastrointestinal transit for absorption. This could include antibiotics, oral contraceptives, and other medications. It’s recommended to take these medications at least one hour before Ozempic or four hours after to minimize potential interactions.
- Warfarin and Other Anticoagulants: GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic may affect the efficacy of warfarin or other anticoagulants. Monitoring of international normalized ratio (INR) may be necessary when these medications are used together.
- Digoxin: There have been reports of increased heart rate when GLP-1 receptor agonists are used with digoxin. Monitoring for signs of digoxin toxicity may be warranted when using Ozempic with digoxin.
- CYP Enzyme Inducers or Inhibitors: Ozempic is metabolized primarily by cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, particularly CYP3A4. Medications that induce or inhibit CYP3A4 activity may affect the metabolism of Ozempic. Examples include rifampin (an inducer) and ketoconazole (an inhibitor).