
Black Walnut (Juglans nigra) have a thick, hard shell that is difficult to crack. The flavor is bold and distinctive, often described as rich and earthy while English Walnut (Juglans regia) have a thinner shell that is easier to crack than black walnuts. The flavor is milder and sweeter than black walnuts, making them a popular choice in cooking and baking.
Black Walnut and English Walnut are distinct species of walnut trees with their own unique characteristics. The Black Walnut, native to North America, boasts prized dark wood used in fine furniture-making due to its durability. Its nuts, encased in a tough shell, offer a robust, earthy flavor utilized in baking and confectionery.
On the other hand, the English Walnut, also known as the Persian Walnut, hails from regions spanning the Balkans to China. Its medium-sized tree yields softer wood, often used for its fine texture. The nuts, larger and easier to crack than their Black Walnut counterparts, present a milder, sweeter taste popular in various culinary applications. Both trees hold economic and cultural significance, contributing valuable resources to industries and finding places in traditional medicine and cuisine.
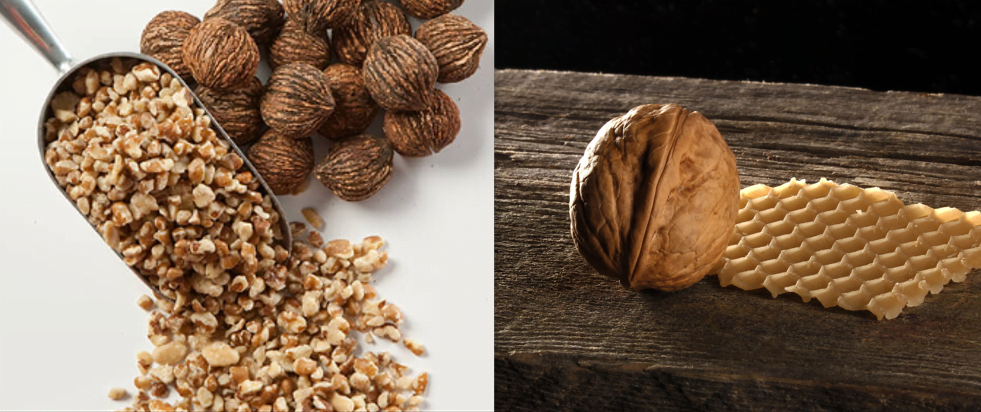

black walnut left vs English walnut right
Identifying Black walnut from appearance to Cultivation
Black walnut refers to several species of walnut trees in the Juglans genus, but it most commonly refers to Juglans nigra, which is native to North America. It is a deciduous tree known for its dark, dense wood and for producing a unique type of walnut, known as the black walnut, which is edible and highly prized for its rich, robust flavor.
- Appearance: The black walnut tree is tall, typically reaching heights of 30-40 meters (100-130 feet). Its bark is dark and furrowed, and the leaves are pinnate (feather-like) with 15-23 leaflets.


2. Wood: The heartwood of the black walnut tree is dark brown to nearly black. It’s a very durable and strong wood, which makes it valuable for woodworking, furniture making, and cabinetry.
3. Nuts: The black walnut tree produces a fruit known as the black walnut. These are round, hard-shelled nuts enclosed in a green, husk-like covering. The nut inside is rich, oily, and has a distinctive strong flavor that’s often used in baking and cooking.

Black walnut in a bowl

4. Habitat: Black walnut trees are native to the eastern United States, ranging from southern Ontario to Georgia and as far west as eastern Kansas. They typically grow in rich, well-drained soils in forests and along riverbanks.
5. Cultivation: Black walnut trees are sometimes cultivated for their wood and nuts. They can be grown for both commercial purposes and as ornamental trees in gardens.
Nutritional comparison: Black walnut vs English walnut
The nutritional information for black walnuts per 1/4 cup serving:
| Nutrient | Amount per Serving |
|---|---|
| Calories | 193 |
| Protein | 8 grams |
| Fat | 18 grams |
| Saturated Fat | 1 gram |
| Carbohydrates | 3 grams |
| Fiber | 2 grams |
| Sugar | 0 grams |
| Vitamin E | Present |
| Folate | Present |
| Melatonin | Present |
| Iron | Present |
| Potassium | Present |
| Magnesium | Present |
Nutritional Content for One Serving (1 ounce) of English Walnuts:
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 ounce (28g) |
|---|---|
| Calories | 185 |
| Total Fat | 18.5g |
| – Saturated Fat | 1.7g |
| – Monounsaturated Fat | 2.5g |
| Protein | 4.3g |
| Carbohydrates | 3.9g |
| – Dietary Fiber | 1.9g |
| – Sugars | 0.7g |
In addition to these macronutrients, an ounce of walnuts also provides:
| Vitamin/Mineral | % of Daily Recommended Amount |
|---|---|
| Calcium | Up to 2% |
| Iron | Up to 4% |
| Potassium | Up to 2% |
| Magnesium | Up to 14% |
| Folate | 7% |
Health Benefits of Black walnut vs English Walnuts

Black walnut health benefits
| Nutrient/Property | Black Walnuts |
|---|---|
| Antioxidant Content | High, rich in tannins and juglone |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) |
| Potential Anti-Cancer | Some studies show anti-cancer properties |
| Anti-Parasitic | Contains juglone with anti-parasitic effects |
- Rich in Antioxidants: Black walnuts are high in antioxidants, particularly polyphenols. Antioxidants help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, which can contribute to chronic diseases and aging.
- Heart Health: They are a good source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health. These fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and lower the risk of heart disease.
- Brain Health: Omega-3 fatty acids are also essential for brain health, and they may help improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: The antioxidants and fatty acids in black walnuts can help reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is associated with various health issues, including heart disease, arthritis, and certain types of cancer.
- Improved Digestive Health: Black walnuts are a good source of dietary fiber. Fiber is crucial for healthy digestion, as it promotes regular bowel movements and prevents constipation.
- Weight Management: The fiber in black walnuts can help promote a feeling of fullness, which may aid in weight management by reducing overall calorie intake.

- Blood Sugar Regulation: Some studies suggest that black walnuts may help regulate blood sugar levels. The fiber content can slow down the absorption of sugars, which can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Boosted Immune Function: The high antioxidant content can help support the immune system by protecting cells from damage and promoting overall health.
- Improved Skin Health: Black walnut oil, extracted from the nuts, is rich in vitamins and antioxidants that can benefit the skin. It may help with conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and acne.
- Antimicrobial Properties: Black walnuts contain compounds that have antimicrobial properties, which can help fight against certain types of bacteria and fungi.
- Potential Cancer-Fighting Properties: Some studies have suggested that compounds found in black walnuts may have anti-cancer properties. However, more research is needed in this area.
- Nutrient-Rich: Black walnuts are a good source of various essential nutrients, including vitamins (like vitamin E), minerals (such as magnesium and phosphorus), and protein.
English walnut health benefits

- High Omega-3 Content: English walnuts are also a good source of ALA, which is beneficial for heart health, brain function, and reducing inflammation.
- Higher Omega-6 to Omega-3 Ratio: English walnuts have a higher ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids compared to black walnuts. While both types are healthy fats, an imbalance between these two types can contribute to inflammation if consumed in excess.
- More Commonly Consumed: English walnuts are the most common variety of walnuts consumed globally, and they are often used in a wide range of culinary applications.
- Rich in Vitamin E: English walnuts are notably high in vitamin E, which is a powerful antioxidant that supports skin health and may help protect cells from damage.
Black Walnut vs. English Walnut: Characteristics and Differences

Black walnut characteristics
- Dark, deeply furrowed bark
- Round, hard nuts with thick shells
- Strong, earthy flavor
- Native to North America
- Used in baking, like cakes and pies
- lack walnuts are slower-growing and can take a long time to produce nuts.
English walnut characteristics

- Lighter, smoother bark
- Oval nuts with thinner shells
- Milder, sweeter flavor
- Native to Persia (modern-day Iran)
- Versatile, used in a wide range of dishes.
- English walnuts are more widely available in stores
- English walnuts grow faster and start producing nuts earlier.
Toxic side of Black walnut
Black walnut trees produce a chemical called juglone, which can be toxic to some plants, inhibiting their growth. This makes them incompatible with certain plants and vegetation.
It’s worth noting that while the nuts of the black walnut tree are edible and highly valued for their flavor, they can be difficult to crack and extract due to their hard shells. Additionally, the husks can stain hands and clothing.
Overall, the black walnut tree is valued for both its wood and the unique flavor of its nuts, making it an important species in various industries and culinary practices.
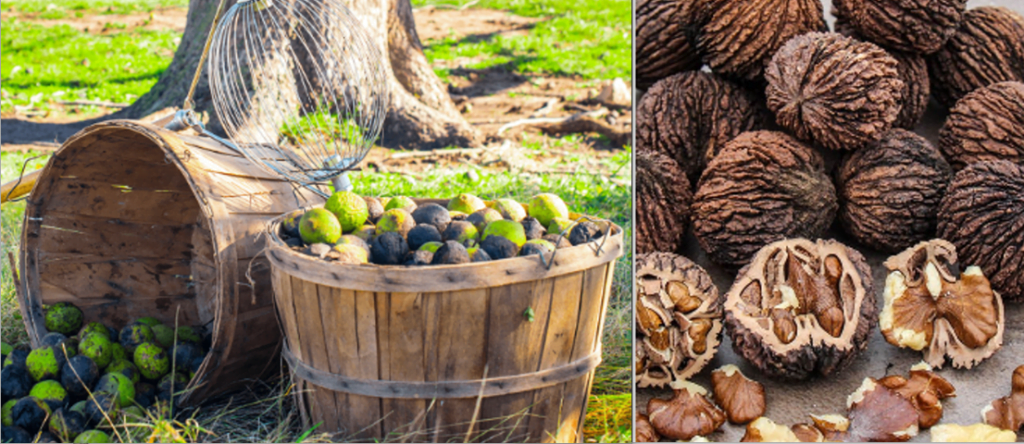

Uses of Black Walnut
Black walnut (Juglans nigra) is a versatile tree with several practical and cultural uses. Here are some of its notable applications:
- Woodworking: Black walnut wood is highly prized for its rich, dark color, fine grain, and workability. It’s used in crafting furniture, cabinetry, flooring, and gunstocks. The wood’s aesthetic appeal and durability make it a favorite among woodworkers.
- Nut Production: The black walnut tree produces edible nuts, which are commonly used in baking, cooking, and for snacking. They have a distinctive flavor and are known for being more flavorful and robust than the English walnut. They are also used in making walnut oil.
- Medicinal Uses: Historically, various parts of the black walnut tree, including the bark, leaves, and nuts, have been used for their potential health benefits. They have been employed in traditional medicine for conditions such as digestive disorders, skin conditions, and even as a vermifuge (against parasitic worms). However, it’s important to note that the efficacy and safety of these uses vary and should be approached with caution.
- Dye Production: The husks of black walnuts can be used to make a natural dye that produces a range of brown to dark brown colors. This dye has been used in textiles and crafts.
- Landscaping and Shade: Black walnut trees are often planted for their ornamental value. They have a stately appearance and provide excellent shade. However, it’s important to note that the roots of black walnut trees release a substance called juglone, which can inhibit the growth of certain plants around them. This should be taken into consideration when planning landscaping around these trees.
- Traditional Crafts: Black walnut shells, especially when dried and ground, have been used in traditional crafts. They can be carved or used in crafting ornaments, jewelry, and other decorative items.
- Cultural and Symbolic Significance: Black walnut trees have cultural and symbolic importance in various societies. They have been used in folklore, art, and as a source of inspiration in literature and poetry.
- Insect Repellent: The scent of black walnut leaves and wood is known to repel certain insects. Some people use black walnut chips or leaves as a natural insect repellent in gardens or to deter pests in stored items like clothing.
- Wildlife Habitat: Black walnut trees provide food and shelter for various wildlife species. Squirrels, in particular, are known to relish the nuts.
- Soil Improvement: Black walnut leaves, when composted, can improve the soil due to their nutrient content. They are rich in elements like potassium and other trace minerals.
- Invasive Species Control: Because of the allelopathic effect of juglone, black walnut trees can inhibit the growth of certain plants beneath their canopy. This characteristic has been used strategically to control or suppress invasive plant species.
- Woodworking: Black walnut wood is highly prized for its durability, workability, and rich color. It’s used in a variety of applications, including furniture, flooring, and cabinetry.
- Nuts: The nuts are harvested for culinary use. They’re used in baking, confections, and as a flavoring in various dishes.
Remember that while black walnuts have a range of uses, there may be some considerations and precautions to take into account, especially regarding their potential impact on plants and their medicinal applications. Always consult with a knowledgeable source or expert before using black walnuts for any specific purpose.
10 Culinary use of black walnut
Here are some common culinary uses for black walnuts:
- Baking: Black walnuts can be chopped or ground and used in a wide range of baked goods. They are particularly popular in recipes like brownies, cookies, cakes, and muffins. Their strong flavor can provide a rich and nutty dimension to your baked treats.
- Ice Cream and Desserts: Black walnuts make a wonderful addition to ice cream, both as a topping and when folded into the ice cream itself. Their distinctive taste pairs well with sweet, creamy desserts.
- Salads: Chopped black walnuts can be sprinkled over salads to add a crunchy texture and a distinctive nutty flavor. They complement salads with fruits like apples or pears, as well as salads with cheese, such as blue cheese or goat cheese.
Apple walnut Salad


- Stuffings and Dressings: Black walnuts can be included in stuffing’s for meats like poultry or used in dressings for salads or side dishes. Their unique flavor can elevate the overall taste of the dish.
- Pasta and Grain Dishes: Black walnuts can be incorporated into pasta dishes, grain salads, and pilafs to provide an extra layer of texture and flavor. They work well with dishes that have a savory or earthy profile.
- Cheese Platters: Black walnuts pair nicely with various cheeses. They can be served alongside a cheese platter or incorporated into cheese-based recipes like cheese balls or cheese spreads.
- Trail Mixes and Snacks: Black walnuts can be included in homemade trail mixes, granola bars, or simply enjoyed on their own as a snack. They provide a hearty and flavorful addition.
- Sauces and Pesto’s: Ground black walnuts can be used as a base for sauces or pesto’s. When mixed with ingredients like garlic, herbs, and olive oil, they create a flavorful and textured sauce that can be used on pasta, meat, or vegetables.
- Garnish: Whole or chopped black walnuts can be used as a garnish for a variety of dishes, adding both visual appeal and a crunchy element.
- Candied or Glazed: Black walnuts can be candied or glazed to create a sweet and crunchy treat. They can be used as a topping for desserts or as a standalone candy.
When using black walnuts in recipes, it’s important to be mindful of their strong flavor. They may overpower more delicate flavors, so it’s a good idea to balance them with other ingredients accordingly. Additionally, keep in mind that black walnuts can be more challenging to find compared to English walnuts, so you may need to seek out specialty stores or online sources.
Identifying English walnut nut
The English walnut, scientifically known as Juglans regia, is a species of walnut tree native to the region stretching from the Balkans to the Himalayas and southwest China. It is commonly referred to as the Persian walnut, as it was introduced to Europe via Persia (modern-day Iran). The term “English walnut” is primarily used in the United States and does not refer to the tree’s place of origin.
The English walnut tree is highly valued for its wood and its delicious nuts. The nuts have a thin shell and a rich, flavorful kernel that is commonly used in baking, cooking, and eaten as a snack. They are a popular ingredient in various cuisines around the world.

English walnuts

- Shape: English walnut nuts are typically oval or round with a smooth surface.
- Shell: The nut has a hard, woody shell that protects the inner seed. The shell is composed of two halves, which can be opened to reveal the seed inside.
- Color: The shell of an English walnut nut is usually light brown, although it can vary in shade.
- Size: The size of English walnut nuts can vary, but they are generally medium to large in comparison to other types of walnuts.
- Flavor: The nut inside is rich, sweet, and mild in flavor. It is a popular ingredient in a wide range of culinary applications.
- Texture: The inner nutmeat has a smooth texture, which makes it versatile for various cooking methods or for eating raw.
- Nutmeat Color: The edible part of the nut, known as the nutmeat, is light in color, ranging from pale beige to a golden brown.
- Nutmeat Lobes: When you open the shell, you’ll find the nutmeat divided into two lobes, separated by a central partition. This gives it a distinctive appearance often likened to a human brain.
- Oil Content: English walnut nuts are known for their relatively high oil content, which contributes to their rich and buttery flavor.
- Nutritional Value: They are a good source of healthy fats, protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They contain nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and various B vitamins.
- Culinary Uses: English walnuts are used in a wide range of culinary applications, including baking, cooking, snacking, and as a topping for salads or desserts.
- Storage: Like many nuts, English walnuts should be stored in a cool, dry place to maintain their freshness and prevent spoilage.

These characteristics make the English walnut nut a popular and versatile ingredient in a wide range of cuisines and culinary creations.
Culinary Uses and Recipes of English walnut
some common uses of English walnuts:
- Culinary Purposes:
- Snacking: English walnuts are often eaten raw as a snack.
- Baking: They are commonly used in a wide range of baked goods, including cakes, cookies, bread, and pastries.
- Cooking: Walnuts can be used in both savory and sweet dishes, such as salads, stuffing, sauces, and marinades.

2. Nut Butter: English walnuts can be ground into a creamy nut butter, which is a popular alternative to peanut butter.
3. Confectionery: They are used in candies, chocolates, and other confectionery items.
4. Nutrition and Health:
- Nutrient Source: English walnuts are a good source of various nutrients, including omega-3 fatty acids, protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
- Heart Health: They are known for their heart-healthy benefits due to the presence of omega-3 fatty acids, which can help reduce cholesterol levels.
- Brain Health: Some studies suggest that the omega-3 fatty acids in walnuts may support cognitive function.

- Antioxidants: Walnuts contain antioxidants, which can help combat oxidative stress in the body.
- Weight Management: Despite being calorie-dense, moderate consumption of walnuts may aid in weight management due to their satiating properties.
5. Cosmetic and Personal Care:
- Skincare: Walnut oil is used in skincare products for its moisturizing and nourishing properties. It is rich in vitamins and antioxidants.
- Hair Care: Walnut oil is also used in hair care products for its potential benefits in promoting hair health and shine.
6. Woodworking:
- The wood of the English walnut tree is highly valued for its fine grain, stability, and beautiful color. It is commonly used in furniture making, cabinetry, and gunstocks.
7. Traditional Medicine
- In some traditional medicine systems, various parts of the English walnut tree, including the leaves, bark, and roots, have been used for their potential medicinal properties. However, it’s important to note that scientific evidence supporting these uses is often limited.
8. Dyeing:
- The outer husk of English walnuts can be used to create natural dyes for fabrics and crafts.
9. Livestock Feed:
- Walnut meal, a byproduct of walnut oil extraction, can be used as a component of livestock feed.
10. Ornamental and Landscaping:
- English walnut trees are sometimes grown for their aesthetic value in gardens and parks.
Allergies to Walnuts: Symptoms and Management
Some people may have allergies to walnuts, but allergies can vary between black and English varieties. Both black and English walnut contains a substance called juglone, which is found in the wood, leaves, and nuts. Some individuals may be sensitive or allergic to juglone.
Direct skin contact with walnut wood can sometimes lead to skin irritation or contact dermatitis in sensitive individuals. This may manifest as redness, itching, or rash.
Respiratory Sensitivity:
- Some individuals may experience respiratory issues, particularly if they are sanding or cutting walnut wood. This can lead to symptoms like coughing or difficulty breathing in this case seek professional help.
Symptoms:
- Skin reactions: Itching, hives, redness, or swelling around the mouth or other parts of the body.
- Gastrointestinal symptoms: Nausea, stomach cramps, vomiting, or diarrhea.
- Respiratory problems: Shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing, or a runny nose.
- Anaphylaxis: In severe cases, a walnut allergy can lead to anaphylaxis, a life-threatening reaction that requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms include difficulty breathing, a drop in blood pressure, rapid pulse, and loss of consciousness.
Management:
- Avoidance: The most effective way to manage a walnut allergy is to avoid consuming walnuts in any form, including whole nuts, walnut oil, and foods containing walnuts as an ingredient.
- Read labels: Always read food labels carefully to check for any traces of walnuts or walnut-derived ingredients in packaged foods.
- Inform others: Make sure friends, family, and caregivers are aware of your walnut allergy, especially when dining out or attending social events.
- Medication: If you accidentally consume walnuts and experience mild symptoms, over-the-counter antihistamines may help relieve symptoms such as itching and hives. Carry an epinephrine auto-injector (such as an EpiPen) if you’re at risk of anaphylaxis and know how to use it.
- Emergency action plan: Develop an emergency action plan with your healthcare provider detailing the steps to take in case of an allergic reaction, including when to administer epinephrine and when to seek emergency medical assistance.
- Allergist consultation: Regularly consult with an allergist to monitor your allergy and discuss any new treatment options or management strategies.
Study done by NIH (National library of medicine) on walnuts

Walnuts are rich in compounds known for their antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties. Both animal and human research, including studies conducted by various scientific groups, indicate that incorporating walnuts into one’s diet may enhance cognitive function and potentially lower the likelihood of developing or advancing Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer’s Disease (AD).
Research indicates that walnuts may not only lower the risk of brain conditions like Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and depression but also offer protection against cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. These benefits stem from the combined effects of walnut components, which work together to combat oxidative stress and inflammation in various chronic diseases.
Both types are nutritious, rich in healthy fats, protein, and vitamins.
Taste and Flavor of black walnut vs English Walnut
Black Walnut
- Bold and Earthy Flavor: Black walnuts are known for their bold and earthy flavor. They have a stronger and more robust taste compared to the milder English walnuts.
- Rich and Nutty: The flavor of black walnuts is often described as rich and nutty, with a deep, almost smoky undertone. This complexity sets them apart from other nuts.
- Astringency: Black walnuts can be slightly astringent, which means they may have a drying or puckering effect on the mouth. This astringency contributes to their unique taste profile.
- Distinctive Aroma: The aroma of black walnuts is also quite distinctive. It has a strong and pungent nuttiness that adds to the overall sensory experience.
- Oil Content: Black walnuts have a higher oil content than English walnuts. This contributes to their rich and moist texture.
- Bitterness: Some people find black walnuts to be slightly bitter, especially if consumed in large quantities or when not properly processed. Properly drying and processing the nuts can help mitigate
English walnut
- Mild and Sweet: English walnuts are known for their mild and sweet flavor. They lack the boldness and earthiness found in black walnuts, making them more versatile for various culinary applications.
- Buttery Texture: English walnuts have a buttery and creamy texture, which contributes to their pleasant eating experience.
- Less Astringent: Unlike black walnuts, English walnuts are generally less astringent, meaning they don’t have the same drying or puckering effect on the mouth.
- Versatile in Cooking: English walnuts are widely used in both sweet and savory dishes. They are a common ingredient in baking, salads, granola, and are often used in making pesto.
- Neutral Aroma: The aroma of English walnuts is mild and neutral compared to the stronger and more pungent aroma of black walnuts.
- Lower Oil Content: English walnuts typically have a lower oil content than black walnuts. This can affect the texture and mouthfeel of dishes in which they are used.
Popular Walnut Varieties: Black vs. English
1. Black Walnut (Juglans nigra): Known for its rich flavor and dark color, black walnuts are native to North America. They have a strong, earthy taste and are commonly used in baking and cooking.
2. English Walnut (Juglans regia): Also known as Persian walnut, this variety is widely cultivated around the world. It has a milder flavor compared to black walnuts and is often eaten raw or used in desserts, salads, and savory dishes.
3. Chandler: Chandler is a popular cultivar of English walnut known for its large size, thin shell, and mild, buttery flavor. It’s often favored by commercial growers for its high yield.

4. Hartley: Another common English walnut variety, Hartley nuts are medium-sized with a thin shell and a rich, sweet flavor. They are often used in baking, confectionery, and as a snack.

5. Howard: Howard walnuts are similar to Hartley in appearance and taste but are slightly larger and have a higher oil content. They are popular for both commercial and home cultivation.
6. Serr: Serr walnuts are a variety of English walnuts with a distinctive elongated shape. They have a mild flavor and are often used in baking and cooking.

7. Franquette: Franquette walnuts are known for their large size and excellent flavor. They have a slightly darker shell compared to other English walnut varieties and are often used in premium nut mixes and desserts.
These are just a few examples of popular walnut varieties, each with its own unique characteristics and culinary uses.
Resources
https://twin-cities.umn.edu/news-events/study-suggests-walnuts-are-bridge-better-health-we-age
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7071526/#:~:text=Walnuts
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Juglans_nigra







