Berberine is a plant base supplement, known for its Anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic properties. It is found in various plants, like barberry, goldenseal, and Oregon grape. Inositol is a naturally occurring sugar alcohol supplement, found in fruits, that plays a crucial role in various cellular processes.
Inositol is It’s often considered a B-vitamin, although it’s not technically a vitamin itself, found in many foods, especially fruits, beans, grains, and nuts.
It’s involved in cell membrane structure, nerve signaling, and the metabolism of fats. Some people also use inositol supplements for potential health benefits, such as supporting mental health and managing conditions like anxiety and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
6 uses of Berberine and Inositol
| Berberine | Inositol |
|---|---|
| Blood Sugar Control Regulates blood glucose levels, helpful for diabetes | Blood Sugar Control improve insulin sensitivity |
| Heart Health Supports cardiovascular health | Metabolic Support Supports metabolism and aid in weight management |
| Anti-Inflammatory Exhibits anti-inflammatory properties | Hormonal Balance May be beneficial for hormonal disorders |
| Antimicrobial Shows potential as an antimicrobial agent | Combat PCOS Inositol Supplements use to manage Polycystic Ovary Syndrome |
| Mental Health May have mood-regulating effects | Mental Health Used to alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression |
| Lower Cholesterol Taking berberine supplements regularly, appears to lower total cholesterol | Hair Growth: Inositol is believed to support healthy hair growth, and it’s often included in hair care products |
While both Berberine and inositol have therapeutic potential, they function through different pathways and may be used to address different health concerns.
Health Benefits of Berberine vs Inositol health benefits
Simple table of the benefits of berberine and inositol:
| Berberine | Inositol |
|---|---|
| Blood sugar regulation: ✓ Improves insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism | Blood sugar regulation: ✓ Improves insulin sensitivity |
| Heart health: ✓ Lowers cholesterol levels, reduces heart disease risk | Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) management ✓ Improves ovarian function, hormone levels |
| Weight management: ✓ Enhances fat metabolism, reduces appetite | Anxiety and mood disorders ✓ Positive impact on mood disorders |
| Antimicrobial properties: ✓ Exhibits activity against various pathogens | Neurological health ✓ Supports healthy brain function, neuroprotective effects |
| Anti-inflammatory effects ✓ Alleviates inflammation | Hair growth ✓ Improves hair growth, reduces hair loss |
| Liver health ✓ Supports liver function, reduces risk of fatty liver disease |

Inositol:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) management: Inositol supplementation has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, ovarian function, and hormone levels in women with PCOS.
- Anxiety and mood disorders: It may have a positive impact on mood disorders like anxiety and depression, potentially by modulating neurotransmitter pathways in the brain.
- Neurological health: Inositol is involved in cell signaling and may support healthy brain function, potentially offering neuroprotective effects.
- Hair growth: It has been studied for its potential to improve hair growth and reduce hair loss, particularly in conditions like alopecia.
- Liver health: Inositol supplementation may help support liver function and reduce the risk of fatty liver disease by aiding in fat metabolism and reducing inflammation.
Berberine:
- Blood sugar regulation: Berberine has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, making it beneficial for individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance.
- Heart health: It may help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease by improving lipid profiles and reducing inflammation.
- Weight management: Berberine has been studied for its potential to aid in weight loss by enhancing fat metabolism and reducing appetite.
- Antimicrobial properties: It exhibits activity against various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, making it useful in treating infections.
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Berberine may help alleviate inflammation, which is implicated in various chronic diseases.
Berberine’s Breakthrough Battle Against Diabetes
High blood sugar levels, indicative of conditions like diabetes and prediabetes, stem from reduced insulin production or diminished insulin sensitivity. While fluctuations in blood sugar are normal, prolonged elevation can lead to severe health complications, such as organ damage.
Numerous studies in animals indicate that berberine might effectively lower blood sugar levels through diverse mechanisms.
-Enhancing the body’s responsiveness to insulin
-Boosting the production of insulin.
-Balancing metabolic processes.
-Boosting glycolysis, the breakdown of glucose.
-Decreasing glucose production in the liver Augmenting nitric oxide (NO) production to widen arteries.
-Slowing down the absorption of carbohydrates from the intestines.
in 1988 hypoglycemic effect of berberine has been reported during the treatment of diarrhea in diabetic patients. Since then, berberine as an anti-diabetic agent has been used on large scale and known as folk medicine of China.
Numerous studies conducted on individuals with type 2 diabetes indicate that daily intake of 600–2,700 mg of berberine can significantly decrease fasting and long-term blood sugar levels by up to 20% and 12%, respectively. This effect is particularly notable when berberine is used in conjunction with conventional blood sugar medications.

Inositol and ADHD benefits
While there is limited research on this specific relationship, inositol, a naturally occurring compound and member of the B-vitamin family, has been explored for its impact on mental health.
Inositol is involved in various cellular processes, including neurotransmitter signaling. Some studies suggest that inositol may play a role in the regulation of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with attention and focus—two key aspects affected in ADHD.
Moreover, inositol has been investigated for its potential benefits in managing anxiety and mood disorders. Since ADHD often coexists with these conditions, exploring inositol’s impact on mood regulation might indirectly contribute to ADHD symptom management.
Here’s how inositol may potentially help with energy, sleep, and depression:
- Energy: Inositol plays a role in cellular signaling pathways and is involved in the metabolism of glucose, which is the primary source of energy for cells. Some people may find that supplementing with inositol helps support their energy levels, although scientific evidence for this specific effect is limited.
- Sleep: Inositol has been studied for its potential role in improving sleep quality, particularly in individuals with certain sleep disorders such as insomnia. Some research suggests that inositol may help regulate neurotransmitters involved in sleep, such as serotonin, which could contribute to better sleep patterns. However, more studies are needed to fully understand its effects on sleep.
- Depression: Inositol has shown promise as a natural treatment for depression and other mood disorders. It is thought to exert its effects by influencing neurotransmitter activity in the brain, particularly serotonin and dopamine, which are involved in mood regulation. Some clinical trials have found that inositol supplementation may be effective in reducing symptoms of depression, but further research is needed to confirm its efficacy

5 pathways Inositol benefit PCOS patients?
1. Improves Insulin Sensitivity: PCOS is often associated with insulin resistance, which can lead to elevated insulin levels in the blood. Inositol supplementation has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, helping to regulate blood sugar levels and potentially reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
2. Regulates Ovarian Function: Inositol may help regulate ovarian function by promoting normal menstrual cycles and ovulation. Women with PCOS commonly experience irregular menstrual cycles and ovulatory dysfunction, and inositol supplementation has been found to improve these aspects of reproductive health.
3. Balances Hormone Levels: PCOS is characterized by hormonal imbalances, including elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) such as testosterone. Inositol supplementation has been shown to reduce androgen levels, leading to improvements in symptoms such as acne, hirsutism (excessive hair growth), and male-pattern baldness.
4. Supports Egg Quality: Inositol may improve the quality of eggs produced by the ovaries, which can enhance fertility outcomes for women with PCOS who are trying to conceive. Better egg quality may also reduce the risk of miscarriage in women with PCOS.
5. Reduces Symptoms: Inositol supplementation has been associated with a reduction in various PCOS symptoms, including irregular menstrual cycles, hirsutism, acne, and hair loss. By addressing the underlying hormonal and metabolic dysregulation in PCOS, inositol can help alleviate these symptoms and improve overall quality of life for affected individuals.
Which is better for PCOS: berberine or inositol?
Inositol is the better choice of supplement for PCOS since its main target is to regulate hormonals level, regulate ovarian functions, improve the quality of egg produce by the ovaries and reduces PCOS symptoms.
While Berberine key focuses is on blood sugar level, heart health, inflammation reduction and weight management.https://abavist.com/ovasitol-vs-inositol-2-amazing-supplements-for-pcos/
5 ways in which Berberine improve weight loss efforts?
1. Enhanced Fat Metabolism: Berberine has been shown to activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), an enzyme involved in regulating cellular energy metabolism. Activation of AMPK can increase the breakdown of fatty acids and inhibit the synthesis of new fat molecules, thereby promoting fat metabolism and potentially leading to weight loss.
2. Reduced Appetite: Some studies suggest that berberine may help reduce appetite and food intake. It may achieve this by influencing certain hormones and neurotransmitters involved in appetite regulation, such as leptin and serotonin. By decreasing appetite, berberine may lead to a reduction in calorie intake, which can support weight loss efforts.
3. Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Berberine has been demonstrated to improve insulin sensitivity, which is beneficial for individuals with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance can contribute to weight gain and difficulty losing weight, so by improving insulin sensitivity, berberine may help facilitate weight loss and metabolic improvements.

4. Effects on Gut Microbiota: Berberine has been shown to modulate the composition of gut microbiota, the community of microorganisms living in the digestive tract. A healthy balance of gut bacteria is important for overall metabolic health, and alterations in gut microbiota composition have been linked to obesity and metabolic disorders. By positively influencing gut microbiota, berberine may support weight loss and metabolic health.
5. Inhibition of Fat Cell Formation: Some research suggests that berberine may inhibit the differentiation of preadipocytes into mature fat cells, a process known as adipogenesis. By reducing the formation of new fat cells, berberine may help prevent weight gain and promote weight loss over time.
How does berberine affect insulin sensitivity?
Berberine exerts its effects on insulin sensitivity through multiple pathways, These mechanisms work together to improve cellular responsiveness to insulin and enhance glucose metabolism, making berberine a promising therapeutic agent for individuals with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes.
1. AMPK Activation: Berberine has been shown to activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), an enzyme that plays a crucial role in regulating cellular energy metabolism. Activation of AMPK leads to increased glucose uptake in cells, enhanced insulin sensitivity, and improved glucose metabolism. By activating AMPK, berberine helps cells respond more effectively to insulin, leading to improved insulin sensitivity.
2. Glucose Transport: Berberine can increase the expression and translocation of glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4), a protein responsible for transporting glucose from the bloodstream into cells. By promoting the translocation of GLUT4 to the cell membrane, berberine enhances glucose uptake by cells, which helps to lower blood glucose levels and improve insulin sensitivity.

3. Inflammatory Pathways: Chronic inflammation is associated with insulin resistance, and berberine has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects. It can inhibit the activation of inflammatory signaling pathways, such as nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), which can impair insulin signaling and contribute to insulin resistance. By reducing inflammation, berberine may improve insulin sensitivity.
4. Gut Microbiota Modulation: Berberine can also influence the composition of gut microbiota, the community of microorganisms living in the digestive tract. Dysbiosis, or imbalance in gut microbiota composition, has been linked to insulin resistance and metabolic disorders. Berberine has been shown to alter the gut microbiota in a way that promotes metabolic health, potentially improving insulin sensitivity indirectly through its effects on gut bacteria.
Inositol: is it the wonder Drug for women with PCOS?
In the realm of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), inositol emerges as a crucial ally in the pursuit of hormonal equilibrium and overall well-being. Specifically, myo-inositol and D-chiro-inositol take center stage in addressing key aspects of PCOS management.
By enhancing insulin sensitivity, inositol contributes to the regulation of glucose metabolism, a pivotal factor in PCOS-related insulin resistance. Moreover, its influence extends to restoring ovulatory function and promoting regular menstrual cycles, offering hope to those navigating the challenges of irregularity.
Beyond this, inositol plays a role in hormonal balance, curbing elevated testosterone levels and alleviating symptoms like hirsutism and acne. The positive impact on ovarian follicular development and egg quality further underscores its significance, promising potential benefits for fertility. With a multifaceted approach that encompasses metabolic health and reproductive function, inositol emerges as a natural and promising supplement in the holistic management of PCOS.
Is inositol safe during pregnancy?
Inositol is generally considered safe for use during pregnancy when taken at recommended doses. It’s a type of sugar alcohol that is naturally present in the human body and can also be found in some foods.
However, as with any supplement or medication, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before taking inositol during pregnancy.

A comprehensive review of 14 studies further supports these findings, suggesting that berberine is comparable in efficacy to common blood sugar medications such as metformin, rosiglitazone, and glipizide. Additionally, research suggests that berberine may enhance the blood-sugar-lowering effects of other diabetes medications when taken together. These findings highlight the potential of berberine as a promising treatment for lowering blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Berberine and Weight Loss vs Inositol and weight loss
Berberine and inositol are both natural supplements that have been studied for their potential effects on weight loss.
Berberine, derived from several plants, has been shown to potentially help with weight loss by improving insulin sensitivity, reducing appetite, and increasing fat burning. It may also aid in lowering cholesterol levels and promoting overall metabolic health.

Inositol, a type of sugar alcohol, is involved in various cellular processes and has been investigated for its role in weight management. It’s believed to potentially improve insulin sensitivity, regulate appetite, and support healthy metabolism.
In the table below breakdown of the link between berberine supplementation and weight loss, including its impact on metabolism and appetite regulation.
| Berberine | Inositol |
|---|---|
| Metabolism Regulation: boosts weight loss by activating AMPK, a key enzyme that regulates energy metabolism. It enhances glucose uptake, improves insulin sensitivity, and encourages fat burning. | Metabolic Regulation: Inositol may improve insulin sensitivity, aiding weight management, particularly for those with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes. |
| Insulin Sensitivity: enhances insulin sensitivity, aiding in better blood sugar regulation, particularly beneficial for overweight individuals by reducing insulin resistance, thereby improving glucose control and decreasing fat storage. | Appetite Control: affect appetite by influencing neurotransmitters in animals, potentially reducing food intake |
| Appetite Regulation: Berberine affects leptin and ghrelin, regulating appetite; reduces overeating, aiding weight loss. | Fat Metabolism: Inositol influences lipid metabolism, potentially reducing triglycerides and aiding fat loss, though evidence is limited. |
| Gut Microbiota: Berberine affects gut microbiota, promoting beneficial bacteria and combating harmful ones, potentially aiding weight loss. | Stress Reduction: regulates serotonin, affecting mood and stress. Improved mood and stress management may indirectly aid weight loss by influencing eating habits. |
| Lipid Metabolism: Berberine lowers blood lipid levels, including total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. High cholesterol is a risk for heart disease; lowering it improves health. Berberine aids lipid metabolism, preventing obesity complications and promoting weight loss.. | PCOS Management: Inositol supplementation has shown promise in managing polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition linked to insulin resistance and weight gain. By improving insulin sensitivity and hormonal balance, inositol may help reduce weight gain associated with PCOS. |
| Liver Health: Inositol supports liver health, vital for fat metabolism. A healthy liver metabolizes nutrients efficiently, aiding weight loss. |

Types of Inositol
Myo-Inositol: The most common and widely studied form, known for its involvement in cell signaling and insulin sensitivity.
D-Chiro-Inositol: Often found alongside myo-inositol, it plays a crucial role in insulin metabolism and has been explored for its potential in conditions like PCOS.
Scyllo-inositol is another stereoisomer of inositol. It’s a rare form and has gained attention for its potential therapeutic use in Alzheimer’s disease. Some studies have suggested that scyllo-inositol may inhibit the formation of beta-amyloid plaques, which are associated with Alzheimer’s pathology. However, research in this area is ongoing, and more evidence is needed to fully understand its effectiveness and safety in treating Alzheimer’s disease.
L-Inositol: This form is less common, and its role in the body is not as well understood compared to myo-inositol and D-chiro-inositol
O-Inositol: This form of inositol is less common and has a slightly different structure compared to myo-inositol. It is not as well-studied as the other forms but may have some unique biological effects.
Dosage of Inositol based on health conditions
| Health Condition | Dosage | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Mental Health Conditions | 12–18 grams of MYO once daily for 4–6 weeks | 4–6 weeks |
| Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) | 1.2 grams of DCI once daily<br>or<br>2 grams of MYO and 200 mcg of folic acid twice daily | 6 months |
| Metabolic Syndrome | 2 grams of MYO twice daily | One year |
| Blood Sugar Control in Gestational Diabetes | 2 grams of MYO and 400 mcg of folic acid twice daily during pregnancy | During pregnancy |
| Blood Sugar Control in Type 2 Diabetes | 1 gram of DCI and 400 mcg folic acid once daily | 6 months |
Side effects of Berberine vs side effects of Inositol
Berberine
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Berberine may cause digestive discomfort, including diarrhea, constipation, flatulence, and stomach upset.
- Low Blood Pressure: It may cause a drop in blood pressure, leading to dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Interactions with Medications: Berberine can interact with various medications, including blood thinners, antihypertensive drugs, and certain antibiotics, potentially leading to adverse effects.
- Liver Toxicity: High doses of berberine may have hepatotoxic effects, although this is rare and more commonly associated with prolonged use or excessive doses.
- Allergic Reactions: Some people may experience allergic reactions to berberine, which can manifest as rash, itching, or swelling.
Inositol
- Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Inositol can cause gastrointestinal discomfort, including nausea, bloating, gas, and diarrhea, especially when taken in high doses.
- Insomnia: Some individuals may experience difficulty sleeping or insomnia as a side effect of inositol supplementation.
- Interactions with Medications: Inositol may interact with certain medications, including antidepressants and lithium, potentially altering their effects.
- Hypoglycemia: Inositol might lower blood sugar levels, so individuals with diabetes or those taking medications to lower blood sugar should monitor their blood glucose levels closely.
- Headaches: Rarely, inositol supplementation may cause headaches or migraines in some individuals.
Long-term risks of taking berberine
According to research done on Berberine by the Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Science, University of Allahabad, Allahabad, India.
Long term use of berberine can result in Toxicological Effects. Research done on Animals.
Daily Dosage of Berberine
| Week | Daily Dosage |
|---|---|
| Week 1 | 500 mg/day ,3 times a day |
| Week 2 | 1000 mg/day, |
| Week 3 | 1500 mg/day |
| Standard dose | is 900-2,000mg a day, divided into 3 to 4 doses. |
Warning! Groups of Medication to avoid when taking Berberine and Inositol
- Medications that Lower Blood Sugar: Berberine may lower blood sugar levels, so combining it with other medications or supplements that have similar effects could lead to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). This includes insulin, sulfonylureas (like glyburide or glipizide), metformin and other antidiabetic drugs.
- Medications Metabolized by CYP450 Enzymes: Berberine may inhibit certain enzymes in the liver, particularly the CYP450 enzymes, which are responsible for metabolizing many medications. This can potentially lead to increased levels of these medications in the bloodstream. Common drugs affected by this interaction include statins, antihistamines, benzodiazepines, and certain antidepressants.
- Lithium: Inositol may have additive effects with lithium, a medication used to treat bipolar disorder. It’s essential to monitor lithium levels closely if taking it concurrently with inositol.
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): Inositol might potentiate the effects of SSRIs, which are commonly prescribed for depression and anxiety. While this can potentially enhance their efficacy, it also raises the risk of side effects.
Effects on Animals: Rats, Cats and Dogs
| Dosage/Route | Effect |
|---|---|
| Rats 50 mg/kg | Diarrhea in 40% of rats |
| Cats 100 mg/kg (oral) | Vomiting in 6-8 hours |
| Cats 100 mg/kg for 8-10 days (oral) | Fatal outcome |
| Cats 50/100 mg/kg for 10 days (oral) | Hemorrhagic inflammatory problems in intestines |
| – | Dogs Salivation, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, muscular tremor, paralysis |
Sub-acute Toxicity:
- Berberine causes gastric ulcers.
- It induces chronic arthritis, liver and kidney enlargement, and weight increase (up to 30%) in rats.
- Berberine decreases bilirubin protein binding in adult rats.
- Immunotoxic effects include reduced number of leukocytes, neutrophils, lymphocytes, spleen weight, and suppression of B- and T-cell generation/differentiation.
The study has proven the toxicity of pure compound is greater than the toxicity of plant extract or plant extract fractions.
5 Plants Natural sources that contain berberine
- Barberry plants, berberine is found in the roots, stem, bark, rhizome, fruit and leaves.


2. Thalictrum rochebrunianum (meadow rue) berberine found in roots, leaves stem and bark.

You can purchase this plant online link is below.
3. Chelidonium majus (celandine) is a perennial herbaceous flowering plant in the poppy family Papaveraceae.
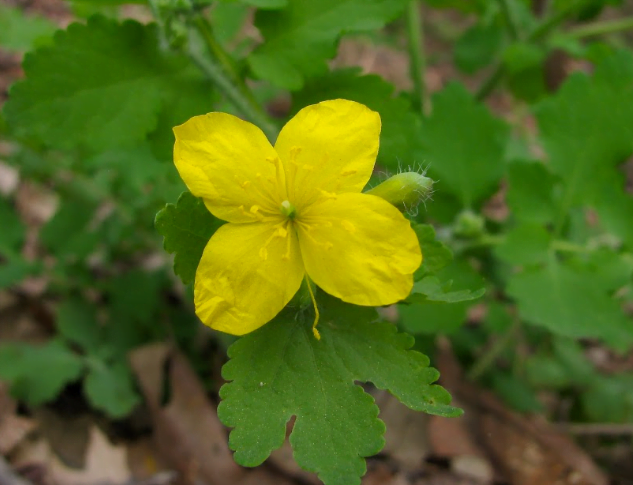

Image by https://www.marylandbiodiversity.com/view/2869 Chelidonium majus (celandine)
4. Hydrastis canadensis (goldenseal) is a perennial, woodland forb in the buttercup family (Ranunculaceae).

5. Phellodendron amurense (Amur cork tree)
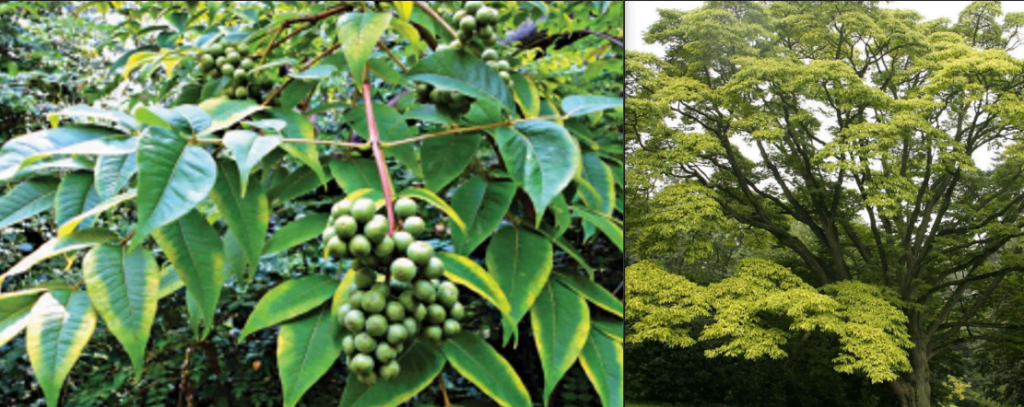

Among these berberine are mainly present in a variety of barberry species and goldenseal species which are native to Asia and America.
Where can you buy Berberine and Inositol supplements?
You can purchase both Supplements online or at any Walmart , pharmacy and other health store online. The plant extract berberine in liquid form is easy to digest.
Personal experiences taking both berberine and inositol together
I have started taking both berberine and Inositol 15th Jan 2024, mostly to combat the excessive weight gained over the holidays. I usually take both 1 hour apart and twice a day , morning and evening. At night I do a scope of the myo-inositol powder in a glass of water.

so far its 2/15/2025 and i have lost 14 lbs, with eating a a healthy meal and walking occasionally when i can.
I noticed I was hungry less, my cravings was gone. I was able to fast for over 12 hrs. without hunger pain.
I did notice a little dizziness once or twice after taking the berberine and i knew right away that’s when my blood sugar drop, so i skip the second dose.
Resources
https://www.fs.usda.gov/wildflowers/plant-of-the-week/hydrastis_canadensis.shtml
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmolb.2018.00021/full
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/berberine-diabetes#berberine-blood-sugar
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6111450/